The domestic practice of transferring property by inheritance is not as wide as foreign experience. At the same time, this issue is of great importance in the lives of citizens. After the death of a person, the values accumulated by him significantly improve the financial situation of the beneficiary. Most often, benefits are received in accordance with the legal order. Considering the average life expectancy of men and women, it is simply necessary for the latter to know the nuances of legal norms. So, who is the first priority heir after the death of the husband?
Regulatory regulation of the issue
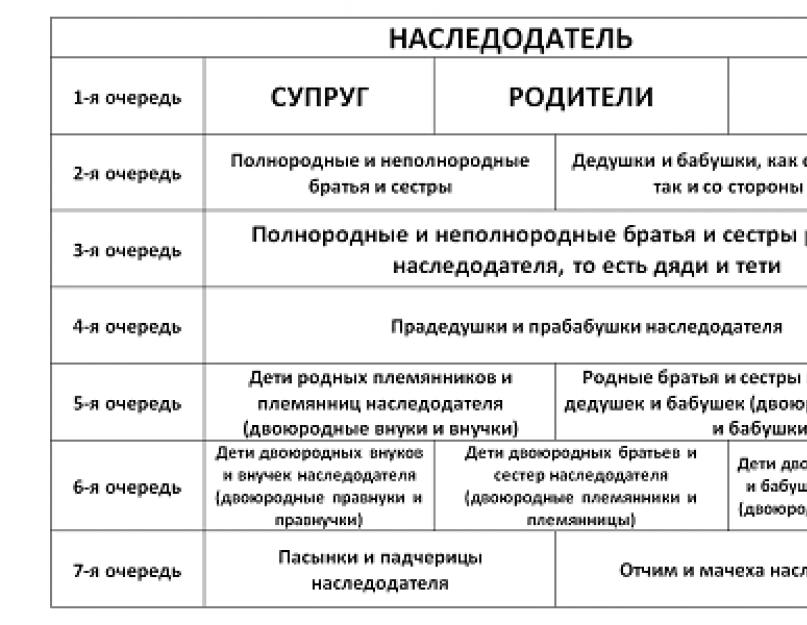
The procedure for acquiring rights to human things is determined by Art. - , 148 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. They establish a sequence based on the degree of relationship. The primary beneficiaries are the spouses, parents and children of the deceased. If there are none, then the opportunity to claim the property passes to the second group and so on.
First priority: Who is the main legal heir after the death of the husband?
Despite the fact that the specified circle of persons is limited and they are easy to identify, the applicant should still remember some nuances.
Spouses
This category includes a husband or wife who have registered their relationship in the prescribed manner. Particular attention must be paid to the fact that cohabitants do not receive value under the law.
Are all items subject to division between loved ones?
When highlighting things that a limited circle of people can claim, it is important to take into account the fact that only the personal property of the deceased, acquired by him during his relationship or before marriage, is subject to distribution. If the second partner is alive, then he receives half of all the benefits acquired through joint efforts. Thus, if a man dies, then his relatives acquire his personal assets, as well as part of the joint objects with his wife.
Parents
In this case, the validity of the relationship at the time the grounds arose does not play a role. That is, the parties can be either divorced or in a registered union. Adoptive parents have similar opportunities if their status in relation to an adult has not been canceled by the court.
Important! Guardians, trustees, adoptive parents are not recognized as heirs according to regulations. The situation is similar with the father and mother, who are deprived of their rights in relation to the baby.
Children
They get into the priority group. At the same time, they claim to receive benefits even when their legal connection with their parents was lost by court decision. At the same time, we are talking about obligations. Thus, the property of the deceased father or mother will in any case be transferred to the children as a matter of priority.
Biological children have the same opportunities as adopted children. If the relationship has not been established or the minor is not a relative of the testator, for example, children of the spouse from a previous marriage, then receiving the items becomes impossible. Eligibility depends solely on getting into the seventh line.
Sometimes the recipient of benefits needs to prove his origin (family connection). This can be done through a genetic examination appointed by the authority. It is worth noting that minors born after the death of a parent also become his heirs.
Direct inheritance
As already noted, the valuables go to the wife (husband) of the deceased, his children and parents. The division of assets is carried out by allocating parts of the deceased from the total mass of jointly acquired property. Distribution occurs depending on the number of applicants. If he is alone, then the citizen gets all the items in dispute. Otherwise, a division occurs.
Nuances of the procedure carried out without a will
According to the law, items in addition to close relatives are transferred to other persons. They are understood as citizens recognized as incompetent, dependents deprived of earnings and the opportunity to work for a year before the death of the owner of the property. They claim half the share. In order to declare themselves, dependents must provide strong evidence of their difficult financial situation to the notary's office. These include receipts, statements, receipts, checks and witness statements.
Important! Some household items used by partners in marriage (household appliances, furniture, dishes, appliances, tools, etc.) go to those who lived with the deceased. They have priority on the specified values.
As with the division of benefits between partners who decide to divorce, inheritance involves compensation for the participants in the process who received a smaller share. This happens due to the impossibility of allocating shares in any object. Therefore, the beneficiary who took possession of it after the death of his loved one must pay part of the cost to the other parties.
What is a will?
A will is a document that acquires legal force after the death of a person and is certified by a notary office. Compared to 2018, the new legislation provides for the possibility of concluding an inheritance agreement that meets similar requirements.
According to a document certified by a lawyer, parts of the assets or all of them are transferred to specific persons in a predetermined volume (shares). If the specified information is not in the text, then the mode of equal distribution of parts between relatives is applied.
The procedure can be carried out through the execution of a closed will. They become familiar with it only after the death of the will-maker. It is worth noting that this also applies to a notary.
Procedure for carrying out the procedure
Heirs have a chance to receive valuables not only according to the legal regime, but also according to a document drawn up by the owner. The procedure involves contacting a notary. To enter into an inheritance, the designated persons will have to write an application, go to a specialist, and accept the things.
Features of inheritance
The priority group implements the requirements in accordance with the standards specified in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. So, within six months from the moment the grounds arise, they must formulate an application for acceptance of assets and submit it to a notary. If the appropriate actions were not taken by potential beneficiaries, then they are excluded from the list of heirs as having renounced their part. The share is redistributed among other relatives.
Sometimes an automatic refusal does not indicate intent on the part of the person. Often the consequence of such situations is ignorance that a close relative has died. If the court determines that the application was not received due to such reasons, then the specified deadlines are extended and the division procedure is revised.
Ignorance of what happened (the loss of her husband) is recognized as a valid reason. This can happen due to a long absence from the territory of the Russian Federation or a change of residence. This situation entails the need for a person to go to court. You must justify your position based on the rules for calculating the statute of limitations. The countdown begins not from the date of loss of a person, but from the moment when the obstacles to receiving an inheritance become irrelevant, for example, receiving relevant information from friends, coming to Russia.
How to make an application?
If the owner’s will was expressed in writing, and a notary certified its text in accordance with current regulations, then applicants must contact the office where the document was drawn up. The will-holder can choose any lawyer at his discretion. In case of legal inheritance, specialists are divided depending on the region of residence of the testator and the capital letter in his surname. Thus, finding a lawyer will not be difficult.
Entering into legal relations involves drawing up an application. The paper is attached to the case and contains:
- personal data of the deceased and degree of relationship with the author of the document;
- information about the applicant (full name, date of birth, place of birth);
- an indication of the queue where the person ends up (if the benefits are transferred according to the legal regime);
- date of;
- visa.
What documents will the applicant need?
To formalize an inheritance, the beneficiary needs to prepare a package of papers that will become the basis for transferring the property to them. The documents are presented to the notary. These include: passport; registration paper (a certificate will do); certificate confirming the death of the will-maker; confirmation of the connection between the applicant and the deceased at the family level (birth certificate, document confirming the registration of the union). Each paper must be accompanied by a copy. All property goes to citizens without restrictions or any reservations. The procedure ends with the registration of ownership of the objects, coinciding with the opening of the inheritance.
Important! Contrary to the will of the deceased, neither party can receive the property. An exception is the circumstances in which incapacitated citizens, minors or persons dependent on the deceased acquire half of the share that would be due to them according to the law.
Conclusion
Thus, issues of inheritance of assets owned by the deceased are resolved by law or in accordance with a will drawn up with the participation of a notary. Legal cases presuppose the order in which property is received. Family members are considered the main contenders. So, if a couple has no children and the father has died, then the wife or mother will acquire the items. Minors have a chance to receive the property of the deceased, even if they were not designated by the will-maker.
The legal practice of drawing up wills in the Russian Federation is not widespread at such a high level as in other developed countries. Most often, first-priority heirs receive property from us after the death of one of the spouses, that is, in order of priority.
The inheritance procedure is regulated by Articles 1142, 1145, as well as Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It is they who establish the so-called queue by kinship, according to which the heirs of the 1st queue are the closest relatives of the testator, who have an advantage over others in receiving the property of the deceased.
If there are no heirs of this group or they have expressed theirs, their right passes to the relatives of the next line of inheritance.
ASK A LAWYER - FASTER than to read! GET FREE CONSULTATION while the rest are for it PAYING!
According to existing legislation, in 2020, first of all, the following are called for inheritance:
- Spouses
The first priority of inheritance by law is the wife or husband who was in an officially registered state marriage with the deceased. At the same time, “common-law” spouses, as well as dependents and cohabitants, do not have the right to claim the property of the testator, except in cases where this is provided for by the laws of the Russian Federation (we will discuss this further).
However, even when inheriting after the death of a spouse, it is necessary to understand that not all property is subject to division between relatives. After all, all real estate, movable property or things acquired during the period of marriage are considered marital property. That is, such property belongs to the wife and husband on equal rights.
That is why experienced lawyers recommend, before proceeding with the registration of an inheritance, to allocate from the joint property of the spouses the share of the one who can further dispose of it. Then you can distribute the remaining inheritance (the deceased's share) among the heirs in order of priority.
It is worth noting that joint property, according to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is not property that is not subject to allocation to the spouses. That is, the property that was received by the testator before marriage, no matter whether it was purchased, received as a gift or inherited.
- Parents
The testator's mother and father are also included in the first priority of inheritance. At the same time, it does not matter at all whether they are married or divorced. Also, adoptive parents, who by law have rights similar to parents, are treated as parents, except in cases where the adoption was canceled according to a court decision.
Parents who are legally deprived of parental rights in court are deprived of their rights of inheritance.
- Children
The same category of primary heirs also includes the children of the testator. Remember that if the latter was deprived of parental rights, he lost the right to inherit property after the death of the child, but children do not lose this right after the death of the parent who did not have parental rights. This fact is due to the fact that a mother or father deprived of parental rights, although they lose their rights to the child by a court decision, are still not released from the responsibilities associated with their children.
Natural or biological children have the same inheritance rights as adopted children. Moreover, if the testator was married to a person who has his own children, they do not have the right of priority inheritance.
According to the existing norms and laws of the Russian Federation, stepdaughters and stepsons are included only in the 7th line of inheritance. Thus, they can claim the property of their stepmother or stepfather only if there are no heirs from the previous 6 lines of inheritance. You can get acquainted with all the stages of inheritance by looking at this table: 
It is worth mentioning separately about children born after the death of the owner of the property, who have the same rights to the inheritance or part of it as children born during the life of the testator.
Who is the first heir after the death of his wife?
The situation is the same with the distribution of property after the death of a spouse. Before the immediate division, the part of the property that was acquired during the marriage to the deceased is separated from the common inheritance. Thus, 50% of such property belongs to the husband, and the remaining half is subject to inheritance by the following persons:
- spouse;
- children;
- parents of the testator.
Who is the first heir after the death of her husband?
So, having considered the information described above, we can conclude that the first heirs after the death of the husband are his:
- spouse;
- children;
- parents (mother and father).
The process of distributing the common inheritance begins only after calculations and the allocation of half the share of property acquired jointly by the spouses during marriage. It is the husband’s part, in this case, that will be the share of the inheritance to be distributed among the remaining heirs.
If only one citizen from the list acts as heir and there are no others, then he will receive all the property of the testator. Well, if the deceased does not have any of the heirs of the 1st category or they refused the inherited property, the right of inheritance passes to the remaining heirs in order of legal priority.
Who is the first heir after the death of the mother?
According to the legislation existing in 2020, among the first applicants for inheritance after the death of the mother are:
- spouse;
- children;
- parents.
 At the same time, the husband has the right to inherited property only if he was in a state marriage with the deceased, which will need to be documented when opening a case.
At the same time, the husband has the right to inherited property only if he was in a state marriage with the deceased, which will need to be documented when opening a case.
The same applies to children and parents - they will also need to present relevant documents proving the degree of relationship with the testator.
If the mother was in an official marriage, then before dividing movable and immovable property, it is necessary to isolate the share of property acquired jointly during the marriage (only necessary if the husband is alive). The second half of the inheritance will be divided among the remaining heirs.
The father and mother (grandfather and grandmother) have the right to inherit property if they have parental rights and have not been deprived of them in court.
Also, instead of the mother’s children, her grandchildren have the right to receive the inheritance first if their parents died with her or before her.
Who is the first heir after the death of his father?
If the head of the family did not leave a will, then the following may inherit his property first:
- spouse;
- children;
- parents of the testator.
As in the case of the mother, before distributing the common inheritance between the above-mentioned persons, the spouse’s share (part of the property acquired during marriage) is allocated. This part of the property is not subject to division and is the property of the mother, while the father's share is distributed among the heirs by law. Wherein, the shares of the heirs of the 1st stage are equal.
In the event that the above persons have renounced their shares or there are none, the right of inheritance passes to the applicants of the 2nd stage of inheritance. It is worth noting that if the testator does not have a single heir in any of the queues, then all of his property will be considered escheat and will become the property of the state.
Features and nuances of receiving an inheritance without a will
Together with relatives who make up the first line of inheritance, other citizens also have the right to claim part of the property. According to the laws of the Russian Federation, incapacitated persons and dependents who have been supported by the testator for the last year can receive property on an equal basis with the primary heirs. In this case, the share of each of them will be equal to half the share if they received the property or in the order of priority.
To claim their rights, incapacitated persons and dependents must provide the notary with undeniable evidence of their dependence on the testator. Such evidence may include receipts, checks, receipts, witness statements, etc.
The preemptive right to this type of property such as dishes, as well as household appliances and furniture belongs to those heirs who lived with the testator, using and maintaining this property. You can learn more about it from this expert video:
If a part of the inheritance of one of the heirs is significantly larger than the other parts, he is obliged to compensate the cost to the other heirs and thereby equalize the shares.
Right to inheritance after the death of a wife
The right to inherit the property of a deceased spouse, first of all, has her legal husband, children of the deceased, as well as parents. All of them are in the first line of heirs, and at the same time, they have priority over other relatives (Article 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The law establishes queues depending on the degree of relationship.
This fact should be called obligatory share of inheritance(Article 1149 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This is part of the testator's property that passes to another person, regardless of whether the testator indicated this person in the will or not. For an obligatory share in the inheritance certain categories of citizens have the right:
- minors or disabled children;
- disabled spouse and parents of the testator;
- disabled dependents;
Refuse the obligatory share in favor of another person, the person has no right. (Article 1158 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The obligatory share is aimed, first of all, at providing material support to those who are most in need of this category of heirs. It is also worth considering that the right to a mandatory share does not pass to the descendants of the deceased heir by right of representation.
After the death of one of the spouses, according to the provisions of Art. 244 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, his share in joint property is subject to allocation for further inheritance. This issue is dealt with by a notary who opens an inheritance case. In legal circles, this process is called the transition of title ownership to real ownership.
This duty is assigned to the notary, Art. 75 of the Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on notaries, and the need for the mandatory allocation of the marital share for inheritance is enshrined in Article 1150 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
This article regulates the rights of spouses to common property in the event of the death of one of them. Although it does not cover all cases of inheritance rights to marital property, it clearly states that the marital share is part of the inheritance due to all heirs of the deceased.
How is the inheritance divided after the death of a wife?
The inheritance after the death of the wife will be divided depending on the type of inheritance, as well as on the relatives who have the right to the property of the deceased. If the inheritance is by will, it will be distributed between the persons specified in the will.
But this will be the case if the deceased wife did not support a dependent during her lifetime, or did not have minor and disabled children and parents. If these persons are not present, then the property will undoubtedly become the property of the people specified in the will, unless, of course, they decide to accept the inheritance.
If the property is abandoned by the heirs of the first priority, then it passes in order to the persons of the second priority, etc.
The day of my wife's death will be day of opening of inheritance(Article 1114 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). It is from this moment that the period will begin during which it is necessary to make a decision about the inherited property, namely: take it for yourself, or refuse it.
How to inherit after the death of your wife
Entry into inheritance depends on the type of inheritance - either inheritance by law or by will.
Inheritance by will
You should contact a notary office to accept the property specified in the will from the deceased spouse within six months from the date of death testator. It is worth knowing that the second copy of the will is kept by the notary who certified this document. The document itself will necessarily indicate the address of the transaction, as well as the person who certified it.
When contacting a notary, you must prepare list of documents, which confirm the identity of the heir, establish the fact of the death of the testator, as well as documents on the subject of the will itself - i.e. inherited property.
Before deciding whether to accept the inherited property or not, it is also worth finding out about the spouse’s existing debts. Perhaps she has there are still loans and debts for a large sum of money. In case of acceptance of inherited property, the husband will be obliged to pay and on debts. (Article 1175 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Sometimes this is disadvantageous for the heir, because the inherited property itself is an order of magnitude lower than the value of the debt that will have to be paid for the deceased wife.
In order to find out the value of inherited property, it is worth inviting an appraiser for a specific type of property, who will conduct an assessment and indicate in an expert opinion the market value of this property. When the assessment is carried out and its result becomes known, conclusions can be drawn about accepting or refusing the inheritance.
Deadline for registration inheritance amounts to six months. It is set taking into account various situations, collecting documents, searching for a will, etc.
In case of cancellation of the will, the property of the deceased wife will be inherited by persons of the appropriate order according to the law.
Inheritance by law
When contacting a notary, you should bring with you all the necessary documentation(copies and originals). The notary will definitely advise the person who contacts him on any questions that have arisen and, after a six-month period from the date of opening of the inheritance, will issue a certificate of the right of inheritance by law. This document is issued personally to each heir who received a certain share of the deceased’s property.
Inheritance of a common-law husband
As a rule, “civil marriage” in society refers to a relationship between a man and a woman that is not registered with the authorized bodies. People can have children together, buy real estate, run a joint household, but they cannot be called legal spouses, because their relationship were not registered with the civil registry office. People living in a civil marriage should be called roommates.
According to the law, the inheritance cannot be transferred in the first place to the cohabitant, i.e. the common-law husband of the deceased. The only option to undeniably receive property as a result of inheritance is to write and execute a will.
If there is one, the share owned as a result of the death of the cohabitant will go to her common-law husband. But it should be taken into account that if the spouse has minor or disabled children or parents, then they have the full right to inherit on a par with the deceased woman's partner.
If the common-law spouse died without leaving a testamentary document, then the heirs specified in Art. 1142 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in the order of priority established by law.
Is my ex-husband entitled to inheritance?
Former means not currently married to the deceased woman. Respectively, he will not have any rights to inheritance. But if his wife names him in the will, then he has every right to inherit a share of the property based on the entry specified in the will.
Due to the fact that at the time of the death of the ex-wife, the marriage was not registered with her in the registry office, accordingly it does not give rise to rights and obligations, except in cases where civil law contracts of a remunerative nature were concluded between people living together. But these cases are not so frequent, and require effort to prove these facts by documenting them.
Inheritance occurs by law and by will. Will– a legally significant document in which a person, while alive, indicates what property he owns and who will receive it after his death.
A will takes precedence over legal inheritance. But there are exceptions when property is not always received in the shares indicated by the deceased.
The inheritance should be registered after opening it, i.e. after the death of a person. It is necessary to collect relevant documents confirming the death of the person, degree of relationship, address of his last place of residence, and others. As for children born out of wedlock, they have the same rights as others to inherit property deceased mother.
Inheritance under a will is formalized by the testator before his death. The initiator is a legally capable person who has reached the age of eighteen.
The composition and content must be kept secret (Article 1123 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This document must be in writing, drawn up in two copies and executed in the presence of a notary. In it, the testator describes the property that he has, as well as the persons who will receive it in the event of his death.
As for inheritance by law, it is valid in the case if there is no will. In inheritance according to the law, a certain order must be observed; it depends on the degree of relationship of the deceased to his relatives (Articles 1142-1145 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
There is such a thing as “inheritance by right of representation.” This term means that the share of the subject of inheritance, which could belong to the heir by law, but who died before the opening of the inheritance, or at the same time as the testator, passes to the descendants of the “deceased heir” by right of representation.
After the death of a husband, how is the inheritance divided between the wife and children from the first marriage?
The answer to the question of how the inheritance is divided between the wife and children from the first marriage depends on a number of circumstances. The key importance when registering property rights is the presence of official registration of relations and recognition of children. The answer to the question of whether a child from a first marriage has the right to receive property depends on the presence of a recorded expression of will.
How is the inheritance divided after the death of a husband or father?
The procedure for dividing shares of inheritance for an apartment and other real estate is established by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In the absence of a recorded expression of will, priority is given to the heirs of the first priority. These include children, legal spouses, as well as parents of the deceased.
In standard cases, the shares of the applicants are equal, but the shares of the ownership of some candidates may be changed. For example, this is possible in the event of the death of a child before or during the division of objects. When transferring inheritance rights, they will be divided equally between the successors of the direct claimant.
If there is a recorded expression of will, only the specified persons can enter into inheritance after the death of the father or husband. Inheritance queues don't matter. The initiator may by orders deprive some of the successors of the objects. However, when drawing up a last will, it must be taken into account that some applicants must receive ½ of the legal share without fail.
To acquire the property of the testator and correctly divide the objects, you must contact a notary. The specialist will competently distribute the shares between the applicants, taking into account the circumstances that arise. The presence of equal rights or the transfer of the opportunity to acquire objects through transmission, the birth of new heirs, the refusal of some candidates, etc. are taken into account. In this case, the relatives must correctly establish the place of opening the case. Otherwise, contradictions will arise during the division. Successors will receive different certificates.
Common-law spouses and unrecognized children are not able to receive an inheritance unless the contrary is indicated in the recorded expression of will. The exception is the presence of common objects or dependency. In such cases, persons whose rights have been violated may file a claim with higher authorities. They will need more evidence. For example, this is registration information, eyewitness testimony, a certificate from the deceased’s place of work, a certificate from the guardianship and trusteeship authorities, etc.
Joint ownership
In a registered joint marriage, the husband and wife can jointly purchase real estate and participate in its improvement. After his death, the widow, upon inheritance, has the right to half of the property received in this way, regardless of the recorded expression of will. If the rights of the legal spouse have been violated, she can appeal to higher authorities. The inclusion of joint property in the disposition is a reason for partial cancellation of the transaction.
Jointly acquired property does not include objects that the deceased acquired before marriage. Additionally, real estate received by a deceased person as a result of a gift or inheritance agreement is not subject to division. However, in some cases, a spouse may receive half the share. This requires proof that the wife took part in improving the objects or increasing their value.
The court can be provided with checks, receipts, etc. The widow could not only invest financial resources in the property, but also make physical efforts. For example, cultivating a site or repairing a vehicle yourself.
After receiving the marital share, the widow retains the right to acquire an additional share on a general basis. In standard cases, debts are not transferred along with joint objects. The exception is the presence of an encumbrance that is associated with the disputed property.
Division between wife and children
If the property is divided by a spouse, the presence of a recorded will matters. Depending on this factor, objects are either divided by law in equal shares or transferred according to orders.
If there is a will
When the father died, it is necessary to try to discover the recorded expression of will. To do this, you can contact your local notary office. It stores information about all transactions concluded in the region. If this document exists, but the orders were not taken into account during the division, those persons whose rights were violated can file a claim with higher authorities and demand a second division.
The rights of the testator include the possibility of depriving some of the legitimate claimants of the objects. However, the testator cannot ignore the rights of some successors to the obligatory share. The state protects disabled representatives of the priority queue and dependents. The first include minor children, pensioners and disabled people. To obtain dependent status, several conditions must occur:
- A person receives financial assistance from the first party for a long time (minimum 12 months). These incomes are the main source of profit. Payments must be regular and substantial.
- The person is disabled.
- The person lives in the same territory as the first party. This is a must for a wife. In the case of children, objects can be obtained without cohabitation, but it increases the chances.
In the absence of a will
If there is no recorded expression of will, the succession of successors is key. Spouses and children belong to the heirs of the first group, therefore they receive equal shares. If the child does not live to see the death of the initiator or dies during the partition, the rights pass to his successors. In this case, the share of the direct heir is distributed equally among his claimants.
Children from first marriage
In standard cases, children from a first marriage can acquire property. It is possible to deprive them of parts of the objects only through a will. However, children from their first marriage can claim an inheritance under any conditions if they are disabled.
Children who have not been recognized by their parents cannot acquire objects by law, since there are no family ties between the first and second parties. In addition, successors who were found unworthy are removed from the case. In the case of children, this most often occurs due to arrears in child support.
Children may be considered unworthy successors if they have committed unlawful acts against the first party or other claimants in order to change shares or accelerate the division of property. However, if there is a will, the candidate can be rehabilitated if he proves that the father knew about the crime, but later still included the child in the list of heirs without pressure from other persons.
How is property divided after the death of one of the spouses?
From the point of view of determining the share of the inheritance, the situation with the death of a spouse is one of the most difficult. Let's consider the main factors and features influencing this process.
What is personal and joint property?
All property of a married couple is divided into personal and joint. This is regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 256.
Personal include:
- Any things, real estate or vehicles that belonged to one of the spouses before the wedding.
- Gifts and inheritance from other relatives.
- Items for personal use such as shoes and clothing. In this case, it does not matter whether they were purchased before or after the wedding.
- Intellectual Property Rights.
If during marriage the spouses made significant investments in property (for example, they made major renovations to an apartment), as a result of which the market value of the property increased significantly, such property may be recognized in court as joint property, even if it was originally personal.
Joint include:
- Almost all things, real estate or vehicles that were acquired after marriage.
- Luxury items and jewelry, even if they were used individually.
- Income from the use of intellectual property rights.
Example: The deceased spouse bought himself an apartment before marriage. After his death, the wife receives an equal share with all other heirs. But if major renovations were carried out after the wedding, the woman can prove in court that this property is joint property. In such a situation, the division into shares will be made according to a different principle. Another example: a spouse has written a book that is actively selling and generating income. After her death, the husband receives the same share as other first-degree heirs, but the proceeds from its sale are divided according to a different principle. Read more about the division below.
An exception is a marriage contract, under which the spouses could agree on a different principle for dividing property.
Marriage contract
Upon marriage, newlyweds have the right to enter into a prenuptial agreement, which provides for ownership rights to both existing property and those items, things, real estate or transport that will be acquired after the wedding.
Example: The agreement states that all property, regardless of when it became the property of one of the spouses and what type it belongs to, is considered jointly acquired. In such a situation, even intellectual property rights are divided equally between the spouses. The opposite situation also occurs, in which even property acquired jointly during marriage is considered personal property.
Mandatory spousal share in inheritance by law
Each spouse is entitled to half of all property acquired during the marriage. After the death of one of the spouses, the remaining second half retains this 50% and additionally receives an equal share with the other heirs in the personal belongings of the deceased.
Example: The deceased Ivan Ivanovich had a car purchased before marriage. After the wedding, he and his wife, Lydia Vasilievna, bought an apartment. The couple has two children. After the death of her husband, Lydia receives 50% of the apartment as joint property. The remaining half is divided equally among all three heirs (wife and two children). Everyone gets approximately 50/3=16.67%. The car, as personal property, is divided into three parts at once, approximately 33.33% for each heir. As a result, Lidiya Vasilyevna owns a third of the cars and 66.67% of the apartment. Each child received 1/3 of the car and 16.67% of the real estate.
Rights of a spouse when inheriting under a will
As part of receiving an inheritance, a will can only be drawn up for one’s half of the jointly acquired property and personal property. It is impossible to deprive one of the spouses of his legal 50% without a trial.
Example: Before his death, Ivan Ivanovich drew up a will in which all his property, including 50% of the joint property, would be inherited by his son. In such a situation, the spouse receives only half of the entire property (as a spouse should), and the rest goes entirely to the child.
Share for disabled people and dependents
Not only spouses receive the right to half of the jointly acquired property. There are other categories of citizens who have the right to an obligatory part of the inheritance (Article 1148 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
They have the right to an equal share with the heirs of the first stage. If there is a will, then the portion of the property received cannot be less than 50% of that which is assumed by law. Let's consider who will get the property and to what extent if there is a disabled person and a will:
Example: The deceased Ivan Ivanovich has a disabled brother (the heir of the second stage), a wife and two children. Among his assets, he has an apartment acquired jointly during marriage and a car purchased before the wedding (personal property). There is also a will in which the brother is not mentioned at all: all things under this document are planned to be divided in equal parts between the wife and children. However, it is impossible to completely deprive a brother of his share.
As a result, the spouse receives half of the apartment as joint property. The remainder of the will must be divided into 3 parts, but the brother is obliged to receive at least 50% of what is due to him. Let's calculate how the inheritance is divided. First, we select 4 parts of the apartment from the remaining half. It turns out to be 12.5%. The brother receives only 50% of the allotted share, because he is not in the will: 12.5/2 = 6.25%. That leaves 50-6.25=43.75%. They are already divided into 3 parts according to the number of remaining heirs: 43.75/3 = 14.58%. The machine is divided in a similar way. First into 4 parts: 100/4=25%. The brother receives half the share: 25/2=12.5%. The remainder is divided into 3 shares: 87.5/3=29.17%.
Inheritance rights are one of the complex areas of jurisprudence. The loss of a close relative is always accompanied by grief and difficulty assessing the actual situation. This entails mistakes, and disputes often arise. Which heirs of the first priority after the death of one of the spouses without a will can claim part of the property, and what to do if there is a deed of gift or other similar document? To answer these questions, you need to understand the nuances of the current legislation.
General provisions
The problem in dealing with inheritance rights lies in the large number of legislative acts. The main provisions are set out in the Civil Code and the Constitution of the Russian Federation. However, in addition to them, there are regulations and decrees, the content of which should not contradict basic legislative acts.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
In practice, disagreements between heirs and relatives of a deceased family member occur frequently. The reason is a conflict of interests, both material and moral. Not only the husband (wife) and children, but also the sister (brother), mother and father of the deceased can claim the share.
What it is
Inheritance is a procedure established by law, according to which the movable and immovable property of the deceased passes to the heirs. In addition, they are obliged to accept rights and responsibilities - paying debts, receiving privileges.
Types of inheritance:
There are many reasons for disagreement among heirs. But first, the rights to the property of immediate relatives are considered.
Who falls under the category
Inheritance by law is described in Chapter 63 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It determines the order and rules for dividing property.
From September 1, 2020, Art. 1150 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, according to which the share of the inheritance does not include all the common property of the surviving spouse. The division of property is carried out on the basis of Article 256 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
The heirs of the first stage include:
Addition - heirs of the first priority after the death of one of the spouses - brothers, sisters, people who are not related to the deceased, who will be dependent on him for at least a year before his death, or who are disabled. Basis – art. 1148 Civil Code.
Distribution Features
The division of the trustee's inheritance can only take place within the framework of the law. To do this, you need to draw up an inventory of property, lists with the degree of relationship of the heirs. With this information, you should go to a notary, who will draw up a statement of consent of all parties.
Shares of inheritance are indicated by a simple fraction - ½, 1/3, ¼. An exception is an indivisible part, which may include a car, house or apartment, the division of which is impossible. Most often, they cause disputes between heirs of the same line.
If there is a will
A will is a unilateral act of a citizen on the order of distribution of his property after death. It is drawn up in writing and certified by a notary or other authorized person.
The number of wills drawn up is not limited, but all previous wills are canceled by the last one. Exception - the document is declared invalid due to violations.
The rules of inheritance by will are described in Chapter 62 of the Civil Code. They are as follows:
From September 1, 2020, the executor of a will has the right to compensation for expenses from the inheritance. If the document provides for the possibility of remuneration for the executor, the source of funds is also the property or cash savings of the testator.
In law
Inheritance by law is carried out by division between all relatives and claimants. The exception is a spouse.
First, joint and personal property is determined. Half of the first belongs to the wife (husband) and does not participate in the division. The personal property of the deceased and the other half of the property are divided among the heirs.
First priority rights belong to the following categories of citizens:
| Indicators | Description |
| Husband wife | the marriage must be officially registered. Civil or church marriage does not give the right to participate in the division of inheritance. The same applies to the dissolution of relations before the death of the testator. |
| Children | born in official marriage, illegitimate and adopted. It is also possible to apply for children who were born after 10 months from the date of death of the parent |
| Parents | it does not matter whether they are officially married or not. Each of them receives equal shares |
| Dependents or obligatory heirs | these are disabled citizens who are not necessarily relatives of the deceased. First of all, minors or disabled children are considered, then spouses and parents. It is possible to transfer the inheritance to persons who were officially dependent on the deceased for at least the last year before his death and lived with him |
If the first-degree heir dies before the testator, the right to distribute the share passes to his children. But at the same time, they can only claim that part of the property that was legally due to their deceased parent.
If there is a deed of gift
Anticipating difficulties with the distribution of property, the testator can make an alternative option - draw up a deed of gift. It confirms the gratuitous transfer of property to one or more persons. However, the conditions may vary. If this concerns real estate, the old owner retains the right of residence until death.
It is difficult to challenge a deed of gift, since it is not one of the ways to distribute an inheritance. An exception is the official recognition of the transaction as illegal.
Peculiarities:
It is important to understand that inheritance by law or will is only possible in relation to property that belonged to the deceased. Real estate or other valuables transferred by gift cannot participate in the process of distribution between heirs.
Video: shares in inheritance
FAQ
When transferring an inheritance, certain regulations must be observed. Often, failure to comply will result in the loss of the right to claim a share.
| Question | Answer |
| What is the deadline for accepting an inheritance? | according to the general rules, it is 6 months (clause 1 of Article 1154 of the Civil Code). Special deadlines are regulated in paragraph 3 of Article 45 of the Civil Code. The six-month period begins to apply only after a court decision is made |
| Can an ex-wife (husband) claim part of the inheritance after a divorce? | the only option if he (she) was dependent on the testator for 1 year before his death |
| Will a child be given a share of the inheritance if the testator and his mother (father) are deprived of parental rights? | the child or his guardians have the right to claim a share within the first line of heirs |
| Can a child claim a share in the inheritance of his biological parents if he was adopted by others? | no, except if the fact of the child’s permanent relationship with his biological parents has been confirmed in court. This is difficult to prove |
| Who is the unworthy heir? | they may be citizens seeking to obtain an inheritance illegally, deprived of their rights by a court decision. Also, the father (mother) does not inherit after the children if the first ones are deprived of parental rights. Basis - Article 1117 of the Civil Code |
| Is it possible to divide inherited property in unequal shares? | This option is possible by prior agreement if all parties agree with the decision made. The document must be certified by a notary |