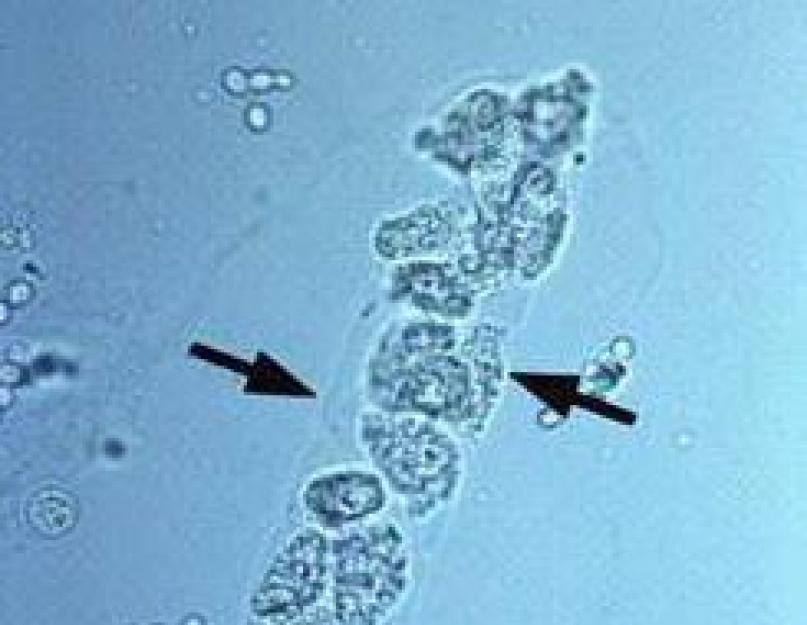
Urinalysis is one of the most important studies reflecting the state of human health. Urine is filtered by the kidneys from the blood, that is, the composition of urine can show how much a person’s filtration system is able to cope with the task assigned to it.
Thus, by comparing blood and urine indicators, you can see the balance of the presence of substances in them. For example, protein should be absent in the urine of a healthy person, but in the blood, on the contrary, should be present in sufficient quantities. The same applies to any substances that make up the blood: urea, creatinine, uric acid, potassium, sodium, and so on.
Therefore, when studying the form of laboratory urine test results, it is important to know what these or other indicators mean, what normal values are typical for a healthy person, and what deviations from normal values indicate.
For example, when considering the research result obtained in the clinic, many people wonder: casts in the urine - what does this mean? Should they be present in urine and if so, what is their rate? And if not, what actions need to be taken and which specialist should I contact to eliminate the pathological phenomenon?
Cylinders - what are they?
The kidneys consist of glomeruli - glomeruli, each of which has membranes, the openings of which are capable of passing through molecules to be excreted from the body. Larger molecules, such as those that make up proteins, are released back into the bloodstream.

If the kidney membranes are damaged, protein leaks into the urine. And when several protein cells are connected to each other using epithelium or fat, cylinders are formed in the urine. The norm provides for the complete absence of both protein and casts in urine.
Normal casts in urine
The presence of casts in the urine can only occur if it already contains protein. And since a healthy person should not have protein in the urine, therefore, casts in the urine are a deviation from the norm.
It is also noteworthy that casts are formed when there is sufficient protein in the urine. That is, with physiologically caused proteinuria, for example, after eating a large amount of protein foods or during intense physical activity, cylinders are not formed.

Not always, even if there is a large amount of protein in the urine (macroproteinuria), casts in the urine may appear. This depends on the degree of acidity of the latter: the higher it is, the more cylinders will be recorded in urine containing protein during analysis. Moreover, in an alkaline environment, cylinders may quickly dissolve or not form at all. Therefore, cylindruria is not considered in nephrology as a specific sign of a particular disease, but is considered only as an additional factor.
Hyaline casts
There are several types of cylinders based on their molecular composition. Hyaline casts in urine consist exclusively of protein. Normally, they can be present in the urine if their indicator in the analysis does not exceed 1-2 units in the preparation. In the case where there are increased cylinders in the urine, it is necessary to continue the examination until a disease is identified that affects the filtration process of the kidneys.

Hyaline casts are not always a marker of the disease, but their appearance is a good reason to diagnose the urinary system to exclude the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- abacterial nephritis.
Grainy cylinders
Granular casts in urine also consist exclusively of protein molecules, but they get their name due to their appearance. Casts begin to form in the renal tubules, where they remain in the process of impaired filtration, being not returned back into the bloodstream. They cover the walls of the tubule, and their fragments end up in the urine.
Thus, these cylinders are a kind of cast of the renal tubule. Like hyaline casts, this indicator can indicate pathological processes occurring in the kidneys:
- about pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- amyloidosis.
Waxy cylinders
When hyaline and granular casts in the urine remain in the renal tubules for a long time, they gradually begin to stick together, forming a dense viscous mass, like plasticine or wax.
The appearance of wax cylinders can never be provoked by physiological processes; they always turn out to be markers of kidney damage, and at a rather serious stage.
Waxy casts in urine appear in the following diseases:
- glomerulonephritis in a malignant form;
Red blood cell casts
Protein is not the only substance that should not penetrate urine, remaining in the bloodstream. Blood cells - red blood cells - are also never detected in a laboratory test of the urine of a healthy person. If blood is present in it in any quantity, this indicates that the kidney vessels are damaged and internal bleeding is occurring. This may be the result of injury or a disease of the vascular tissue, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.

If red blood cells combine with protein, then the study reveals red blood cell casts in the urine. Considering that the fact of the presence of red blood cells in urine indicates the fragility of the kidney vessels, the diseases that cause this phenomenon are associated with this fact:
- glomerulonephritis (usually acute);
- renal artery thrombosis;
- kidney infarction;
- kidney cancer
Leukocyte casts
During inflammatory processes of bacteriological origin, a large number of leukocytes are formed in the urine. When they combine with protein, leukocyte casts appear. The presence of the latter in the urine almost always gives good reason to diagnose pyelonephritis.
Epithelial casts
When the protein combines with the epithelial cells lining the inner walls of the kidney tubules, epithelial casts are formed.
They are a marker of a pathological process aimed at the destruction of kidney tissue and its scarring. This happens in autoimmune processes, nephritis and nephrosis. And when epithelial casts appear in urine after kidney transplantation, there is reason to suspect the process of rejection of the donor organ by the body.

Thus, any pathological processes occurring in the urinary system can be shown by a urine test. Cylinders are a marker of diseases that subsequently, without timely and proper treatment, can lead to organ failure and disability.
Therefore, it is necessary to submit urine for laboratory testing at least once a year, and more often if there are symptoms of kidney disease (swelling, lower back pain, changes in the amount of urine excreted, its color, smell).
Norm and reasons for the appearance of casts in urine: hyalon, granular, waxy, pathological
Casts are microscopic casts of the cavity of the renal tubules. The presence of casts in the urine is commonly called cylindruria.
They are formed when the filtration activity of the kidneys is insufficient, caused by some pathology, and have a specific shape and size.
Depending on the etiology and composition, they can serve as an indirect symptom of kidney pathology or a specific area of the urinary tract.
Casts in urine - what does it mean?
Normally, urine is defined as a substance with a slightly acidic reaction - from 5.5 to 7.0 pH. Cylinders are formed and detected in urine with a pronounced acidic reaction. This is characterized by the presence of an increased amount of protein - proteinuria.
With an alkaline reaction of urine, casts either do not form at all or quickly dissolve, which complicates testing. The alkaline reaction itself is a pathology and indicates kidney problems.
The process of formation of cylinders at the mouths of the renal tubules is directly related to disease and dysfunction of the kidneys. The norm allows the presence of only single protein (hyaline) cylindrical bodies - no more than 1-2 in the field of view. The presence of other types of cylindrical bodies during microscopic examination of urine is unacceptable.
In the video about what cylinders in urine mean:
Detection methods
Cylindruria is often detected during a general urinalysis. It is prescribed as a standard procedure for determining the patient’s health level for various diseases, as well as during a comprehensive examination.
For a specific examination, the following may be carried out:
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko (more accurate and complete than a general analysis);
- collection of daily urine output;
- Zimnitsky test (to determine the excretory function of the kidneys);
- Reberg-Tareev test (determination of renal filtration rate);
- clinical examination of urine for protein.
Analysis according to Nechiporenko is more often carried out in hospitals, as it gives more accurate results. In an outpatient setting, it is an additional research method and is prescribed when the general clinical urine analysis is insufficiently informative. The quantitative content of cylinders in 1 ml of urine along with sediment is revealed.
Daily urine output is collected for qualitative and quantitative urine testing. This allows you to determine how well your kidneys are functioning. The number of cylinders in the urine collected per day is measured, their chemical composition and physical parameters are determined, which contributes to a more accurate diagnosis.
The Zimnitsky test is performed not to determine the number of casts in the urine, but to determine the level of kidney function.
The specific gravity and density of urine is calculated, which suggests certain diseases:
- specific gravity from 1002 to 1008 - remission of chronic pyelonephritis, renal failure;
- a specific gravity over 1025 indicates severe acute pyelonephritis, dehydration, and uric acid diathesis in children.
The Reberg-Tareev test allows you to assess the excretory capacity of the kidneys. Used for differential diagnosis of kidney lesions of various etiologies, affecting functional features or tissues directly.
A clinical urine test for protein is performed to determine the level of proteinuria. In addition to this study, an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder is often prescribed.
Types and reasons of education
The cylinders can be formed by: protein, desquamated epithelial cells of the renal tubules, erythrocytes. After physical exercise or during a diet with a predominance of animal (protein) foods, single cylindrical protein bodies (hyaline cylinders) can be detected in the urine.
Types of casts in urine
Hyaline
Hyaline casts are formed by a special protein produced by the epithelial cells of the kidney tubules. They are colorless, completely or semi-transparent, have rounded ends and are quite often detected by microscopic analysis of urine.
In men, hyaline casts may appear due to the large amount of meat products consumed in the diet. This increases the acidity of the urine and often leads to physiological proteinuria. In addition, hyaline cylindrical bodies appear after intense physical activity.
In the urine analysis of a pregnant woman, an increased content of hyaline casts most likely indicates a latent course of pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis.
It may also indicate a violation of the filtration, concentration, and excretory functions of the kidneys, which is very typical for the last trimester of pregnancy.
In a child, an increased content of hyaline casts may indirectly indicate a number of diseases not directly related to the kidneys:
- polio;
- mumps (mumps);
- rubella;
- chickenpox;
- measles;
- whooping cough.
When the temperature rises to subfebrile (37-38°C) levels, the percentage of protein excretion increases, and with febrile (38.5-39°C) levels and insufficient drinking, dehydration of the child’s body may develop. Therefore, high temperature can also serve as a provoking factor for the formation of hyaline casts in the urine in children.
Hyaline casts in urine
Grainy
The composition of granular casts is very similar to hyaline casts: they are also based on protein produced by the tubular epithelium. In this case, disintegrated epithelial cells of the tubule cavity “stick” to the homogeneous surface of the hyaline bodies, forming a granular structure. They are determined in case of serious pathologies of the renal tubules, accompanied by their degenerative changes.
In children and pregnant women, the presence of granular casts most often indicates a hidden course of glomerulonephritis, in which damage occurs to the glomeruli of the kidneys, which are responsible for filtering the blood, the formation of primary urine and reverse osmosis.
In adults, the presence of granular casts may also indicate glomerulonephritis, but often in the course of further differential diagnosis other tubulopathies are determined:
- general damage to the tubular apparatus;
- increased tortuosity of the distal or proximal tubules;
- nephrolithiasis (kidney stone disease);
- polyuria - excretion of large amounts of fluid; characteristic of diabetic kidney damage.
Waxy
They are formed by protein denatured in the wide lumens of the renal tubules. Much shorter than hyaline, opaque, have a yellowish tint. The formation of waxy casts is associated with stagnation or poor urine flow.
Against the background of these conditions, the initially formed hyaline cylinders are first transformed into granular ones, but as they remain in the lumen of the tubule, more and more destroyed cells of the lining epithelium settle on their surface.
If waxy casts in the urine are elevated in all groups of patients, this indicates destructive changes in the epithelial layer of the renal tubules.
A frequently associated condition is nephrotic syndrome:
- severe proteinuria;
- massive swelling of the face and limbs;
- hypoproteinemia (decreased protein concentration in blood plasma);
- hyperlipidemia (increased cholesterol levels in the blood).
This condition is especially dangerous for pregnant women and children, so the detection of waxy casts in the urine requires immediate further examination in order to identify the primary pathology.
Waxy casts in urine
Pathological
By and large, all casts found in urine should be called pathological, since normally they should not exist.
You can consider separately the presence of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and epithelial casts.
For all groups of patients, especially pregnant women, young children and the elderly, the presence of the casts described below in the urine is a serious signal for a comprehensive examination.
Erythrocyte
Their origin is associated with the layering of red blood cells - erythrocytes - on the hyaline base. The appearance of red blood cell casts in the urine is often accompanied by the presence of blood impurities in the urine (hematuria) and indicates its renal origin.
The presence of erythrocyte cylindrical bodies is a sign of:
- renal vein thrombosis;
- exacerbation of chronic glomerulonephritis;
- acute glomerulonephritis;
- fornical bleeding;
- malignant neoplasm in the kidney cavity.
Leukocyte
Their appearance is associated with severe inflammatory processes, accompanied by significant pyuria (the presence of leukocytes in the urine). Most often, leukocyte casts are detected in the urine of patients with acute chronic pyelonephritis, complicated by purulent formations. Extremely rare in children.
Epithelial
The epithelial variety of cylinders is extremely rare.
Their appearance is associated with severe degenerative changes in the glomeruli and tubules of the kidney, which can be caused by:
- rejection of a transplanted kidney;
- heavy metal poisoning (for example, lead);
- overdose of drugs (for example, salicylates).
Epithelial cylinders in urine
Pigment
Pigment cylinders are cylindrical bodies of rich yellow, brown, yellow-brown color, having a fine-grained structure.
For the most part they consist of hemoglobin, which has a free sediment during some pathological reactions of the body:
- When transfusion of incompatible blood.
- With myoglobinuria, urine turns brown under the influence of the myoglobin pigment, released during the pathological breakdown of muscle protein.
- In case of poisoning with toxic substances.
- For extensive injuries.
In pregnant women, in extremely rare cases, it can develop against the background of anemia caused by malnutrition. In children, the appearance of pigmented hemoglobin casts in the urine may be associated with an ultra rare disease - paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Marchiafava-Micheli.
First of all, cylindruria indicates damage and degenerative changes in the parenchyma (body) of the kidney. It is generally accepted that the type of cylindrical bodies is not of particular importance, since if they are present, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination and differential diagnosis.
Shown:
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract.
- X-ray using a radiopaque contrast agent.
- MRI or CT.
It is important to study the cylinders in order to determine the composition, since sometimes there are false cylindrical bodies - cylindroids formed from mucus. They may be present in the urine and do not indicate the presence of renal pathologies.
Source: http://gidmed.com/nefrologiya/simptomy/cilindri-v-moche.html
What do casts in urine mean?

If a patient has casts in his urine, what does this mean? The attending physician will answer this question. Looking ahead a little, it should be noted that we will be talking about the renal tubules, since urine is produced there.
The kidneys play an important role in the human body - the role of filters. They are located in the lumbar region and are connected to arteries, veins and drainage tubules through which urine enters the bladder. The kidneys cleanse the blood, maintain salt balance and the ratio of other substances needed by our body.
These organs have a complex structure, but they act very effectively. They consist of many small capillaries - nephrosis, woven into glomeruli, which have afferent and efferent arterioles.
Primary urine is formed in Bowman's capsule, which is similar to a cup. Each kidney consists of one million nephrons. They are connected to each other so tightly that if they were stretched out in length, it would be equal to the length of 5 thousand cars lined up in a row.
Nephrons purify the blood entering the glomeruli. A renal artery approaches each kidney, through which blood is pumped and flows back through a vein. What remains is purified fluid, which enters the renal tubule. The walls of the tubule absorb substances that are beneficial to our body. And the residual liquid turns into urine, in which breakdown products unnecessary for the body remain.
All toxic substances are eliminated from the human body by the kidneys through the urinary tract. The liquid containing this waste is urine. During the day, the kidneys filter 100-200 liters of liquid (primary urine).
To begin with, it would be good to understand some of the terms that will be most often encountered later. The renal tubule is a tube that has the following segments:
- proximal,
- loop of Henle, or thin bend,
- distal,
- connective.
All these tubules and tubes perform one characteristic function - they transport substances through the cells, dissolving them and subjecting them to reverse absorption, returning them through the capillaries to the blood (glucose, amino acids, water).
Other substances (urea, uric acid, drugs) pass through the tubules and are eliminated from the body. Normally, this entire transport process is regulated by the kidneys by acid-base balance.
What does the presence of casts in urine mean? When the kidneys become diseased, protein begins to accumulate in the kidney tubules. Enveloping them from the inside and passing through these channels, they take their shape, resembling a cylinder. An accurate impression of the canal is created. That is why they are called cylinders, and their sediment in urine analysis is called cylindruria.
Cylinders are one of the indicators of a general urine analysis. At the conclusion of a laboratory examination, this is one of the indicators of a urine test, which informs doctors that there is an inflammatory process in the kidneys and urinary tract.
If a person is healthy, then there should be no casts in the urine. They can only exist if the urine is acidic. There is no cylindrical factor in alkaline urine.
If the analysis showed the presence of cylinders, then this always indicates the renal origin of the disease. Depending on the composition, they take one or another shape, size, color. Therefore, when all the features of the cylinders are indicated in a urine analysis, the doctor, by determining their origin, can find out about the appearance of a particular disease in a particular patient.
If, according to the results of a laboratory analysis, there are cylinders in the urine, this shows the reaction of the kidneys to a general infection, intoxication and the presence of changes in the kidneys themselves. But if the test shows a small number of cylinders, this can be considered normal.
What types of casts are there in urine?
There are several types of casts, and each of them reports the specifics of the disease and whether the infection is a genitourinary tract disease or a kidney disorder is occurring.
Types of casts in urine:
- hyaline,
- grainy,
- waxy,
- erythrocyte,
- leukocytes,
- pigmented.
Hyaline casts in urine are serum proteins that coagulate and are filtered through the glomeruli, the site where blood is filtered to form primary urine and protein metabolism occurs. Further, not being absorbed in the proximal sections of the tubules, but passing through their distal remote sections, these proteins acquire a cylindrical shape.
The reaction of the tubular fluid is acidic, and this environment promotes blood clotting and, accordingly, the formation of hyaline casts. They are not present in an alkaline environment. Therefore, if the analysis shows the presence of hyaline formations, this indicates the patient’s nephrotic syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by swelling of the arms and legs.
Granular casts in the urine arise from altered tissue cells of the proximal tubules and have the form of grains and granules. Hence their name.
If the analysis showed that they are present, this indicates diseases such as glomerulonephritis (diseases of the glomeruli of the kidneys), amyloidosis (kidney disease due to diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis, etc.
), diabetic glomerulosclerosis (a disease caused by diabetes) and other viral diseases that occur with fever. The study shows the characteristic granularity of such formations.
Waxy - consist of a homogeneous, non-structural, wax-like material, yellow in color. They are formed in the sections of the tubules, due to changes in the tubular layer of these sections. This sediment occurs with malignant kidney tumors.
Erythrocyte is a protein with red blood cells. Talks about a tumor, renal infarction, thrombosis and high blood pressure.
Leukocytes are an indicator of pyelonephritis (disease of the renal pelvis).
Pigmented are blood pigments with a brownish, brown color. In the analysis, this is an indicator of different types of hemoglobinuria (hemolytic diseases during blood transfusion, when blood incompatibility occurs).
What are the signs that require a test for the presence of casts in the urine?
Usually the kidneys properly perform their main function - to maintain a constant volume of water in our body. In healthy people, urine is light yellow, transparent and does not have an unpleasant pungent odor.
The appearance of a bad smell should alert you. This may be a sign of diseases such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis.
Pain in the lumbar region, burning sensation when urinating, cloudy urine - all these signs should be alarming.
A general urine test will show all the abnormalities that occur in our body. Moreover, the disease can be detected at the earliest stages, when the patient himself has not yet felt the symptoms of the disease.
Swelling, high blood pressure, and an unpleasant odor of urine should prompt a person to undergo a general urine test, since kidney diseases can occur under the guise of other diseases.
Therefore, before self-medicating, it would be correct to first undergo a general analysis, which will reveal the full picture of the person’s condition.
In order for the test to be reliable, morning urine is collected; it can be stored for analysis for no more than an hour and a half.
Source: http://pochke.ru/moch_pyz/an_moch_kr/gialinovye-cilindry-v-moche.html
Cylinderuria or casts in the urine: types of formations, rules for preparing and taking the test, deciphering the results

The cylinders in the patient’s urine are special particles of sediment that have a unique shape and characteristic and are formed in the renal tubules. There are several types of formations, each differing in size and composition at the cellular level. The name of the particles is formed on the background of their shape (cylindrical).
The process of formation of cylinders in human urine is called cylindruria. What does the presence of casts in urine mean? What types indicate serious kidney pathologies and how to deal with them? The answers to the questions are described in detail in the following material.
General information
Kidney disease is characterized by the accumulation of protein in the kidney tubules. Red blood cells, fat particles, leukocytes, and epithelial cells can also be detected. All elements are capable of enveloping the renal tubules from the inside, forming their “casts”, in other words, cylinders. Formations are formed only in the presence of protein; it acts as glue; without it, cylinders cannot appear.
Cylinders in urine sediment are well preserved only in the presence of an acidic environment; in alkaline urine they quickly dissolve or do not form at all. For this reason, the small number of urine casts cannot reflect the real state of things. Formations can be of different shapes and composition. For this reason, the analysis indicates not only the number of formations, but also their type.
There are several types of cylindrical formations; in a healthy person, only hyaline cylinders can be detected (1–2 in the preparation). Other types of formation should not be found normally. It is important to correctly collect a urine test and prepare for the procedure.
Types of formations
Depending on the type of cylinders in the patient’s urine, doctors can determine the course of a specific pathology and the state of the patient’s body.
Learn about the typical symptoms and treatments for urethral inflammation in women.
Read about the normal relative density of urine and the reasons for deviations at this address.
Experts distinguish the following types of cylinders in urine:
- hyaline. They are formed only from protein, they are easy to detect in urine only in the presence of proteinuria (there is protein in urine), even if the pathology is not associated with kidney diseases, also with all ailments of the paired organ (pyelonephritis, nephritis, glomerulonephritis and other diseases that are accompanied by an increased amount of squirrel);
- grainy. They are protein casts of the renal tubules, to which degenerated epithelial cells have joined. Against the background of this process, the formations acquire a granular appearance. This type of formation appears in the patient’s urine against the background of the disease, accompanied by damage to the renal tubules, the presence of protein in the patient’s urine (diabetic nephropathy, pyelonephritis, viral diseases with fever, glomerulonephritis in acute and chronic forms);
- waxy. They consist of granular and hyaline formations that are retained in the kidney tubules. Waxy cylinders have a shapeless mass, reminiscent of wax. The presence of these formations in the patient’s urine indicates the course of serious kidney diseases (malignant glomerulonephritis, late stages of diseases of the paired organ);
- erythrocyte. Formed from protein and small clusters of red blood cells. A urine test will not show them due to the fragility of the formations. Cylinders of this type indicate the renal origin of hematuria; they appear in urine against the background of a kidney infarction, a tumor in the organ, thrombosis of the renal veins and other serious diseases;
- leukocyte. From the name it is clear that the formations are formed from protein and leukocytes; such cylinders are very rare, often against the background of pyelonephritis of various etiologies;
- epithelial. Formed from exfoliated epithelial cells of the kidney tubules, observed against the background of acute nephritis or nephrosis. The detection of this type of cylinders in urine always indicates serious kidney disease. If epithelial formations appear in the urine after transplantation, this indicates its rejection;
- cylindroids are formations of mucus, single formations sometimes appear in a healthy person, a large number of formations indicate the course of inflammatory processes;
- pigment appear as a result of myoglobinuria, hemoglobinuria.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
A general analysis of urine is carried out for almost all diseases, for preventive purposes or to monitor the results of treatment. In addition to detecting cylinders, clinical examination of urine provides characteristics of transparency, acidity, and specific gravity of the liquid. The analysis also helps determine the presence of bile pigments, red blood cells, white blood cells, glucose, hemoglobin, and protein in the patient’s urine.
A urine test is considered a simple test, but deciphering it requires a lot of specific knowledge. The composition of urine is affected not only by the functioning of the kidneys, but also by the functioning of other organs and metabolism. Also, the specific components of urine determine the functioning of the reproductive system, but in any case, the study shows the condition of the patient’s kidneys and excretory system.
Note! For preventive purposes and for timely diagnosis of diseases, doctors recommend taking a urine test once a year.
Proper conduct of the study itself and collection of biomaterial will help to obtain reliable results. The rules for collecting urine include several important aspects.
- Forget about mayonnaise jars and other “homemade” containers for storing urine. Only special sterile containers are suitable for collecting material. Thus, the entry of foreign substances into the patient’s urine is minimized, which can distort the test results. Also, compliance with this rule increases the shelf life of biomaterial and helps preserve it during transportation;
- Hygiene procedures are a mandatory aspect. Sebaceous secretions and sweat should not get into the urine. Antibacterial agents cannot be used, otherwise the results of the study may be distorted;
- Do not use specific medications or food products that may distort the results of the study. The specific list of substances is indicated by the doctor. The night before, avoid eating any coloring foods (beets, carrots). Remember, the color of urine is also important during analysis;
- Before conducting a urine test, do not drink alcohol, and the water regime cannot be changed either (drink water as usual). It is not recommended to be sexually active 12 hours before the test, or to collect urine during menstruation.
The appearance of cylindrical bodies in the patient’s urine indicates the presence of renal pathology. An increase in the norm is over 20 y in 1 ml of liquid. Each type of cylinder indicates a specific type of disease, which makes it easier to diagnose the disease in the patient.
Find out about the causes of cystitis in women and how to treat the pathology with a special diet.
The list and rules for the use of antibiotics for acute pyelonephritis can be seen on this page.
Go to http://vseopochkah.com/lechenie/narodnye/romashka.html and read about the benefits of chamomile and the use of the plant to treat the kidneys and urinary tract.
The presence of formations in a child’s urine is a bad signal that indicates the course of diseases of the excretory system. Children are rarely diagnosed with serious kidney ailments due to their age, so excess casts in the urine should attract the attention of the doctor and parents. Often this situation is caused by improper collection of biomaterial.
To prevent trouble, following the rules that apply to collecting urine from children will help:
- collect material not from the pot, such urine has many impurities, which distorts the results of the study;
- undress the child first; in most cases, emptying the bladder occurs reflexively;
- it is important to prevent urine from mixing with feces (in children, these two processes usually occur simultaneously). Covering the anus with a napkin or clean rag will help prevent an unpleasant situation. If you were unable to collect a “clean” urine sample, repeat the procedure later.
Most “bad” tests are due to violation of the rules for collecting urine from a child. Therefore, if you detect casts in your urine, do not panic, take the test again, and follow the recommendations described above.
Cylindrical formations in the patient’s urine indicate unpleasant pathologies of the patient’s excretory system and kidneys. Sometimes the test result indicates the course of other diseases.
It is important to consult a doctor in time if discomfort occurs and begin treatment immediately to avoid sharply negative consequences.
Take care of your health, because it is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it later.
Casts were found in the urine: is it dangerous and to what extent? The answer will be given by a specialist in the following video:
Source: http://vseopochkah.com/diagnostika/analizy/tsilindry-v-moche.html
Casts in urine - what are they: causes, types, photos

Diseases of the genitourinary system are a common pathology among children and adults. The main indicator of the health of the excretory system organs is urine readings that correspond to the norm.
Microscopic examination of urinary fluid can detect sedimentary elements. These are the so-called casts in the urine (cylindruria). They are an indicator of the presence of a disease of any organ of the urinary system.
What does “casts in urine” mean?
Cylinders in urine are particles that are formed from accumulations of microelements of the renal tubules.
As a result of pathological processes in the kidneys, sedimentary microparticles of epithelium, protein elements, blood cells, and leukocytes accumulate in the parenchyma. The main component of the cylinder elements is protein, which forms a cylindrical body.
Microscopic particles, in contact with the walls of the tubules, formed into cylindrical casts. The etiology of their formation depends on the molecular structure of the cylinders, indicating the nature of the kidney disease.
To determine whether there are casts in the urine, a general urine test is often not enough. However, if proteins are detected in the urine, the presence of casts can be assumed. To more accurately determine the presence of cylinders in urine, you should series of analyzes:
- Zimnitsky test (characterizes the excretory function of the kidneys);
- determination of urine filtration rate using the Reberg-Tareev method;
- study according to Nechiporenko;
- urine analysis for the amount of protein elements;
- daily urine collection.
Read our article about why you need daily urine collection for analysis.
These studies help not only to determine the presence of cylinders, but also to find out their shape, size, number, and structure.
Urine is a slightly acidic medium, so the pH (hydrogen index) level in it should not exceed more than 7. If the acidic environment in the urine is increased, then it is a favorable condition for the formation of cylinders. If the pH value of urine is below 5.5, then the cylinders do not form in it, or dissolve completely, which makes them difficult to identify.
An indicator in which the number of visible cylindrical structures exceeds two units in the field of view may indicate the presence of renal pathology.
It should be noted that the acceptable presence of only one or two hyaline bodies may be a temporary phenomenon. Most often, about two cells are found in a healthy person after physical exertion. If many hyaline bodies or other types of cylindrical elements are found, then we can talk about the presence of pathological processes.
Species
Determining the type of cylinder, their number, and the nature of the accumulation can help a specialist determine the nature of the disease of the urinary system. Cylindrical bodies that can be found in urine are:
- Hyaline. This type of cylinders is a protein structure; they are completely or half transparent and can be detected under a microscope.
- Epithelial. Cylinders of this type are formed from protein bodies and dead epithelium formed on the walls of the renal canals.
- Grainy. The disintegrated epithelial elements are attached to the protein casts and form another type of cylinders.
- Waxy. They are a collection of granular and hyaline bodies of cylinders.
- Erythrocyte. The structure of such cylinders consists of protein and a small amount of red blood cells.
- Leukocyte. This type of body is quite rare. The cylinders consist of protein and clusters of leukocytes. Most often they are a sign of pyelonephritis. Staining them during analysis helps to distinguish this type of bodies from erythrocytes.
- Cylinders. Formed from mucous formations. Indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. A small amount of this type of cast in the urine is not a deviation from the norm.
- Pigmented. The bodies resemble granular formations. Formed from sedimentary hemoglobin. They have a brown or dark brown color. They may be a sign of poisoning, severe injuries, myoglobinuria, and rejection due to transfusion of the wrong blood type.
A small amount of them in the urine may be normal. A pathological number of hyaline bodies may indicate the development of pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis. In pregnant women, the detection of hyaline bodies may indicate a latent course of inflammatory kidney diseases, or impaired renal function (especially in the third trimester). In children, elevated temperature can provoke the formation of hyaline casts.
Can be detected in cases of serious kidney pathologies. Precipitates of this type are especially pronounced in case of poisoning with mercury products or salicylate, which is characteristic of rejection of the implant of a paired organ, as well as during the course of an acute form of nephritis or nephrosis.
This type of cylindrical bodies can be formed when the renal tubules are damaged, in the presence of excess protein in the urine. Diseases in which granular cylinders appear are pyelonephritis, viral diseases accompanied by a febrile state, glomerulonephritis occurring in an acute form, nephropathy due to diabetes, kidney stone disease.
Their shapeless elements resemble a waxy structure. The presence of these cylinders in the urine may indicate the presence of serious renal pathologies, such as malignant glomerulonephritis, advanced stages of kidney disease. The presence of waxy bodies in the urine indicates a violation of the outflow of urine, or its stagnation. The prognosis for the presence of waxy casts in the urine can be disappointing.
A general urine test cannot detect such bodies. The presence of red blood cell casts may be a sign of hematuria. The reason for the formation of such bodies can be tumor processes in the kidney, thrombosis of the kidney veins, as well as infarction of the organ.
Causes of cylindruria
The main causes of cylindruria in the urine are diseases that occur in chronic or acute form:
- pulmonary failure;
- heart failure;
- insufficient myocardial tone;
- previous myocardial infarction;
- narrowed lumen of the kidney artery, as a result of which the supply of nutrients to the organ is insufficient;
- inflammatory course in the kidneys;
- malignant formations in the organs of the urinary system;
- various types of intoxication;
- infections of various kinds, resulting in fever and dehydration;
- medications.
Infectious processes in any organ of the urinary system can provoke the development of cylinruria.
The main problem of cylindruria in pregnant women is a high load on the kidneys. During pregnancy, a woman's body also loses a lot of protein. Against the background of toxicosis, fluid loss may occur in the presence of vomiting, which contributes to changes in the structure of urine.
A common pathology in pregnant women is glomerulonephritis. This is due to a decrease in the body’s immune system during pregnancy and a heavy load on the organs of the urinary system.
Cylindruria in children may result from:
- presence of high temperature;
- physical activity;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- presence of glomerulonephritis;
- severe damage to the renal tubule.
Kidney damage and urinary tract infections can cause the development of cylindruria in children and adults. In children, the most common cause of casts in urine is kidney pathologies.
Associated symptoms
The presence of sedimentary cylindrical formations in the urine is not a disease, but indicates about the presence of a problem in the urinary system.
It is cylindruria that does not cause any symptoms. Undesirable symptoms can be caused by the disease itself, which results in cylindrical sediments in the structure of the urinary fluid. Main symptoms diseases of the urinary system are:
- urinary incontinence;
- urinary retention;
- high temperature;
- cloudy urine structure;
- fever.
Symptoms of diseases vary. Often the patient is unaware of the presence of the disease, as well as of casts in the urine: the disease is discovered during examination of other pathologies. The presence of bodies in the urine does not manifest itself in any way.
Treatment
Direct therapy for cylindruria depends on the identified pathology. By eliminating the cause of the formation of sedimentary bodies in the urine, that is, the disease itself, its consequences can be eliminated.
Thus, the cause of the presence of cylinders in the urine are pathologies of the urinary system of various types. By identifying the nature of the cylindrical body, the disease can presumably be diagnosed.
Comprehensive diagnostics will help identify the disease that leads to the formation of sediment in the urine. Timely treatment is the key to a healthy urinary system.
Find out what casts in urine mean in the video.
Urine casts are a type of sediment in the fluid during urination that has a cylindrical shape.
Different types of cylinders make it possible to recognize diseases of the lower zone of the genitourinary tract (etc.), as well as developing disorders of the functional capabilities of the kidneys.
Cylinders detected during a urine test, which include red blood cells, indicate an aggravated diffuse infection.
If bacterial casts were detected in the urine, this indicates the presence of a bacterial infection. In addition, the cylinders carry only those harmful microorganisms that provoked the onset of the disease.
Introduction to the topic
Cylinders always imply renal origin. Their appearance occurs in the distal nephron. Their presence in the fluid sediment during urination is directly related to the protein sediment in the lumen of the channels.
The basis of the cylinders of protein origin includes Tamm-Horsfall uroprotein, which is produced by the epithelium of the convoluted tubules of the kidneys, and aggregated serum proteins.
In addition, the cylinders can have an exclusively protein or cellular composition.
Protein-based cylinders, including cellular components, are externally covered with erythrocytes, epithelial cells and leukocytes.
This is what wax cylinders look like in a child's urine
Granular - the protein base is covered with particles of dying cells. It must be remembered that in urine with alkali they easily disintegrate. Their volume and shape completely correspond to the shape of the kidney tubules and collecting ducts.
It is extremely necessary to thoroughly examine them, since all the components of the cylinders originate from kidney tissue (most rarely, they can come from the lower urethral tract).
Often, hyaline cylinders can be found in urea, which are created from transparent homogeneous tissues excluding cellular components.
They are also present during urination in healthy people who have recently engaged in physical activity. Therefore, they do not have valuable diagnostic information.
If the presence of waxy and/or granular casts was detected in the urine during testing, this indicates serious problems with the functioning of the kidneys.
Basically, the presence of almost any cylinders in the urine indicates a violation of the functional abilities of the kidneys. Therefore, after passing urine, you should undergo a full diagnosis in order to begin treatment on time.
Each cylinder has its own composition and meaning
The wide variety of species of cylinders makes it necessary to clearly distinguish and classify formations when.
They are coagulated plasma serum protein, which passed through the renal globules and was not reabsorbed in the proximal sections of the canals, but, moving through the distal zones, received the shape and volume of the lumen of the canals, namely cylindrical.
Protein coagulation, as well as the appearance of hyaline casts, is affected by the oxidized environment of urine and tubular secretions. Their presence in alkaline urine is excluded.
The more protein tissues are filtered in the tangles and the less they are reabsorbed in the proximal channels, the more cylinders of this type are created.
This explains why patients with a diagnosis, which is also accompanied by increased, notice more active production of cylinders during urination.
They are like grain
Granular casts are created from reformed epithelial cells of the proximal zones of the tubules. They are characterized by a granular (granular) appearance, which is where their name comes from.
Granular casts in the urine are found in various kidney diseases: as well as acute glomerulonephritis, renal, etc.
This type of cylinder includes a homogeneous, shapeless and structureless material that has some resemblance to wax  yellow tint.
yellow tint.
Waxy casts are produced in the distal zones of the tubules due to atrophy and degeneration of the tubular epithelium of these sections.
This is due to serious kidney damage (for example, with moderate malignancy), as well as the last stages of kidney disease and the chronic type.
Therefore, most often, their presence during urination indicates an unfavorable outcome.
Red blood cell casts
Leukocytes, in turn, during the period of pronounced leukocyturia of extensive origin.
Pigment formations
Their formation in urine is due to the manifestation of various types of hemoglobinuria. It is activated by transfusion of incompatible plasma groups or from exposure to toxic substances on the body.
Such cylinders contain brown blood pigments.
Cylinders
They are mucus filaments that are rounded at one end and rounded at the other. Often observed in urine at the final stage of the nephrotic process.
It must be remembered that all cylinders can be detected and remain for a long time exclusively in acidic urine. In alkaline urine the reaction does not occur or is rapidly destroyed.
For this reason, during microscopy of liquid sediment during urination, it is either not found at all, or is found, but in small quantities.
You should also know that urine may contain pseudo-cylinders, which are created from clots and have an external resemblance to hyaline casts and a sediment of uric acid salts, which are red in color. They look like blood cylinders.

What diseases can be diagnosed?
The presence of each cylinder indicates the presence of a specific disease.
Hyaline casts in the urine indicate the following disorders and pathologies:
- the presence of pathologies associated with the kidneys (and of acute origin, in the organ);
- congestive heart failure;
- hyperthermic effects;
- use of diuretics;
- constant physical activity;
- high blood pressure.
Grainy:
- the presence of viral infections;
- fever;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- lead poisoning of the body.
Waxy cylindruria:
- chronic liver enzyme deficiency;
Red blood cells: 
- hypertension of malignant type;
- renal infarction;
- renal vein thrombosis;
Epithelial (the rarest):
- amyloidosis;
- viral type infection;
- intoxication of the body due to excess salts of heavy metals;
- rejection of a transplanted kidney;
- overdose effect of salicylates.
Provoking factors
There are a number of unfavorable factors that several times accelerate the degree of formation of cylinders in urine.
Among them:
- the presence of cells in the fluid during urination;
- osmotic pressure 200-400 mOsm/kg;
- depressed glomerular filtration activity;
- urine having a concentrated composition;
- the presence of individual proteins (hemoglobin, Bence Jones, etc.);
- albumen.
This is worth paying attention to!
 If a person is completely healthy and does not have any kind of disease associated with the functional ability of the kidneys, then in the liquid When urinating, only hyaline casts can be detected(the quantity does not exceed 2 in the preparation).
If a person is completely healthy and does not have any kind of disease associated with the functional ability of the kidneys, then in the liquid When urinating, only hyaline casts can be detected(the quantity does not exceed 2 in the preparation).
Other types of cylinders are not detected in absolutely healthy people. Their presence can be detected by
This helps specialists significantly narrow the scope of their diagnostic search and much more quickly determine what kind of disease the patient is suffering from, and therefore prescribe the necessary treatment or supportive therapy.
If casts are found in the urine, then you should stop using any pharmacological agents that negatively affect the kidneys. You also need to give up all bad habits, especially alcohol abuse.
Cylinders are elements of cylindrical sediment (a kind of cast of renal tubules), consisting of protein or cells, and may also contain various inclusions (hemoglobin, bilirubin, pigments, sulfonamides). Based on their composition and appearance, there are several types of cylinders (hyaline, granular, erythrocyte, waxy, etc.).
Normally, renal epithelial cells secrete the so-called Tamm-Horsfall protein (absent in blood plasma), which is the basis of hyaline casts. Hyaline casts can be found in urine in all kidney diseases. Sometimes hyaline casts can be found in healthy people. As a pathological symptom, they acquire significance when they are constantly detected and in significant quantities, especially when erythrocytes and renal epithelium are superimposed on them.
Grainy cylinders are formed as a result of destruction of tubular epithelial cells. Their detection in a patient at rest and without fever indicates renal pathology.
Waxy cylinders are formed from compacted hyaline and granular cylinders in tubules with a wide lumen. They occur in severe kidney diseases with predominant damage and degeneration of the tubular epithelium, more often in chronic than in acute processes.
Red blood cell casts are formed when erythrocytes are layered on hyaline cylinders, leukocytes - leukocytes. The presence of red blood cell casts confirms the renal origin of hematuria.
Epithelial casts(rarely) formed when the tubular epithelium is detached. Occurs with severe degenerative changes in the tubules at the onset of acute diffuse glomerulonephritis, chronic glomerulonephritis. Their presence in a urine test a few days after surgery is a sign of rejection of the transplanted kidney.
Pigment (hemoglobin) casts are formed when pigments are included in the cylinder and are observed with myoglobinuria and hemoglobinuria.
Cylinders- long formations consisting of mucus. Single cylindroids are found in urine under normal conditions. A significant number of them occur during inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane of the urinary tract. They are often observed when the nephritic process subsides.
Reference values: hyaline cylinders – single, the rest – absent
Hyaline casts in urine:
- renal pathology (acute and chronic glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, kidney stones, renal tuberculosis, tumors);
- congestive heart failure;
- hyperthermic conditions;
- high blood pressure;
- taking diuretics.
Granular casts (nonspecific pathological symptom):
- glomerulonephoritis, pyelonephritis;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- viral infections;
- lead poisoning;
- fever.
Waxy cylinders:
- chronic renal failure;
- kidney amyloidosis;
- nephrotic syndrome.
Red blood cell casts (hematuria of renal origin):
- acute glomerulonephritis;
- kidney infarction;
- renal vein thrombosis;
- malignant hypertension.
Leukocyte casts (leukocyturia of renal origin):
- pyelonephritis;
- Lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Epithelial casts (most rare):
- acute tubular necrosis;
- viral infection (for example, cytomegalovirus);
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals, ethylene glycol;
- overdose of salicylates;
- amyloidosis;
- kidney transplant rejection reaction.
M. V. Markin " General clinical tests of blood, urine, their indicators, reference values, changes in parameters in pathology", Novosibirsk, 2006
Casts are inclusions in urine that form sediment. Depending on the type of formations, a disease can be suspected and more accurate studies can be prescribed. The presence of cylinders in the urine indicates an inflammatory process affecting the organs of the urinary system - urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis. If red blood cells are attached to the cylinders, most likely we are talking about an exacerbation of diffuse glomerulophritis.
The identified bacteria help determine bacterial inflammation; it can be localized in the bladder, urethra, or, with a prolonged course of the disease, rise to the renal pelvis.
It is important for the laboratory technician not only to determine the presence of casts in the urine, but also their type. The classification of cylindrical inclusions is as follows:
- Hyaline casts in the urine may be present even if the person is completely healthy. The acceptable standard is 1-2 inclusions.
- Granular - the tubules are stuck together into a protein formation; there is an admixture of renal epithelial cells.
- Waxy - inclusions consisting of a translucent mixture of a uniform format.
- Red blood cells are an alarming sign indicating acute inflammation in serious illnesses, for example, kidney cancer, bleeding of the fornical type.
- Epithelial - fixed if kidney function is impaired. The doctor may suspect a serious illness, such as sublimate or nephrosis.
- Pseudocylinders are mucus similar to hyaline cylindrical inclusions. Formed from a precipitate of uric acid salts, the formations are colored red, at first glance they resemble pigmented bloody inclusions.
As you can see, there are many diseases indicated by sediment in the urine. In any case, they always determine kidney damage, because it is in  kidneys and cylinders are formed.
kidneys and cylinders are formed.
Characteristics of hyaline inclusions in urine
When acidic urine reacts, the protein in the kidney tubules becomes denatured. It is extremely difficult to see such inclusions even under a microscope, so laboratory assistants add iodine tincture and blue substances to the liquid. Hyaline casts in urine are found in the following diseases:
- increased physical activity and stress;
- excess body temperature;
- neurotic deviation;
- flu;
- parainfluenza;
- infection caused by adenovirus;
- polio;
- mumps;
- AIDS with accompanying whooping cough, meningitis, tuberculosis.
Features of granular formations
Granular formations are obtained from protein that has coagulated in acidic urine if dystrophically renewed kidney tubular epithelial cells are attached to the surface. As a result, the inclusion is painted in a dark golden hue.
Diseases that provoke granular casts in the urine:
- chronic glomerulonephritis;
- amyloidosis affecting the kidneys;
- diabetic nephropathy;
- illnesses caused by a virus that occur with fever.
Waxy casts in urine
The composition of the inclusions is without a clear structure, similar to wax. Formed due to atrophy or dystrophy of the epithelium in the tubules. IN  In tests, waxy inclusions are sown if the patient has chronic renal failure.
In tests, waxy inclusions are sown if the patient has chronic renal failure.
It happens that the condition of the kidneys already leaves much to be desired, but the disease has not yet reached an acute peak. Wax formations make it possible to determine an accurate diagnosis and promptly begin effective treatment.
Remaining types of inclusions in urine
Leukocyte casts in the urine are a clear sign of lupus nephritis. Epithelial ones determine the death of renal tubular cells, this is possible if heavy metal poisoning has occurred. Doctors pay special attention to the presence of epithelial formations if the patient had an allograft inserted several days ago.
Cylinders - an increased number is determined if the inflammatory process spreads in the organs of the urinary system.
What can provoke an increase in the number of cylinders in urine
There are factors that increase the increase in the number of inclusions in urine:
- if the osmotic pressure reaches 200-400 mOsm/kg;
- glomerular filtration activity is suppressed;
- urine that is too concentrated due to the acidic environment, the presence of salts;
- there are individual proteins, for example, hemoglobin, Bence-Jones;
- presence of albumin.
How to treat casts in urine
In a healthy person, hyaline formations may be detected in the urine. Everything else is extra inclusions. The appearance of cylinders is a consequence of inflammation, so the disease itself should be treated.
For cystitis and urethritis, the following therapeutic course is prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory - Cyston, Furagin, Canephron.
- Antibiotic therapy - if a urine test for bacteria has identified bacterial flora.
- Infusions of knotweed herbs, chamomile, St. John's wort, diuretic collection Nephrofit. It is better to buy the latter not in infusion bags, but in a mixture.
- Painkillers.
- Spicy foods, juices, and citrus fruits are excluded from the diet.
If your kidneys hurt, treatment should be long-term. Only an experienced doctor can select effective therapy. To avoid the negative impact of drugs on other systems, concomitant medications are selected.