Pregnancy- This is a physiological process in which a new organism develops in the uterus, resulting from fertilization. Pregnancy lasts an average of 40 weeks (10 obstetric months).
In the intrauterine development of a child, two periods are distinguished:
- Embryonic(up to 8 weeks of pregnancy inclusive). At this time, the embryo is called an embryo and acquires the features characteristic of a person;
- Fetal(from 9 weeks to birth). At this time, the embryo is called a fetus.
The growth of a child, the formation of his organs and systems proceeds naturally in different periods of intrauterine development, which is subject to the genetic code embedded in the germ cells and fixed in the process of human evolution.
Embryo development in the first obstetric month (1-4 weeks)
First week (1-7 days)
Pregnancy starts from the moment fertilization- the fusion of a mature male cell (sperm) and a female egg. This process usually occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. After a few hours, the fertilized egg begins to divide exponentially and descends through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity (this journey takes up to five days).
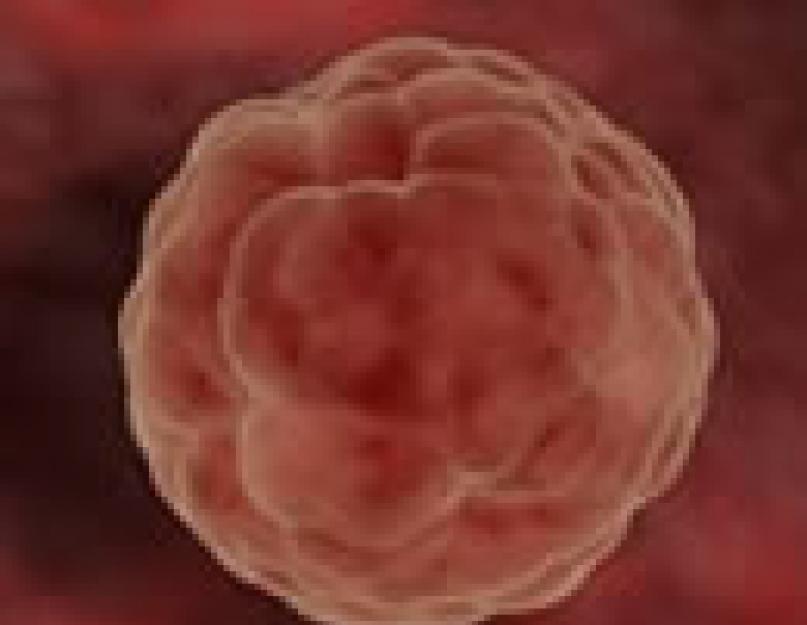
As a result of division a multicellular organism, which looks like a blackberry (in Latin "morus"), which is why the embryo at this stage is called morula. Approximately on the 7th day, the morula is introduced into the wall of the uterus (implantation). The villi of the outer cells of the embryo are connected to the blood vessels of the uterus, subsequently the placenta is formed from them. Other outer cells of the morula give rise to the development of the umbilical cord and membranes. After some time, various tissues and organs of the fetus will develop from the internal cells.
Information At the time of implantation, a woman may have small bleeding from the genital tract. Such secretions are physiological and do not require treatment.
Second week (8-14 days)
The outer cells of the morula grow tightly into the lining of the uterus. At the fetus the formation of the umbilical cord, placenta, as well as neural tube from which the fetal nervous system subsequently develops.
Third week (15-21 days)
The third week of pregnancy is a difficult and important period.. At that time important organs and systems begin to form fetus: the beginnings of the respiratory, digestive, circulatory, nervous and excretory systems appear. In the place where the fetal head will soon appear, a wide plate is formed, which will give rise to the brain. On day 21, the baby's heart begins to beat.
Fourth week (22-28 days)
This week fetal organ laying continues. The rudiments of the intestines, liver, kidneys and lungs are already present. The heart begins to work more intensively and pumps more and more blood through the circulatory system.
From the beginning of the fourth week in the embryo body wrinkles appear, and appears rudiment of the spine(chord).
Ends by day 25 neural tube formation.
By the end of the week (approximately 27-28 days) muscular system, spine are formed, which divides the embryo into two symmetrical halves, and upper and lower limbs.
During this period begins formation of pits on the head, which will later become the eyes of the fetus.
Development of the embryo in the second obstetric month (5-8 weeks)
Fifth week (29-35 days)
During this period, the embryo weighs about 0.4 grams, length 1.5-2.5 mm.
The formation of the following organs and systems begins:
- Digestive system: liver and pancreas;
- Respiratory system: larynx, trachea, lungs;
- Circulatory system;
- reproductive system: precursors of germ cells are formed;
- sense organs: eye and inner ear formation continues;
- Nervous system: the formation of brain regions begins.
At that time a faint umbilical cord appears. The formation of limbs continues, the first rudiments of nails appear.
On the face upper lip and nasal cavities formed.
Sixth week (36-42 days)
Length embryo during this period is about 4-5mm.
Starts in the sixth week placenta formation. At this time, it is just beginning to function, the blood circulation between it and the embryo has not yet been formed.
Continues formation of the brain and its parts. At the sixth week, when performing an encephalogram, it is already possible to fix signals from the fetal brain.
Begins facial muscle formation. The eyes of the fetus are already more pronounced and uncovered by the eyelids, which are just beginning to form.
During this period, they begin upper limbs change: they lengthen and the rudiments of hands and fingers appear. The lower limbs are still in their infancy.
Changes in important organs:
- Heart. The division into chambers is completed: ventricles and atria;
- urinary system. Primary kidneys have formed, the development of the ureters begins;
- Digestive system. The formation of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract begins: the stomach, small and large intestines. By this period, the liver and pancreas had practically completed their development;
Seventh week (43-49 days)
The seventh week is significant in that the final the formation of the umbilical cord is completed and uteroplacental circulation is established. Now the breathing and nutrition of the fetus will be carried out due to the circulation of blood through the vessels of the umbilical cord and placenta.
The embryo is still bent in an arcuate manner; there is a small tail on the pelvic part of the body. The size of the head is at least the entire half of the embryo. The length from the crown to the sacrum grows by the end of the week up to 13-15 mm.
Continues upper limb development. The fingers are clearly visible, but their separation from each other has not yet occurred. The child begins to perform spontaneous hand movements in response to stimuli.
Good eyes formed, already covered with eyelids that protect them from drying out. The child can open his mouth.
There is a laying of the nasal fold and nose, two paired elevations are formed on the sides of the head, from which they will begin to develop ear shells.
Intensive development of the brain and its parts.
Eighth week (50-56 days)
The body of the embryo begins to straighten, length from the crown of the head to the coccyx is 15 mm at the beginning of the week and 20-21 mm on day 56.
Continues formation of important organs and systems Key words: digestive system, heart, lungs, brain, urinary system, reproductive system (boys develop testicles). The organs of hearing are developing.
By the end of the eighth week the face of the child becomes familiar to a person: well-defined eyes, covered with eyelids, nose, auricles, lip formation ends.
Intensive growth of the head, upper and lower horses is noted. particularities, ossification of the long bones of the arms and legs and the skull develops. Fingers are clearly visible, there is no skin membrane between them.
Additionally The eighth week ends the embryonic period of development and begins the fetal. The embryo from this time is called the fetus.
Fetal development in the third obstetric month (9-12 weeks)
Ninth week (57-63 days)
At the beginning of the ninth week coccygeal-parietal size fetus is about 22 mm, by the end of the week - 31 mm.
going on improvement of the vessels of the placenta which improves uteroplacental blood flow.
Development of the musculoskeletal system continues. The process of ossification begins, the joints of the toes and hands are formed. The fetus begins to make active movements, can squeeze fingers. The head is lowered, the chin is closely pressed to the chest.
Changes occur in the cardiovascular system. The heart makes up to 150 beats per minute and pumps blood through its blood vessels. The composition of blood is still very different from the blood of an adult: it consists only of red blood cells.
Continues further growth and development of the brain, structures of the cerebellum are formed.
The organs of the endocrine system are intensively developing in particular, the adrenal glands, which produce important hormones.
Improved cartilage tissue: auricles, cartilages of the larynx, vocal cords are being formed.
Tenth week (64-70 days)
By the end of the tenth week fruit length from coccyx to crown is 35-40 mm.
Buttocks begin to develop, the previously existing tail disappears. The fetus is in the uterus in a fairly free position in a half-bent state.
The development of the nervous system continues. Now the fetus performs not only chaotic movements, but also reflex ones in response to a stimulus. When accidentally touching the walls of the uterus, the child makes movements in response: he turns his head, bends or unbends his arms and legs, pushes himself to the side. The size of the fetus is still very small, and the woman cannot yet feel these movements.
The sucking reflex develops, the child begins reflex movements of the lips.
Diaphragm development completes, which will take an active part in breathing.
Eleventh week (71-77 days)
By the end of this week coccygeal-parietal size fetus increases to 4-5 cm.
The body of the fetus remains disproportionate: small body, large head, long arms and short legs, bent at all joints and pressed to the stomach.
The placenta has already reached sufficient development and copes with its functions: it provides oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and removes carbon dioxide and metabolic products.
Further formation of the fetal eye occurs: at this time, the iris develops, which will later determine the color of the eyes. The eyes are well developed, semi-lidded or wide open.
Twelfth week (78-84 days)
Coccygeal-parietal size fetus is 50-60 mm.
Goes distinctly the development of the genital organs according to the female or male type.
going on further improvement of the digestive system. The intestines are elongated and fit in loops, as in an adult. Its periodic contractions begin - peristalsis. The fetus begins to make swallowing movements, swallowing amniotic fluid.
The development and improvement of the fetal nervous system continues. The brain is small, but exactly repeats all the structures of the brain of an adult. The cerebral hemispheres and other departments are well developed. Reflex movements are improved: the fetus can squeeze and unclench its fingers into a fist, grabs the thumb and actively sucks it.
In the blood of the fetus not only erythrocytes are already present, but the production of white blood cells - leukocytes - begins.
At this time the child single respiratory movements begin to register. Before birth, the fetus cannot breathe, its lungs do not function, but it makes rhythmic movements of the chest, imitating breathing.
By the end of the week, the fetus eyebrows and eyelashes appear, the neck is clearly visible.
Fetal development in the fourth obstetric month (13-16 weeks)
13 weeks (85-91 days)
Coccygeal-parietal size by the end of the week is 70-75 mm. The proportions of the body begin to change: the upper and lower limbs and torso lengthen, the size of the head is no longer so large in relation to the body.
Improvement of the digestive and nervous systems continues. Germs of milk teeth begin to appear under the upper and lower jaws.
The face is fully formed, clearly visible auricles, nose and eyes (completely closed for centuries).
14 weeks (92-98 days)
Coccygeal-parietal size by the end of the fourteenth week increases up to 8-9 cm. The proportions of the body continue to change to more familiar ones. The forehead, nose, cheeks and chin are well defined on the face. The first hair appears on the head (very thin and colorless). The surface of the body is covered with fluffy hairs, which retain the lubrication of the skin and thus perform protective functions.
Improving the musculoskeletal system of the fetus. Bones become stronger. Increased motor activity: the fetus can roll over, bend, make swimming movements.
The development of the kidneys, bladder and ureters is completed. The kidneys begin to excrete urine, which mixes with the amniotic fluid.
: pancreatic cells begin to work, producing insulin, and pituitary cells.
There are changes in the genitals. In boys, the prostate gland is formed, in girls, the ovaries migrate into the pelvic cavity. At the fourteenth week, with a good sensitive ultrasound machine, it is already possible to determine the sex of the child.
Fifteenth week (99-105 days)
Coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus is about 10 cm, fruit weight - 70-75 grams. The head still remains quite large, but the growth of the arms, legs and torso begins to outpace it.
Improves the circulatory system. In a child in the fourth month, it is already possible to determine the blood type and Rh factor. Blood vessels (veins, arteries, capillaries) grow in length, their walls become stronger.
The production of original feces (meconium) begins. This is due to the ingestion of amniotic fluid, which enters the stomach, then into the intestines and fills it.
Fully formed fingers and toes, they have an individual pattern.
Sixteenth week (106-112 days)
The weight of the fetus increases to 100 grams, the coccygeal-parietal size - up to 12 cm.
By the end of the sixteenth week, the fetus is already fully formed., he has all the organs and systems. The kidneys work actively, every hour a small amount of urine is released into the amniotic fluid.
Fetal skin is very thin, subcutaneous fatty tissue is practically absent, so blood vessels are visible through the skin. The skin looks bright red, covered with downy hairs and grease. Eyebrows and eyelashes are well defined. Nails are formed, but they cover only the edge of the nail phalanx.
Mimic muscles are formed, and the fetus begins to "grimace": a frown of eyebrows is observed, a semblance of a smile.
Fetal development in the fifth obstetric month (17-20 weeks)
Seventeenth week (113-119 days)
The weight of the fetus is 120-150 grams, the coccygeal-parietal size is 14-15 cm.
The skin remains very thin, but under it, subcutaneous fatty tissue begins to develop. The development of milk teeth, which are covered with dentin, continues. Under them, the germs of permanent teeth begin to form.
Reaction to sound stimuli. From this week, you can say for sure that the child began to hear. When strong sharp sounds appear, the fetus begins to move actively.
Fetal position changes. The head is raised and is almost vertical. The arms are bent at the elbow joints, the fingers are clenched into a fist almost all the time. Periodically, the child begins to suck his thumb.
Becomes distinct heartbeat. From now on, the doctor can listen to him with a stethoscope.
Eighteenth week (120-126 days)
The weight of the child is about 200 grams, length - up to 20 cm.
The formation of sleep and wakefulness begins. Most of the time the fetus sleeps, movements stop for this time.
At this time, a woman may already begin to feel the movement of the child, especially with repeated pregnancies. The first movements are felt as gentle jolts. A woman can feel more active movements during excitement, stress, which affects the emotional state of the child. At this time, the norm is about ten episodes of fetal movement per day.
Nineteenth week (127-133 days)
The weight of the child increases to 250-300 grams, body length - up to 22-23 cm. The proportions of the body change: the head lags behind the body in growth, arms and legs begin to lengthen.
Movements become more frequent and noticeable. They can be felt not only by the woman herself, but also by other people, putting their hand to their stomach. Primigravida at this time can only begin to feel movements.
Improves the endocrine system: the pancreas, pituitary, adrenals, gonads, thyroid and parathyroid glands are actively functioning.
The composition of the blood has changed: in addition to erythrocytes and leukocytes, there are monocytes and lymphocytes in the blood. The spleen begins to take part in hematopoiesis.
Twentieth week (134-140 days)
Body length increases to 23-25 cm, weight - up to 340 grams.
Fetal skin is still thin, covered with a protective lubricant and fluffy hairs that can persist until the very birth. Intensively develops subcutaneous adipose tissue.
Well formed eyes, at twenty weeks the blink reflex begins to appear.
Improved movement coordination: the child confidently brings his finger to his mouth and begins to suck it. Expressed facial expressions: the fetus can close his eyes, smile, frown.
This week, all women feel the movements regardless of the number of pregnancies. Movement activity changes throughout the day. When irritants appear (loud sounds, stuffy room), the child begins to move very violently and actively.
Fetal development in the sixth obstetric month (21-24 weeks)
Twenty-first week (141-147 days)
Body weight grows up to 380 grams, fetal length - up to 27 cm.
The subcutaneous tissue layer increases. The skin of the fetus is wrinkled, with many folds.
Fetal movements become more and more active and tangible. The fetus moves freely in the uterine cavity: lies down with its head or buttocks, across the uterus. It can pull the umbilical cord, push off with hands and feet from the walls of the uterus.
Changes in sleep and wake patterns. Now the fetus spends less time sleeping (16-20 hours).
Twenty-second week (148-154 days)
At week 22, the size of the fetus increases to 28 cm, weight - up to 450-500 grams. The size of the head becomes proportional to the trunk and limbs. The legs are almost all the time in a bent state.
Fully formed fetal spine: it has all the vertebrae, ligaments and joints. The process of strengthening bones continues.
Improvement of the fetal nervous system: the brain already contains all the nerve cells (neurons) and has a mass of about 100 grams. The child begins to take an interest in his body: he feels his face, arms, legs, tilts his head, brings his fingers to his mouth.
Significantly enlarged heart improving the functionality of the cardiovascular system.
Twenty-third week (155-161 days)
The body length of the fetus is 28-30 cm, weight - about 500 grams. The pigment begins to be synthesized in the skin, as a result, the skin acquires a bright red color. The subcutaneous fatty tissue is still quite thin, as a result, the child looks very thin and wrinkled. Lubrication covers the entire skin, is more abundant in the folds of the body (elbow, axillary, inguinal, and other folds).
The development of the internal genital organs continues: in boys - the scrotum, in girls - the ovaries.
Increased respiratory rate up to 50-60 times per minute.
The swallowing reflex is still well developed: the child constantly swallows amniotic fluid with particles of a protective lubricant of the skin. The liquid part of the amniotic fluid is absorbed into the blood, a thick green-black substance (meconium) remains in the intestines. Normally, the intestines should not be emptied until the baby is born. Sometimes swallowing water causes hiccups in the fetus, a woman can feel it in the form of rhythmic movements for several minutes.
Twenty-fourth week (162-168 days)
By the end of this week, the weight of the fetus increases to 600 grams, body length - up to 30-32 cm.
The movements are getting stronger and clearer. The fetus occupies almost the entire place in the uterus, but can still change position and roll over. Muscles grow strongly.
By the end of the sixth month, the child has well-developed sense organs. Vision begins to function. If a bright light falls on the woman's stomach, the fetus begins to turn away, tightly closes the eyelids. Hearing is well developed. The fetus determines for itself pleasant and unpleasant sounds and reacts to them in different ways. With pleasant sounds, the child behaves calmly, his movements become calm and measured. With unpleasant sounds, it begins to freeze or, conversely, moves very actively.
An emotional bond is established between mother and child. If a woman experiences negative emotions (fear, anxiety, longing), the child begins to experience similar feelings.
Fetal development in the seventh obstetric month (25-28 weeks)
Twenty-fifth week (169-175 days)
The length of the fetus is 30-34 cm, body weight increases to 650-700 grams. The skin becomes elastic, the number and severity of folds decreases due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fatty tissue. The skin remains thin with a large number of capillaries, giving it a red color.
The face has a familiar human appearance: eyes, eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, cheeks, auricles are well expressed. The cartilages of the ears are still thin and soft, their curves and curls are not fully formed.
Bone marrow develops, which takes on a major role in hematopoiesis. The strengthening of the bones of the fetus continues.
There are important processes in the maturation of the lungs: small elements of lung tissue (alveoli) are formed. Before the birth of the child, they are without air and resemble deflated balloons, which straighten out only after the first cry of the newborn. From the 25th week, the alveoli begin to produce a special substance (surfactant) necessary to maintain their shape.
Twenty-sixth week (176-182 days)
The length of the fetus is about 35 cm, the weight increases to 750-760 grams. The growth of muscle tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue continues. Bones are strengthened and permanent teeth continue to develop.
The formation of genital organs continues. In boys, the testicles begin to descend into the scrotum (the process lasts 3-4 weeks). In girls, the formation of the external genitalia and vagina is completed.
Improved sense organs. The child develops a sense of smell (smell).
Twenty-seventh week (183-189 days)
Weight increases to 850 grams, body length - up to 37 cm.
Organs of the endocrine system are actively functioning in particular the pancreas, pituitary gland and thyroid gland.
The fetus is quite active, makes various movements freely inside the uterus.
From the twenty-seventh week of the child individual metabolism begins to form.
Twenty-eighth week (190-196 days)
The weight of the child increases to 950 grams, body length - 38 cm.
By this age the fetus becomes practically viable. In the absence of organ pathology, a child with good care and treatment can survive.
Subcutaneous adipose tissue continues to accumulate. The skin is still red in color, vellus hair begins to gradually fall out, remaining only on the back and shoulders. Eyebrows, eyelashes, hair on the head become darker. The child begins to open his eyes frequently. The cartilages of the nose and ears remain soft. The nails do not yet reach the edge of the nail phalanx.
This week starts over active functioning of one of the hemispheres of the brain. If the right hemisphere becomes active, then the child becomes left-handed, if the left, then right-handedness develops.
Fetal development in the eighth month (29-32 weeks)
Twenty-ninth week (197-203 days)
The weight of the fetus is about 1200 grams, growth increases to 39 cm.
The child has already grown enough and takes up almost all the space in the uterus. The movements are not so chaotic. The movements are manifested in the form of periodic pushes with the legs and arms. The fetus begins to take a definite position in the uterus: head or buttocks down.
All organ systems continue to improve. The kidneys excrete up to 500 ml of urine per day. The load on the cardiovascular system increases. The circulation of the fetus is still significantly different from the circulation of the newborn.
Thirtieth week (204-210 days)
Body weight increases to 1300-1350 grams, growth remains about the same - about 38-39 cm.
Constant accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue, skin folds are straightened. The child adapts to the lack of space and assumes a certain position: curled up, arms and legs crossed. The skin still has a bright color, the amount of lubrication and vellus hair is reduced.
Continues development of alveoli and production of surfactant. The lungs prepare for the birth of the baby and the start of breathing.
The development of the brain continues brain, the number of convolutions and the area of the cortex increase.
Thirty-first week (211-217 days)
The weight of the child is about 1500-1700 grams, growth increases to 40 cm.
The child's sleep and wake patterns change. Sleep still takes a long time, during this time there is no motor activity of the fetus. During wakefulness, the child actively moves and pushes.
Fully formed eyes. During sleep, the child closes his eyes, during wakefulness, the eyes are open, periodically the child blinks. The color of the iris in all children is the same (blue), then after birth it begins to change. The fetus reacts to bright light by constriction or dilation of the pupil.
Increases the size of the brain. Now its volume is about 25% of the volume of the brain of an adult.
Thirty-second week (218-224 days)
The height of the child is about 42 cm, weight - 1700-1800 grams.
Continued accumulation of subcutaneous fat, in connection with which, the skin becomes lighter, there are practically no folds on it.
Improved internal organs: organs of the endocrine system intensively secrete hormones, surfactant accumulates in the lungs.
The fetus produces a special hormone, which promotes the formation of estrogen in the mother's body, as a result, the mammary glands begin to prepare for the production of milk.
Fetal development in the ninth month (33-36 weeks)
Thirty-third week (225-231 days)
The weight of the fetus increases to 1900-2000 grams, growth is about 43-44 cm.
Skin becomes brighter and smoother, the layer of adipose tissue increases. Vellus hair is more and more wiped, the layer of protective lubricant, on the contrary, increases. The nails grow to the edge of the nail phalanx.
The child becomes more and more crowded in the uterine cavity, so his movements become more rare, but strong. The position of the fetus is fixed (head or buttocks down), the likelihood that the child will roll over after this period is extremely small.
The work of internal organs is improving: the mass of the heart increases, the formation of the alveoli is almost completed, the tone of the blood vessels increases, the brain is fully formed.
Thirty-fourth week (232-238 days)
The weight of the child ranges from 2000 to 2500 grams, height is about 44-45 cm.
The baby is now in a stable position in the uterus. The bones of the skull are soft and mobile thanks to the fontanelles, which can close only a few months after childbirth.
The hair on the head grows intensively and take on a certain color. However, hair color may change after childbirth.
Significant strengthening of bones, in connection with this, the fetus begins to take calcium from the mother's body (a woman at this time may notice the appearance of seizures).
Baby swallows amniotic fluid all the time, thereby stimulating the gastrointestinal tract and the functioning of the kidneys, which secrete at least 600 ml of clear urine per day.
Thirty-fifth week (239-245 days)
Every day the child adds 25-35 grams. Weight in this period can vary greatly and by the end of the week is 2200-2700 grams. Height increases to 46 cm.
All the internal organs of the child continue to improve, preparing the body for the upcoming extrauterine existence.
Fatty tissue is intensively deposited, the child becomes more well-fed. The amount of vellus hair is greatly reduced. The nails have already reached the tips of the nail phalanges.
A sufficient amount of meconium has already accumulated in the intestines of the fetus, which normally should depart 6-7 hours after childbirth.
Thirty-sixth week (246-252 days)
The weight of the child varies greatly and can range from 2000 to 3000 grams, height - within 46-48 cm
The fetus already has well-developed subcutaneous adipose tissue, skin color becomes light, wrinkles and folds completely disappear.
The baby takes a certain position in the uterus: more often he lies upside down (less often, legs or buttocks, in some cases, transversely), the head is bent, the chin is pressed to the chest, arms and legs are pressed to the body.
Skull bones, unlike other bones, remain soft, with cracks (fontanelles), which will allow the baby's head to be more pliable when passing through the birth canal.
All organs and systems are fully developed for the existence of a child outside the womb.
Fetal development in the tenth obstetric month
Thirty-seventh week (254-259 days)
The height of the child increases to 48-49 cm, the weight can fluctuate significantly. The skin has become lighter and thicker, the fat layer increases by 14-15 grams per day every day.
Cartilages of the nose and ears become tighter and more elastic.
Fully formed and mature lungs, the alveoli contain the necessary amount of surfactant for the breath of the newborn.
Completion of the digestive system: In the stomach and intestines, there are contractions necessary to push food through (peristalsis).
Thirty-eighth week (260-266 days)
The weight and height of the child varies greatly.
The fetus is fully mature and ready to be born. Outwardly, the child looks like a full-term newborn. The skin is light, fatty tissue is sufficiently developed, vellus hair is practically absent.
Thirty-ninth week (267-273 days)
Usually two weeks before delivery fetus starts to drop clinging to the bones of the pelvis. The child has already reached full maturity. The placenta begins to gradually grow old and metabolic processes worsen in it.
The mass of the fetus increases significantly (30-35 grams per day). The proportions of the body change completely: the chest and shoulder girdle are well developed, the belly is rounded, and the limbs are long.
Well developed sense organs: the child picks up all sounds, sees bright colors, can focus vision, taste buds are developed.
Fortieth week (274-280 days)
All indicators of fetal development correspond to the neonatal born. The child is completely ready for childbirth. Weight can vary significantly: from 250 to 4000 and above grams.
The uterus begins to contract periodically(), which is manifested by aching pains in the lower abdomen. The cervix opens slightly, and the fetal head is pressed closer to the pelvic cavity.
The bones of the skull are still soft and pliable, which allows the baby's head to change shape and easier to pass through the birth canal.
Fetal development by week of pregnancy - Video
Most often, in the first month of pregnancy, a woman does not suspect that she is carrying a little man under her heart. During this period, there are no obvious changes in the body of the expectant mother. However, there are signs that make it possible to recognize pregnancy already in the first month. What you need to know and what happens during this period. How the fetus develops, and what the expectant mother experiences.
The entire pregnancy is divided into three periods - trimesters. The first trimester lasts 13 weeks, the second - 14-26 weeks and the third - from 27 weeks until delivery. When calculating the term, concepts such as obstetric week and obstetric month are used. Such a definition is necessary for the convenience of calculating the duration of pregnancy. The obstetric week consists of seven days. Obstetric month is 4 weeks. The first obstetric month of pregnancy is counted from the first day of the last menstruation.
How many weeks are there in the first month of pregnancy? A constant unit was found - a week, which lasts seven days. This choice was made in order to make it easier to track how the baby develops. Thus, one month of pregnancy is only 4 weeks.
What happens in the first month of pregnancy
Let's take a look at what happens in the first month of pregnancy. A fertilized egg begins to rapidly divide. After seven days, the embryo will look like a small ball filled with water. It moves along the fallopian tube towards the uterus. Having reached it, the embryo is attached to the wall with the help of villi. The formation of the placenta begins. With its help, the fetus will receive all the necessary nutrients from the mother's body. Along with this is the development of the umbilical cord and neural tube. There is a laying of vital organs and systems. The respiratory, digestive, circulatory, nervous and excretory systems are being formed. During this period, the fetus has a heartbeat. The brain is being formed. The size of the fetus in the first month of pregnancy is 4 millimeters. It can be compared to the size of a grain of rice. The embryo can be divided into two sections: head and abdominal. The body of the fetus is asymmetrical. This is what a baby looks like in the first month of pregnancy.
It is rather problematic to determine exactly how long the fetal movement will be in the first month of pregnancy. For each woman, these numbers will be different and depend on the following factors:
- what kind of pregnancy
- during the first pregnancy, movements are felt at about 19 weeks. With the second - at 17 weeks;
- the position of the fetus;
- the constitution of a pregnant woman;
- activity of the expectant mother
With high physical activity, the chance to feel the child's weak tremors is significantly reduced.
What does the belly look like in the first month of pregnancy
Does the belly grow in the first month of pregnancy? Is the belly visible in the first month of pregnancy? These are some of the most exciting questions for expectant mothers. Visually, there have been no changes so far. All important processes go gradually, and therefore in the first month of pregnancy, the belly grows slowly. And it becomes visible only by 4 months.
What does a woman feel in the first month of pregnancy
The main signs at 1 month of pregnancy after conception are hormonal disruptions and physiological changes. They are aimed at preparing the female body for gestation and childbirth.
Physiological changes include:
- Cessation of the menstrual cycle.
- Another sign of pregnancy is a periodic feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Sudden change in taste.
- The chest is swollen, and painful sensations appear in the nipples.
From the moment of conception, hormonal changes occur in a woman's body:
- The lining of the uterus thickens to receive a fertilized egg.
- Decreased smooth muscle tone by the hormone progesterone.
- Enlargement of the mammary glands due to the large amount of the secreted hormone progesterone.
- The hormone chorionic gonadotropin is formed, which stimulates the production of progesterone.
First month of pregnancy: symptoms and sensations
Let us consider in more detail what a woman feels in the first month of pregnancy. Despite the fact that the fact of conception has already taken place, there are no obvious visible changes yet. Therefore, the sensations in the first month of pregnancy will at first resemble the sensations characteristic of ordinary days of menstruation.
Symptoms in the first month of pregnancy:
- 1. Small brown discharge a week before the expected start of the cycle. Appear at the moment of attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus. These signs of pregnancy may not be for everyone.
- Increase in basal body temperature. Measured in the morning at rest. You can measure under the armpit, in the mouth or rectally. A sign of pregnancy will be its increase to 37.2 degrees. Then the basal temperature decreases, and then again reaches 37 degrees.
- Drowsiness, fatigue. Occur due to hormonal changes. The main reason for this is a decrease in blood pressure.
- Toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy. Nausea, vomiting, intolerance to smells are among the first signs of pregnancy.
- Feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Sensitivity and breast enlargement. Associated with an increase in progesterone. Getting ready for breastfeeding.
Thus, the symptoms and sensations in the first month of pregnancy will be mostly relative. To confirm the signs of pregnancy, you must consult a doctor.
Then you will remember this month and look for a premonition of such an important event. Perhaps it was the most unexpected, or maybe you deliberately prepared for it. What happens in the body of a woman in this mysterious month? In most cases, women do not know the exact date of conception of a child, but they can say exactly when the last menstruation began. Therefore, it is customary for obstetricians around the world to count pregnancy from the first day of the last menstruation. Although for most women, the most likely period of fertilization is in the middle of the menstrual cycle. If you count from the first day of menstruation, pregnancy lasts an average of 280 days or 40 weeks. In everyday life, we still operate by counting the months of pregnancy.
What happens in the body of the expectant mother?
So, oddly enough, the first week of a future pregnancy falls on menstruation. During this period, the brain actively rebuilds your endocrine system, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland secrete special hormones that prepare one of the thousands of eggs in the ovaries for fertilization, and the uterine mucosa for the reception of a fertilized fetal egg. The body of a newly born girl contains about 2 million eggs. Their number is reduced to about 400 thousand by the beginning of puberty. During each cycle, 20 or more eggs begin the process of maturation, however, in the second week from the onset of menstruation, a "leader" can already be distinguished among them. This is most often a single egg, located in a special vesicle (called a graafian), which protrudes above the surface of the ovary.
By the end of the second week, the graafian vesicle ruptures, and the egg is released from the ovary into the abdominal cavity. This moment is called ovulation. After ovulation, the egg is captured by the processes of the fallopian tube, where it remains viable for up to 24 hours. Some women experience pain in the lower abdomen or discomfort on the day of ovulation or the next day. In addition, the day of ovulation can be determined by dividing the menstrual cycle (the time from the first day of the previous period to the first day of the next) in half - for example, with a 28-day cycle, this is the 14th day. Naturally, this method of determining ovulation is only suitable for women with a constant cycle. If the cycle is irregular, then special devices or pharmacy tests that determine ovulation by urinalysis will help to find out when ovulation occurred. You can also use the measurement of basal temperature (i.e. temperature in the rectum).
On the day of ovulation, there is a jump in basal temperature. It must be at least 0.6°C. If a meeting with a spermatozoon occurs, then pregnancy occurs. In the place where the Graafian bubble was, a special formation is formed - the corpus luteum. It looks like a small sac of fluid on the wall of the ovary. It rapidly develops blood vessels to produce various hormones needed to support early pregnancy, most notably progesterone. The formation of a corpus luteum may be accompanied by pain. The development of early toxicosis of pregnancy is associated with the functioning of the corpus luteum. This is confirmed by the fact that most often early toxicosis disappears by the 16th week of pregnancy, when the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development, and the placenta takes over its functions.
By the end of the first month of pregnancy, the fertilized egg will implant (implant) into the wall of your uterus. When implantation occurs, the cervix will swell, become softer, and a dense mucous plug will appear in it, preventing infection from entering the uterus. The first changes in your immune system are starting to happen - early pregnancy factor (EPF) is produced. This substance helps the fetal egg "deceive" your body, prevents conflict between your immune system and "foreign" fetal cells.
fertilization process
The fertilization process takes place in the upper part of the fallopian tube. Many spermatozoa go to the egg, releasing a special substance that dissolves its shell, and only one manages to break through the defenses of the protective layer of the egg. This is the moment of conception. After it, a chemical process begins in the shell of the egg, which does not allow other spermatozoa to get inside. The sperm inside the egg is resorbed, and its nucleus is combined with the nucleus of the egg, resulting in the genetic information of the father and mother. Approximately 266 days should pass from the moment of conception to the birth of a child. The sex of the unborn child is determined by the chromosome set of the sperm. Spermatozoa are of two types - with X- or Y-chromosome, and the egg always has only the X-chromosome. If a sperm with a Y chromosome enters the egg, then a boy will be born, and if with an X chromosome, then a girl. A "boy" sperm cell moves faster, but lives less than a "girl" one, so the coincidence of sexual intercourse with ovulation increases the likelihood of having a boy, and the birth of a girl is more likely if sexual intercourse occurs 2-3 days earlier. As a result of fertilization, a unicellular embryo is formed - a zygote.
By the end of the first day after fertilization, the division of the zygote begins. After 30 hours, 2 cells are formed, after another 10 hours - 4, and by 6-7 days after fertilization, the number of cells will reach 250, while the shape of the embryo will resemble a hollow ball with a diameter of 0.1-0.2 mm. Your unborn baby is called a blastocyst. At this time, the embryo moves through the fallopian tube to the uterus, the movement continues for three days, for another two days the embryo is freely in the uterine cavity. If the movement of the embryo is slowed down, then an ectopic pregnancy may occur, if accelerated, then the embryo enters the uterus at the stage of development when it cannot engraft or the fetal egg is attached too low, which leads to a complication of pregnancy - placenta previa or its low attachment; in this case, the placenta either blocks the exit from the uterus, or is located too close to the exit. The first 6 days of life, the embryo is not connected with the mother, it feeds on those substances that have been accumulated in the egg. From the 7th day after fertilization, implantation begins - the introduction of the embryo into the wall of the uterus. The blastocyst secretes special enzymes that destroy a section of the uterine mucosa. The outer cells of the blastocyst form villi and connect with the blood vessels of the uterus to form the placenta, an organ through which the fetus will receive oxygen and nutrients. If implantation is successful, then the development of the embryo will now be provided by your organs and systems, and not by the modest reserves of nutrients made by the egg. The implantation period lasts about 40 hours and is a critical period for the development of the embryo. If, in the period from fertilization to implantation, a woman is affected by serious damaging factors - for example, she suffers from some serious disease or is exposed to toxins, ionizing radiation, etc. - then the further development of the embryo can go in only two ways. He either finds reserves to correct damage (then, if there are no unpleasant surprises in the future, then there will not even be traces of any influences), or these reserves are insufficient (then the embryo dies, the pregnancy does not continue, but normal menstruation occurs at the right time or with a short delay of a few days). This is the so-called “all or nothing” law, a kind of natural selection manifestation. Every second woman loses a pregnancy at this stage of her development, not even knowing that there was a conception and she could have a child.
On the 9th day after fertilization (on average, on the 25th day of the menstrual cycle), the fetal egg is arranged in a new place, and the mother begins to truly feed and protect her unborn child. By this time, the outer layer of the embryo begins to produce a special hormone - human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). It is he who gives the mother's body information that pregnancy has occurred, and encourages all organs and systems to rebuild. During the last week of the first month of pregnancy, the fetus becomes an embryo, as we will call it until the 10th week. The embryo consists of three layers of tissue, the development of which will go in different ways. Nerves and skin are formed from the outer layer, bones, muscles, the circulatory system, kidneys and genital organs are formed from the middle layer, and the respiratory and digestive systems are formed from the inner layer. By the end of the first month, the head of the embryo is formed. On the 4th week from the last menstruation, very important extra-embryonic organs (chorion, amnion) are formed. And although the tissues and organs of the baby are not formed from them, the further development of the embryo without them is impossible. After some time, the chorion will turn into a placenta, and the amnion will become a fetal bladder - it will contain the fetus and amniotic fluid. At the end of the 4th week, your baby is 0.4-1 mm in size - like a grain of sand.
What does a pregnant woman feel?
In the first month, you do not even suspect that the pregnancy has come. Still exactly the same as it was before. The main work is done imperceptibly: the body gradually increases the volume of blood, forcing the heart, kidneys and lungs to work more energetically. Many expectant mothers remember that even before the delay of menstruation, some changes also appeared in their well-being. About a third of women note sensitivity or mild soreness of the mammary glands. In some of them, the chest "swells", increases in size. Some experience strange sensations in the lower abdomen, a kind of “foreboding” of pregnancy, the moment of implantation is often accompanied by scant spotting. There is no toxicosis yet, it may appear a little later, but eating habits are already changing (as the people say, “pulls for salty”), a metallic taste in the mouth and hypersensitivity to odors may appear. And you no longer like your favorite perfume, your favorite coffee is unbearable, and there is nothing worse than the smell of food in your favorite restaurant.
Very often, the first sign of pregnancy is increased fatigue and drowsiness. Nature seems to give a signal to our body: “Stop! Stop! You no longer need to be in time anywhere, you have a completely different task. There are two more signs of an impending pregnancy, which should be treated with caution. The first is an increase in the overall body temperature to 37.0-37.5 ° C. It has already been proven that a normal pregnancy can be accompanied by such phenomena, but a viral infection too. Therefore, it is necessary to visit doctors - a general practitioner and a gynecologist - in such cases. As well as with the appearance of frequent urination, which, in addition to pregnancy, can accompany a urinary tract infection. There are quite a few signs of pregnancy, and they appear in a variety of combinations. Some women feel almost all of them, for others, the absence of menstruation is the only sign.
Psychology of the first month
Considering that most often the first month of pregnancy goes unnoticed, the mother does not have any special psychological problems at this time. It is more difficult for women who are planning a pregnancy for a long time. Then the last week of the first month is associated with a severe stressful state of waiting for the result: will pregnancy occur? At the same time, a lot of stress hormones are produced in the woman's body, which prevent the normal implantation of the embryo and the functioning of the corpus luteum. So it turns out that the more we expect pregnancy, the less likely it is to occur. Remember, you probably have friends who have been unsuccessfully treated for infertility for a long time and, only giving up all hopes, got a sudden long-awaited pregnancy.
Deviations from the norm
In the first month, the following complications of pregnancy are possible:
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg develops outside the uterus. Most often, during an ectopic pregnancy, a fetal egg develops in one of the sections of the fallopian tube, in rare cases - in the ovary, abdominal cavity or cervix. The conditions for the development of the fetal egg there are unfavorable, therefore, such a pregnancy is interrupted within 4-8 weeks.
In this case, most often the fallopian tube is torn, which is accompanied by severe internal bleeding. Signs of an ectopic pregnancy are recurring pain in one of the inguinal regions, scanty dark bloody discharge from the vagina, feeling lightheaded, dizziness. When the tube breaks, there is a sudden sharp pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, pallor, cold sweat, loss of consciousness is possible. The only treatment is emergency surgery.
A corpus luteum cyst is a vesicle up to 6-8 cm in size, which forms in place of the corpus luteum. Such formation requires additional monitoring and usually resolves on its own by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy. In very rare cases, there is a rupture of the cyst of the corpus luteum, which requires surgery, as bleeding occurs. After removal of the cyst of the corpus luteum, pregnancy most often continues to develop safely.
What to do?
It is necessary to start taking vitamins if you have not already started doing so at the planning stage of pregnancy.
The main vitamin for both future parents is folic acid (vitamin B9). It provides the necessary speed of growth and development of the unborn child, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy significantly increases the risk of congenital malformations in the fetus, in particular the nervous system, as well as malnutrition and prematurity. Malformations such as cleft lip and cleft palate can also result from vitamin B9 deficiency in pregnant women. To prevent developmental disorders, multivitamins should contain at least 800 micrograms of folic acid. Women who already have children with similar problems are prescribed 4 mg of pure folic acid per day (4 tablets). The natural analogue of folic acid - folate, found in green leafy vegetables, beans, asparagus, citrus fruits - is unfortunately very poorly absorbed from food.
In addition to folic acid, multivitamins for the expectant mother should contain vitamin E. This vitamin in early pregnancy contributes to the normal production of female sex hormones. The recommended dose of vitamin E at this stage of pregnancy is 1500 IU per day. If you live in an iodine-deficient area and don't use iodized salt, your multivitamin should include iodine at a dose of 150-200 mcg per day. Instead of multivitamins, you can take separate preparations of folic acid, vitamin E and iodine. When choosing vitamin preparations, do not forget to consult with your doctor.
Necessary medical measures
The normally normal first month of pregnancy does not require any medical supervision.
To verify the fact of the onset of pregnancy, you can conduct a test at home. These systems are freely sold in pharmacies. They are based on the definition of chorionic gonadotropin, which is secreted by the chorion of the fetal egg. This hormone enters the bloodstream of the expectant mother and is excreted from there along with urine.
In fairness, it should be noted that it is better to carry out this test against the background of a delay in menstruation, when the level of chorionic gonadotropin is quite high. At home, hCG is determined in the urine, in the laboratory this hormone is also determined in the blood, in addition, the laboratory will show the amount of hCG. By the amount of this hormone, one can judge how the pregnancy develops. With an ultrasound with a vaginal probe, by the end of the first month, you can see the fetal egg and corpus luteum. But if nothing bothers you, the doctor will prescribe your first ultrasound at 12-16 weeks. Nowadays, especially in the presence of complications in previous pregnancies, ultrasound is often prescribed even earlier - at 9-10 weeks, to make sure that the fetal egg has attached itself in the uterus (uterine pregnancy), and to measure the cervical fold, the increase in the thickness of which makes it possible to suspect defects fetal development.
household affairs
Already at the stage of pregnancy planning, it is worth reconsidering your views on many domestic problems. The main condition is to ensure a good rest. Listen to yourself: if you want to lie down and sleep during the day, then you should do it. This is more important than keeping the house clean or preparing meals. Moreover, even after a short sleep, the necessary things will no longer seem so burdensome. Rest always gives chances to do any work faster and with pleasure. There are no restrictions on physical activity, if it is familiar to you, yet.
The egg matures and is ready for fertilization. It is excreted from the ovary and enters the fallopian tube, where it is viable for up to 24 hours, if fertilization does not occur, then the egg dies and comes out during the next menstruation.
Development in the first month of pregnancy (from conception to two weeks of fetal life)
When the egg meets the sperm and it penetrates the egg, fertilization occurs. The egg has membranes that prevent more than one sperm from entering the egg and the rest of the sperm die. At the time of fertilization, the sex of the unborn child is determined (males develop from some spermatozoa, and females from others).
From the very beginning, a fertilized egg contains a complete genetic set: 23 maternal chromosomes and 23 chromosomes from the father. Sometimes two eggs are fertilized by two sperm cells, resulting in the birth of fraternal twins. Less commonly, one egg is fertilized by one sperm and then splits in two, resulting in identical twins.
During a four-day journey through the fallopian tube for a distance of 10-12 centimeters, a fertilized egg quickly transforms from one cell to many and divides every half hour into two cells, then four, eight, etc. And by the time this clot cells called morula (future baby) reaches the uterus, it consists of at least sixteen cells.

By the end of the first week - on the seventh day from conception, the blastocyst (as it is now called), resembling a microscopic raspberry in appearance, finds a suitable place and usually implants (attaches) to the mucous membrane of the upper part of the uterus.
When the embryo is introduced into the mucous membrane penetrated by blood vessels, a few drops of blood may be released. The resulting embryo develops thin "roots" (chorionic villi), which penetrate the uterine mucosa and receive nutrition from there.
The uterus, reacting to the presence of the embryo, begins to form the rudiment of the placenta, which transfers nutrients from the mother's blood to the developing child and removes the waste products of the fetus. As the placenta develops, it begins to produce the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which strengthens the uterine lining and stimulates the growth of the embryo, maintaining high levels of estrogen and progesterone. With the development of the placenta, hCG enters the mother's blood.

The germ moves
through the fallopian tube
By the end of the second week from conception (fourth from the onset of menstruation), this hormone is also detected in the mother's urine during a pregnancy test.
By this time, menstruation has already been missed. A woman may suspect that she is pregnant, and rising levels of hormones in the blood cause symptoms that confirm her suspicions. Pregnancy hormones block the ovulation of the ovaries, and the ovaries, with the help of hormones, signal the pituitary gland in the brain to no longer stimulate menstruation.
Congratulations, YOU ARE PREGNANT! One of the most exciting periods of your life is ahead of you. You will need to do a lot to prepare for the birth of a child - the most important moment in the life of most women. To get started, visit a antenatal clinic or a gynecologist.
Visit to the doctor at the end of the first month of pregnancy
What can you expect during your first visit to the doctor:
- establishing the fact of pregnancy; the doctor will ask for symptoms of pregnancy, what you feel, the date of the last menstruation, to determine the date of delivery;
- establishment of a medical card;
- general examination;
- blood tests: hemoglobin and hematocrit to check for anemia, blood type, rubella titer, hepatitis B test (tests for HIV, sexually transmitted diseases);
- analysis for vaginal infections;
- urinalysis for infections, for sugar and protein;
- weight and pressure check;
- recommendations regarding proper nutrition and elimination of adverse environmental factors.
How do you feel in the first month of pregnancy?

Regardless of where you heard the news - at a gynecological appointment or at home, after a pregnancy test - you can experience conflicting feelings: joy, fear, relief, distrust, confusion, or all of the feelings mentioned above. Of course, your first reaction will largely depend on whether the pregnancy is desirable for you, unexpected, or is it the result of many months of hopes and expectations. Here's what may lie ahead for you.
Mood changes. You can feel at the top of bliss, and the next day becomes sad and whiny. There are several reasons behind these mood swings. One is the normal emotional decline that follows strong experiences; in humans, emotional ups and downs are usually accompanied by downs. Another reason is purely physiological: hormones. The rush of pregnancy hormones that change your body contributes to the fickleness of your feelings. Of course, feeling overwhelmed can take you by surprise, especially if you have been looking forward to pregnancy for a long time. Mood changes should be expected in the first three months, when the level of hormones in the blood changes especially strongly, as well as in the last weeks, when fatigue accumulates and the expectation of childbirth increases. Do not be surprised, for most expectant mothers, the mood can change several times a day.
Fatigue. Pregnancy brings with it a strange fatigue that may not be like anything you've experienced before. This is especially noticeable in the first trimester, when the body literally forces you to sleep. At times you feel completely exhausted. You want to sleep all the time. You can fall asleep right at your desk in the morning. Realizing how much the load on your body increases, you will no longer be surprised at your fatigue. Virtually every organ in your body is working extra stress to accommodate the new being inside of you, and every cell in your body is affected by the hormonal and physiological changes that occur during pregnancy. At the same time, new organs are being formed in your body: a placenta is being formed in the uterus to feed the baby, the baby's own organs are developing. Cell growth requires huge amounts of energy. Add to this the nausea in the morning and the enormous physiological changes that pregnancy brings with it, and you will realize that you will not avoid fatigue.
Ailments- nausea, vomiting and general discomfort in the stomach that many women experience can ruin all the joyful feelings associated with pregnancy (toxicosis). It's hard to be happy about your child's development when you're feeling awful, and especially when morning sickness stretches all day. The intensity and duration of morning sickness is different for every woman - just like weight gain. A small percentage of women go through the first stage of pregnancy without any signs of nausea. Some have indigestion, others only occasionally experience mild nausea, but in general, a pregnant woman develops an increased sensitivity to smells and an aversion to certain foods at the beginning of pregnancy. Some smells can "act directly on the stomach", causing an attack of vomiting. Some women are particularly irritated by strong odors such as garlic, fish or coffee, regardless of how they have reacted to these foods in the past. Others complain that ordinary household smells that did not bother them at all before pregnancy suddenly began to cause strong dislike. Favorite perfumes can cause an attack of vomiting, so you have to urgently run to the bathroom.
Aversion to food can also take on a variety of forms. Sometimes a woman is unable to eat certain foods (meat, herbs, milk) that cause her to vomit. In other cases, only a few types of products are acceptable.
Some mothers-to-be notice nausea at certain times of the day, while others feel sick all the time. It is very common for a woman to feel great, and then suddenly experience a severe attack of nausea - for no reason or an unpleasant smell.
If you have mild nausea, shortness of breath, dizziness, feeling short of breath, or throwing up, you can consider yourself a "pregnancy club member."
You need to see a doctor urgently if:
- Abundant bleeding from the vagina;
- Sudden drawing pains in the underbelly;
- Vomiting does not stop;
- The amount of urine decreases and it becomes darker in color;
- Mouth, eyes and skin become dry;
- You feel more and more tired;
- Weakness increases, fainting occurs;
- The body does not retain food and drink for twenty-four hours.
Avoid hard-to-digest fatty foods and fried foods such as fatty ice cream, chips and fried meats.
Choose foods that are high in nutrients: avocados, beans, cheese, fish, wholemeal pasta, shelled (brown) rice, turkey.
Don't let saliva go into an empty stomach. An empty stomach is more sensitive to saliva, which can lead to rapid onset of nausea. Most pregnant women produce an excess amount of saliva, and even the thought of food can provoke saliva. Many pregnant women claim that mints or chewing gum help fight nausea, but it's best to refrain from eating them on an empty stomach, as these foods cause increased salivation but do not fill the stomach.
If you're feeling nauseated with prenatal vitamins, try taking them with your biggest meal of the day.
Foods high in water not only make digestion easier, but also prevent dehydration and constipation, which can make nausea worse. Try to include in your diet fresh fruits and vegetables, greens, drink more compotes, fruit drinks.
Your body is working on creating a new little man, so try to adhere to certain rules - more rest, less worry. Also during pregnancy, it is very important to have a proper balanced diet, taking a complex of vitamins for pregnant women. Refusal of alcohol and tobacco smoking, taking medications without the participation of a doctor.
Photos: Lennart Nilsson

In the first month of pregnancy, the formation and maturation of the egg, which is the carrier of 23 maternal chromosomes, occurs. After about 2 weeks, the mature egg cell enters the fallopian tube, where it is waiting for a meeting with that single sperm cell - the carrier of 23 chromosomes of the father, which will give rise to a new life. The inner layer of the uterus at this time thickens, becomes covered with a network of blood vessels, preparing the "soil" so that the fertilized egg can attach to the uterus.
As a rule, fertilization occurs during the third week. After the contact of the nuclei and the dissolution of the membranes of the sperm and the egg, all 46 chromosomes merge and separate into pairs. From this moment on, all the physical characteristics and signs of the new little man are determined. And only one 23rd pair of chromosomes determines the sex of the unborn child. The result of this historic meeting, sperm and egg, becomes a zygote - the progenitor of all cells and organs of the unborn baby. The zygote begins to actively divide, still traveling through the fallopian tube, on the way to the uterus. Approximately 72 hours after fertilization, the fetus already has 32 cells. In this form, it will begin to attach to the uterine cavity. The size of the fetus in the first month of pregnancy by the 3rd week will reach a diameter of 0.1-0.2 mm, the number of cells will be 250, and outwardly the unborn child looks like a hollow ball.
By the end of the 3rd week of the term, the fertilized egg is implanted in the soft wall of the uterus. As soon as it attaches securely, you can safely say that the conception has taken place, and you are officially pregnant!
The first month of pregnancy ends with the fact that the fetal egg turns into an embryo. Now your blood is more like a flat disk, consisting of layers-leaves, which will soon be transformed into organs and systems.
- Symptoms andsensations in the first month of pregnancy

1. Delayed menstruation. Menstruation in the first month of pregnancy, as well as in the next nine, should be absent. A delay in menstruation in a woman who is sexually active without reliable protection is most often a symptom of pregnancy. However, the delay may have other reasons not related to pregnancy, for example: a common cold, stress, exacerbation of some chronic disease, ovarian or thyroid pathology, etc.
2. Toxicosis. AT the first month of pregnancy, signs of an interesting situation are precisely the sensations of nausea and vomiting. These symptoms are common to many women, but to varying degrees. Someone feels a slight nausea before breakfast, and someone “sends out” everything they eat or drink, toxicosis can be so severe that hospital treatment is required. Defeat toxicosis - the prospect is doubtful, it must be endured, and, if possible, alleviated. Usually, such feelings of malaise disappear by 12-14 weeks of the term.
3. Breast engorgement. AT the first month of pregnancy there is swelling and engorgement of the breast. Moreover, it is so noticeable that it is incomparable with the situation characteristic of almost everyone before the onset of menstruation. The chest may increase, become "full". In the first month of pregnancy, the feeling of fullness of the mammary glands occurs in most women, multiparous describe that this feeling is like a rush of milk. Sometimes already at such an early date, colostrum can stand out a little from the breast.
4. Increased basal and body temperature. This is due to the action of the hormone progesterone. Usually (in the anus) above 37 degrees. You may also feel hot during the first weeks. This, of course, is an unpleasant phenomenon, but temporary. The main thing is not to confuse it with an infection or an exacerbation of some chronic disease.
5. Allocations in the first month of pregnancy are often plentiful and transparent. This is also a characteristic sign of conception associated with hormonal changes in the body - a normal phenomenon. Another thing is when there is bloody spotting in the first month of pregnancy, or with an admixture of pus and an unpleasant odor - in this case, you should definitely go to the gynecologist and take smears for analysis. A couple of drops of blood or barely noticeable spotting in the second or third week may be the norm, as a result of the introduction of the fetal egg into the uterus.
6. It happens that in the first month of pregnancy, the stomach hurts. These sensations are unpleasant, but if they do not cause much discomfort, are not frequent and not regular, then you have no reason to worry.
These, of course, are not all possible signs and symptoms of pregnancy, but the main ones. There may also be a loss or, on the contrary, an increase in appetite, frequent urination, fatigue, etc. But these signs are considered to be individual, they can be observed in very sensitive non-pregnant women.
Precisely determining pregnancy in the first month is possible only with the help of a blood test for hCG and ultrasound. Pregnancy tests are often wrong at such an early date, however, as well as doctors during the examination.
- Possible pathologies
The first months are the most dangerous miscarriages. In some cases, this cannot be avoided in any way, and, perhaps, it is not worth it ... chromosomal or other pathologies in the fetus are often incompatible with life. In other cases, it is not difficult to change the situation for the better if measures are taken in time.
1. Uterine hypertonicity. Separate contractions of the muscles of the uterus, short, infrequent, may well be a variant of the norm, but for your own peace of mind, be sure to inform the doctor about the tone of the uterus. It is also normal if in the first month of pregnancy the stomach hurts in the uterus. But if uterine contractions began to bother you regularly, became more intense and lasted for several minutes, be sure to see a doctor. They may threaten to terminate the pregnancy.
2. Allocations. Normal discharge should be clear and odorless. An unpleasant odor may indicate an infection or vaginal dysbiosis. It is easily and without consequences treated if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Much more dangerous is spotting in the first month of pregnancy. Expectant mothers do not have periods, and blood from the vagina, as a rule, indicates placental abruption, which threatens spontaneous abortion. If at the same time the stomach also hurts, and the body temperature has risen above 37, we recommend calling an ambulance.
3. Frequent urination. Many women mistakenly believe that frequent urination is a sign of pregnancy. But in the early stages, this is rather a sign of a disease of the urinary system, often inflammation of the bladder, cystitis. Urination in this disease is usually painful.
4. Severe toxicosis, frequent vomiting. Toxicosis, as you already know, can be different and it is important to understand this difference. If the food is not digested at all, vomiting occurs after every meal or drink, the pregnant woman needs urgent treatment to avoid dehydration.
- Food
.jpg)
Nutrition in the first month is an extremely important component, on which a lot depends. The lack of any nutrients in the early stages can have a very negative impact on the development of the embryo.
The expectant mother should eat a little denser than before pregnancy. Approximately 300 kcal per day. At the same time, protein foods should prevail in the diet, but preferably not animal proteins and fats, since they lead to undesirable rapid weight gain. The average daily norm of a future mother should be 2500 kcal.
Among the vitamins, it is especially necessary to highlight. The need for vitamin B9 in expectant mothers is 2 times greater than in an ordinary person - at least 400 mcg daily. Getting that much vitamin from food can be quite difficult. At the same time, only vegetarians do not lack folic acid, since it is found in green salad, peas, parsley, etc. - in products that are not on the table every day, especially in winter. Therefore, doctors recommend taking folic acid tablets, even (2-3 months before conception), and even more so in the early stages. You need to continue taking the vitamin throughout the first half of pregnancy. It is necessary to prevent pathologies of the neural tube of the fetus and other pathologies of the development of the child. selected individually. For women who have previously had miscarriages, the dosage is large.
The recommended nutrition of the expectant mother varies somewhat in different trimesters. For example, in the first trimester of pregnancy, it is important to have a varied, rich in fresh food, sufficient and even plentiful nutrition. In the third trimester, you need food containing a large amount of calcium, since the child especially needs it at this time, the development of the skeletal system takes place. If there is a lack of calcium, the baby will take its own from the mother's body reserves, from which her teeth will begin to deteriorate, nails and hair will crumble. It is also important for the mother not to gain weight above the norm, since obesity negatively affects gestation.
- What else do you need to know?
It is time for every future mother to realize that her lifestyle, her habits and nutrition affect the health of her unborn baby. Therefore, you should at least get rid of especially dangerous habits that are “poisonous” for a child, such as smoking and drinking alcohol in any form and quantity. There is a widespread myth that quitting smoking during pregnancy is harmful - this is not true. Quitting smoking is always useful for everyone, but now it’s also easy - the body is rebuilding in a new way, the psyche stimulates. In the early stages, thanks to hormones, the so-called “pregnancy dominant” is formed in the brain, pushing all the needs of a woman into the background.
The potentially dangerous diet should now be abandoned. Potentially dangerous and simply useless foods include: convenience foods, fried pies, fast food, etc.
All pregnant women have reduced immunity, and it is very easy to catch all kinds of infections. Therefore, it is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible from potential sources of infection. Try to use public transport less often and visit crowded places. Try to get used to using oxolinic ointment, lubricating the nasal cavity with it in winter and in the off-season, during the raging SARS and flu.
If any treatment is required, do not do it yourself, tell any doctor about the pregnancy. For example, fluorography for future mothers is contraindicated, and many medicines are also prohibited. Some drugs are generally toxic to the fetus, and can threaten him with death. Therefore, any drugs and procedures should be prescribed by a doctor who is aware of the condition and situation of the patient.
And, of course, do not forget about psychological comfort. Try to worry less, read less and listen to scary stories about pregnancy and childbirth. Sleep well, rest, gain strength. It does not matter that the belly in the first month of pregnancy is completely invisible, it is important that a tiny child develops inside and feels the same as the mother.
Happy and easy pregnancy!
Yana Lagidna, especially for mymom . en
1 monthpregnancy, video: