The human head grows up to the age of 17 and stops at approximately 56 cm (+/- a few cm). In young children, the head is disproportionately large in comparison with the body and is somewhere between 1 / 3-1 / 4 of the height (here we mean not the circumference of the head, but its height itself). For comparison: in an adult, this ratio is 1/8 to 1/10 of the body part.
In addition to weight and height, the circumference of the child's head and chest is usually also determined (Fig. 10, 11). These measurements give an idea of \u200b\u200bthe harmonious development of the organism.
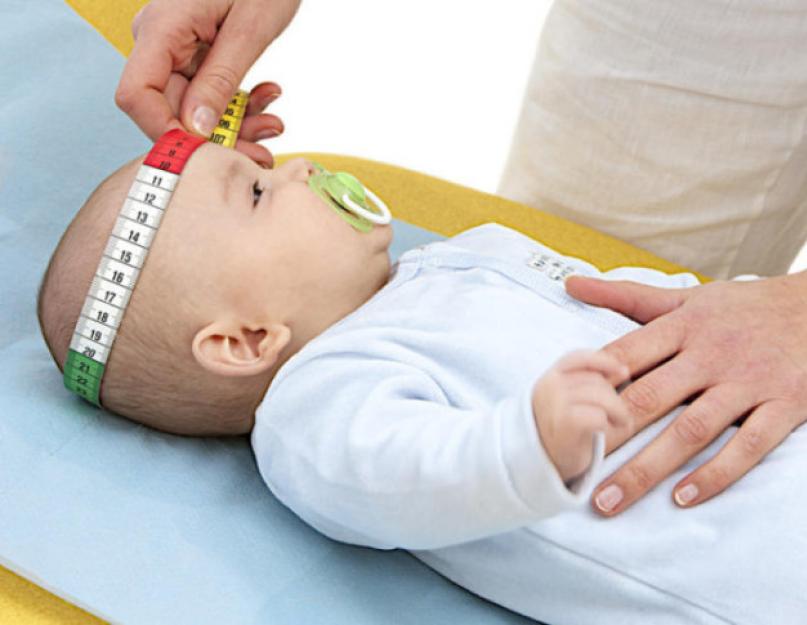
When measuring the head, the measuring tape should tightly surround it through the occipital protuberance and brow ridges. The chest circumference is measured at the level of the nipples; behind the tape is held at the level of the lower corner of the scapula.
The circumference of the head of a newborn is on average 34-35 cm, the circumference of the chest is 32-34 cm. During the first year of life, the circumference of both the head and chest increases intensively.
In a year head circumference increases by 12 cm, that is, an average of 1 cm per month. In the first months of life head grows more intensively.
However, during the first year of life, the rate chest growth higher, as a result of which on the 3-4th month the value circumferences of the chest and head becomes the same, and by the year chest circumference exceeds head circumference on average 2 cm; it increases by 16 cm per year.
With proper development, by 4-5 months, the head circumference becomes equal to the chest circumference, and later the chest circumference exceeds the head circumference.
At the age of 1 year, the head circumference is 46-47 cm, the chest circumference is 48-49 cm.At 5 years, the head circumference is 50 cm, and the chest is 55 cm.
In the future, in a healthy child chest circumference there will always be more head circumference.
Doctors measure children's head circumference to see if the child's head circumference continues to increase at a normal rate. The size of a child's head is naturally influenced by heredity - some people just have big heads, some on the contrary - not very much. But the deviation from normal head circumference in a one-year-old child deserves attention. It is important to exclude disorders that are evidenced by too large (macrocephalus and hydrocephalus) or too small a head (microcephaly).
Physical development is understood as the intensity of the increase in height, weight of the child, head and chest circumference. If the child has small head sizes, then the increase in head volume in such children will be more intense.
Table of typical children's measurements according to Ptenert, Heine
| Age | Head circumference | Chest circumference | Age | Head circumference | Chest circumference | ||||
| cm | % body length | cm | % body length | cm | % body length | cm | % body length | ||
| Boys | Girls | ||||||||
| Up to 1 month | 35 | 69 | 34 | 67 | Up to 1 month | 34 | 68 | 33 | 66 |
| 1 month | 37 | 69 | 36 | 67 | 1 month | 36 | 68 | 35 | 66 |
| 2 months | 39 | 68 | 38 | 66 | 2 months | 38 | 68 | 37 | 66 |
| 3 months | 41 | 67 | 39 | 64 | 3 months | 40 | 68 | 38 | 64 |
| 6 months | 44 | 65 | 43 | 63 | 6 months | 43 | 65 | 42 | 64 |
| 9 months | 46 | 64 | 45 | 63 | 9 months | 45 | 64 | 44 | 63 |
| 1 year | 47 | 63 | 47 | 63 | 1 year | 46 | 62 | 47 | 63 |
| 2 years | 49 | 57 | 51 | 59 | 2 years | 48 | 56 | 50 | 58 |
| 3 years | 50 | 52 | 52 | 54 | 3 years | 49 | 52 | 51 | 54 |
| 4 years | 51 | 50 | 53 | 51 | 4 years | 50 | 50 | 52 | 51 |
| 5 years | 51 | 47 | 55 | 50 | 5 years | 50 | 47 | 53 | 49 |
| 6 years | 51 | 45 | 57 | 49 | 6 years | 50 | 44 | 55 | 48 |
| 7 years | 52 | 43 | 58 | 48 | 7 years | 51 | 43 | 57 | 48 |
| 8 years | 52 | 41 | 59 | 47 | 8 years | 51 | 41 | 59 | 47 |
| 9 years | 52 | 40 | 61 | 47 | 9 years | 61 | 39 | 61 | 47 |
| 10 years | 52 | 38 | 64 | 47 | 10 years | 51 | 38 | 63 | 48 |
| 11 years | 53 | 38 | 66 | 46 | 11 years | 52 | 37 | 66 | 48 |
| 12 years old | 53 | 37 | 68 | 47 | 12 years old | 52 | 36 | 71 | 49 |
| 13 years old | 53 | 36 | 71 | 48 | 13 years old | 53 | 35 | 74 | 49 |
| 14 years old | 54 | 35 | 74 | 48 | 14 years old | 53 | 34 | 76 | 49 |
| Adult | 56 | 32 | 87 | 50 | Adult | 55 | 33 | 82 | 50 |
Children's size chart, or rather typical measurements that you need to know if you are going to sew or buy clothes for your child. Having determined the height of your baby from the table, you will see what the waist or chest circumference of the child should be. Of course, the table gives information for standard figures, individual deviations from the standard, I think, mothers will determine themselves.
Basic measurements of typical preschool children
| Measure name | Measurement conventions | Height, cm | ||||||||||
| 74 | 80 | 86 | 92 | 96 | 98 | 104 | 110 | 116 | 122 | 128 | ||
| Neck girth | OSH | 25 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 27 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 30 |
| Chest girth | OG | 51 | 53 | 55 | 56 | 56,5 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 | 62 | 66 |
| Waist circumference | FROM | 48 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 52,5 | 53 | 54 | 55 | 56 | 57 | 60 |
| Hip girth | ABOUT | 52 | 54 | 56 | 58 | 59 | 59 | 61 | 63 | 65 | 67 | 70 |
| Shoulder width | Shp | 6 | 6,5 | 7 | 7 | 7,5 | 8 | 8,5 | 9 | 9,5 | 10 | 10 |
| The length of the sleeve | AP | 23 | 26 | 28 | 31 | 32 | 33 | 36 | 38 | 41 | 43 | 46 |
| Back width | SHS | 18 | 19,5 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 24 | 24,5 | 25 | 25,5 | 26 | 27 |
| Back length to waist line | dst | 19 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 23,5 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 29 | 30 |
| Front length to waist | dpt | 18 | 19 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 24,5 | 25 | 25 | 26 | 28 | 29 |
| Upper arm girth | OR | 16 | 16,5 | 17 | 17,5 | 17,5 | 18 | 18 | 18,5 | 18,5 | 19,5 | 21 |
The head circumference of a newborn baby is measured on the birthday and each subsequent month (mothers should regularly carry their baby to a pediatrician for examination). Together with other parameters - such as height, weight, chest girth, head circumference data indicate compliance or non-compliance with developmental norms (we recommend reading :). Too large or too small a head size in a newborn indicates pathological processes - hydrocephalus or microcephalus. Often small deviations from the norms are a consequence of the genetic predisposition of the toddler.
If you compare several newborns, their head circumference will be approximately the same. A small gap to the side of the norm is most often indicative of genetic characteristics.Normative indicators of head circumference
As soon as the baby is born, doctors will certainly take all the necessary measurements, including measuring the volume of the baby's head. The found indicator is compared in relation to the parameter of the chest girth. For example, on the day of childbirth, the head parameters of the toddler exceed the chest parameters by 2 cm, by the 4th month these indicators level out, and closer to the year the girth of the chest region exceeds the parameter of the head region by 2 cm.
The average parameters of the head circumference at birth are 34-35 cm, and the chest girth is 32-34 cm. The size of the baby's head has a very active increase in the first year of life and by 1 year its volume will increase by 12 cm.
In the first trimester, the baby's head grows especially quickly. At the 4th month of life, its volume will be equal to 40-42 cm, since each lived month adds 1.5-2 cm to the circumference of the newborn's head. The breast increases in volume no less intensively and by this time the two parameters will have approximately equal values.
After 3-4 months, head growth will no longer be as intense in relation to the breast. Subsequently, as in an adult, the chest girth indicators exceed the head circumference.
Calculation formulas
Each parent can independently measure the head circumference of their newborn child and compare it with the standard indicators. For this, there is a special calculation formula, which will tell you whether the volume of your child's head matches the average data.

 To measure the volume of the head and the circumference of the chest, you will need a regular measuring tape. Further, the obtained indicators are compared with the standards from the table
To measure the volume of the head and the circumference of the chest, you will need a regular measuring tape. Further, the obtained indicators are compared with the standards from the table The age of 6 months is taken as a guideline, when the baby's head circumference is 43 cm.To calculate the standards of previous months, you need to subtract 1.5 cm from this value for each month:
- for example, the head size of a 4 month old baby is 40 cm (43 - 1.5 - 1.5 \u003d 40).
After six months, the formula changes slightly and you need to add 0.5 cm for each month of life:
- for example, the head circumference of a 9 month old baby is 44.5 cm (43 + 0.5 + 0.5 + 0.5 \u003d 44.5).
Such a calculation will help to calculate the size of the child's head, but these will only be approximate figures, because the data for boys and girls will differ due to their physiological characteristics. There are also indicators for children of each individual age.
Average tables
Below is a table showing, according to the WHO, the average chest and head circumference between the ages of 1 month and 1 year.
| Age in months | Chest circumference, cm | Head circumference, cm | ||
| The average | Lagging behind | The average | ||
| 1st degree | 2nd degree | |||
| Boys | ||||
| 1 | 36,3 | 32,1 | 30,0 | 37,3 |
| 2 | 39,0 | 35,2 | 33,3 | 38,4 |
| 3 | 41,3 | 37,1 | 35,0 | 40,9 |
| 4 | 42,8 | 39,0 | 37,1 | 41,9 |
| 5 | 44,3 | 40,7 | 38,9 | 43,2 |
| 6 | 45,4 | 41,6 | 39,7 | 44,2 |
| 7 | 46,4 | 42,6 | 40,7 | 44,8 |
| 8 | 47,2 | 42,8 | 40,6 | 45,4 |
| 9 | 47,9 | 43,5 | 41,3 | 46,3 |
| 10 | 48,3 | 44,5 | 42,6 | 46,6 |
| 11 | 48,7 | 45,1 | 43,3 | 46,9 |
| 12 | 48,9 | 44,9 | 42,9 | 47,0 |
| Girls | ||||
| 1 | 35,9 | 32,5 | 30,8 | 36,6 |
| 2 | 38,1 | 34,1 | 32,0 | 38,4 |
| 3 | 40,0 | 35,8 | 33,7 | 39,9 |
| 4 | 41,8 | 38,4 | 36,7 | 41,1 |
| 5 | 43,1 | 39,3 | 37,4 | 42,2 |
| 6 | 44,3 | 40,5 | 38,6 | 43,2 |
| 7 | 45,1 | 40,9 | 38,8 | 43,9 |
| 8 | 46,0 | 41,4 | 39,1 | 44,3 |
| 9 | 46,7 | 42,7 | 40,7 | 45,3 |
| 10 | 47,0 | 42,0 | 39,5 | 45,6 |
| 11 | 47,7 | 43,1 | 40,8 | 46,0 |
| 12 | 47,7 | 43,9 | 42,0 | 45,9 |
There are separate parameters for measuring head size in premature infants, since their indicators are less than average values \u200b\u200band they do not grow as intensively as in babies born on time.

 The above indicators are relevant only for those babies who were born on time. Premature babies have their own tables and standards for anthropometry.
The above indicators are relevant only for those babies who were born on time. Premature babies have their own tables and standards for anthropometry. Below is a table of values \u200b\u200bfor children from 1 to 7 years old:
| Age, year | Index | ||
| Above the average | Middle | Below the average | |
| 1 | 48,2-49,2 | 45,0-48,2 | 44,2-45,0 |
| 1 and 3 months | 48,7-49,6 | 45,9-48,7 | 45,1-45,9 |
| 1 and 6 months | 49,0-49,9 | 46,4-49,0 | 45,7-46,4 |
| 1 and 9 months | 49,4-50,2 | 46,9-49,4 | 46,1-46,9 |
| 2 | 49,7-50,5 | 47,3-49,7 | 46,6-47,3 |
| 2 and 3 months | 50,0-50,7 | 47,8-50,0 | 47,0-47,8 |
| 2 and 6 months | 50,4-51,0 | 48,0-50,4 | 47,5-48,0 |
| 2 and 9 months | 50,6-51,4 | 48,4-50,6 | 47,9-48,4 |
| 3 | 51,0-51,7 | 48,6-51,0 | 48,1-48,6 |
| 3,5 | 51,5-52,3 | 49,0-51,5 | 48,3-49,0 |
| 4 | 51,9-52,7 | 49,3-51,9 | 48,6-49,3 |
| 4,5 | 52,3-52,9 | 49,7-52,3 | 48,9-49,7 |
| 5 | 52,5-53,2 | 50,0-52,5 | 49,1-50,0 |
| 5,5 | 52,7-53,5 | 50,2-52,7 | 49,4-50,2 |
| 6 | 52,8-53,7 | 50,3-52,8 | 49,6-50,3 |
| 6,5 | 53,0-53,9 | 50,6-53,0 | 49,8-50,6 |
| 7 | 53,3-54,1 | 50,7-53,3 | 50,0-50,7 |
Deviations from the norms in the volume of the head
The volume of the head of a child by itself does not carry any information if it is not measured in conjunction with other parameters that will determine the pace of development and growth of the newborn. Sometimes even small deviations from the norms do not indicate any diseases, if, together with other indicators, the picture is normalized.
If a dad or mom in childhood had a large or, on the contrary, a small head, then the baby may well inherit such a feature. It is important that this parameter does not exceed the chest index except for the period when these values \u200b\u200bshould be equal.
Strong deviations from the norms signal that parents should pay more attention to the appearance of the baby:
- Too large head in combination with other features (large protruding forehead, diverging sutures, bulging large fontanelles, venous mesh and neurological disorders) are signs (for more details in the article:) hydrocephalus. This disease is associated with the accumulation of fluid in the brain.
- A newborn with an excessively small head and a number of side symptoms (small forehead, closed fontanelles, neurological disorders) may have microcephaly. Both of these diseases require urgent medical treatment. Accurate diagnoses can be found using ultrasound.
Correct measurement of head diameter
In order to avoid possible errors and false assumptions, the child's head volume must be measured correctly. Readings should be taken with a centimeter tape so that from behind it passes clearly through the occipital protuberance, and in front - through the brow ridges. When measuring the chest, place the tape strictly at the nipple level in front, and at the back at the level of the lower corner of the scapula. When measuring the parameters, the child must be in a calm state (not cry or scream), otherwise the indicators will be incorrect.
In relation to the body, the head of a newborn always looks a little disproportionate - this is a normal situation. The proportions will even out and approach the usual adult appearance. Parents themselves will be able to notice that something is wrong and suspect the development of any pathology, and an experienced pediatrician will undoubtedly help with this. Children with hydrocephalus or microcephalus noticeably feel unwell and change in appearance. With pathological hydrocephalus, there is a sharp increase in the head circumference in comparison with the indicators of previous months.
From the moment the baby is born, doctors perform many manipulations with him, one of which is measuring the volume of the newborn's head. This figure can tell a lot for pediatricians. In order to prevent the development of certain dangerous diseases in a child in time, parents themselves can determine the size of the head circumference of their child.
How is a child born?
A newborn has a slight swelling of the head in the first days. This is completely normal and should not be feared. The tumor occurs due to the stress experienced during the passage through the birth canal. Since a child is normally born head first, the skull takes on the bulk of the load. The swelling disappears a couple of days after birth.
Depending on the anatomical structure of the maternal organism, two forms of the newborn's skull are distinguished:
- tower, like an oval;
- brachycephalic, round, with bumps on the forehead.
If during childbirth the baby has a slight shift in the cranial bones, do not worry. This phenomenon is also considered the norm. Gradually, the bones will fall into place by themselves.
Much more dangerous can be the discrepancy between the growth of the volume of the newborn's head and medical standards. This fact can become a symptom of dangerous diseases.
How to take measurements?
The volume of the head of a newborn is usually a couple of centimeters larger than the chest and averages 33-34 cm. In boys and girls, these indicators may differ: girls have a naturally smaller head circumference than boys.
Within a month, the volume of the newborn's head increases by 2-3 cm. Already at 3-4 months, the head and chest circumference will become equal, but by the age of six months, the growth of the chest will outstrip the size of the head. If at 4-6 months the growth of the skull is about 1 cm, then after 6 months it will grow no more than half a centimeter per month.
The table below will give a complete idea of \u200b\u200bwhat should be the size of the newborn's head by month.
Table
| Age | Extreme points of growth | Average volume |
| 1 month | 34-40 cm | 37 cm |
| 2 months | 35-41 cm | 38 cm |
| 3 months | 37-43 cm | 40 cm |
| 4 months | 38-44 cm | 41 cm |
| 5 months | 39-45 cm | 42 cm |
| 6 months | 40-46 cm | 44 cm |
| 7 months | 41-47 cm | 45 cm |
| 9 months | 42-48 cm | 45 cm |
| 10 months | 43-49 cm | 46 cm |
| 12 months | 45-50 cm | 47 cm |
The table is indicative, because the child's development occurs individually, however, significant deviations cannot be ignored by the doctor.
When should you sound the alarm?
The rapid growth of a newborn's head in the first months and a clear non-compliance with the norm can be a sign of hydrocephalus. The disease is that too much fluid accumulates in the spinal cord, which presses on the skull. A child whose head size is too enlarged should be under constant supervision of a neuropathologist.
In medicine, the reverse process is also known, when the head circumference is less than the required norm. This disease is called microcephaly and can be diagnosed during pregnancy. In this case, the woman undergoes an abortion for medical reasons.
If microcephaly develops in a born child, it requires immediate complex treatment.
How to measure head volume yourself?
Parents can determine the size of their child's head themselves, without going to a doctor. To do this, you need to take an elastic tape on which centimeter divisions are applied. If there is no one at home, use ordinary braid or tape. Wrap the tape around the child's head at eyebrow level and fix the meeting point of both ends. If you are using a tape without divisions, you can measure the resulting segment with a ruler.
During the procedure, the baby must be absolutely calm, otherwise the dimensions obtained will be inaccurate. Thanks to this simple manipulation, parents will be able to control the physical development of their baby and be the first to "sound the alarm" if something went wrong.
The size of the head circumference is an important indicator of the health of a newborn, which should not be ignored. Thanks to him, it is possible to prevent and timely treat many serious diseases.
Every month, at the pediatrician's appointment, the main indicators of the normal development of the child from birth to one year are measured. Important values \u200b\u200binclude height, weight, head and chest circumference. These figures make it possible for the doctor to adjust the care of the baby, if necessary, send him for additional examination.
Parents can purchase scales, a height gauge and learn how to measure themselves. For a healthy baby, there is no such need, a routine doctor's examination is enough for him. However, you need to know which values \u200b\u200bof the head circumference for a newborn are normal and which are not, in order to seek the advice of a specialist in time.

Head size and shape in children
In a newborn baby, the size of the head is disproportionately large, this can be seen with the naked eye. It makes up one third or one fourth of the total body length. For an adult, the ratio will be different - one eighth or one tenth. At the same time, the skull in children continues to grow up to 17 years in proportion to the body.
The normal shape of the skull of a newborn baby is round, small changes are possible, which quickly disappear with proper care. Babies born as a result of a cesarean section do not have deformities, because they do not pass through the birth canal.

When examining a child's skull in a maternity hospital, a specialist will pay attention to its shape, symmetry and size. The oblong, elongated shape becomes such as a result of childbirth. This feature is considered normal until a certain point and disappears without assistance. Also, the baby may have minor soft bumps, hematomas, which he acquires during his birth. They pass on their own and do not bother the child in the future.
It is important to feel the baby's head. The specialist assesses the integrity of the cranial bones, their density, the absence of pain on palpation. The seams of the skull and fontanelles must be examined; their softening cannot be missed.
If there are minor changes, doctors will recommend that the mother more often turn the baby from one side to the other so that it does not stay in one position for a long time. Gradually, the shape of the skull will return to normal and will grow proportionally: the bones are still very malleable and lend themselves well to correction without medical intervention.
What should be the size of a child's head by age? There are generally accepted medical indicators of head circumference in children under one year old, broken down by month. They depend not only on age, but also on the gender of the baby.
For girls:
| Age | Very low | Low | Below the average | Middle | Above the average | Tall | Very tall |
| Newborn | 30.3 | 31.5 | 32.7 | 33.9 | 35.1 | 36.2 | 37.4 |
| 1 month | 33.0 | 34.2 | 35.4 | 36.5 | 37.7 | 38.9 | 40.1 |
| 2 months | 34.6 | 35.8 | 37.0 | 38.3 | 39.5 | 40.7 | 41.9 |
| 3 months | 35.8 | 37.1 | 38.3 | 39.5 | 40.8 | 42.0 | 43.3 |
| 4 months | 36.8 | 38.1 | 39.3 | 40.6 | 41.8 | 43.1 | 44.4 |
| 5 months | 37.6 | 38.9 | 40.2 | 41.5 | 42.7 | 44.0 | 45.3 |
| 6 months | 38.3 | 39.6 | 40.9 | 42.2 | 43.5 | 44.8 | 46.1 |
| Seven months | 38.9 | 40.2 | 41.5 | 42.8 | 44.1 | 45.5 | 46.8 |
| 8 months | 39.4 | 40.7 | 42.0 | 43.4 | 44.7 | 46.0 | 47.4 |
| 9 months | 39.8 | 41.2 | 42.5 | 43.8 | 45.2 | 46.5 | 47.8 |
| 10 months | 40.2 | 41.5 | 42.9 | 44.2 | 45.6 | 46.9 | 48.3 |
| 11 months | 40.5 | 41.9 | 43.2 | 44.6 | 45.9 | 47.3 | 48.6 |
| 1 year | 40.8 | 42.2 | 43.5 | 44.9 | 46.3 | 47.6 | 49.0 |
For boys:
| Age | Very low | Low | Below the average | Middle | Above the average | Tall | Very tall |
| Newborn | 30.7 | 31.9 | 33.2 | 34.5 | 35.7 | 37.0 | 38.3 |
| 1 month | 33.8 | 34.9 | 36.1 | 37.3 | 38.4 | 39.6 | 40.8 |
| 2 months | 35.6 | 36.8 | 38.0 | 39.1 | 40.3 | 41.5 | 42.6 |
| 3 months | 37.0 | 38.1 | 39.3 | 40.5 | 41.7 | 42.9 | 44.1 |
| 4 months | 38.0 | 39.2 | 40.4 | 41.6 | 42.8 | 44.0 | 45.2 |
| 5 months | 38.9 | 40.1 | 41.4 | 42.6 | 43.8 | 45.0 | 46.2 |
| 6 months | 39.7 | 40.9 | 42.1 | 43.3 | 44.6 | 45.8 | 47.0 |
| Seven months | 40.3 | 41.5 | 42.7 | 44.0 | 45.2 | 46.4 | 47.7 |
| 8 months | 40.8 | 42.0 | 43.3 | 44.5 | 45.8 | 47.0 | 48.3 |
| 9 months | 41.2 | 42.5 | 43.7 | 45.0 | 46.3 | 47.5 | 48.8 |
| 10 months | 41.6 | 42.9 | 44.1 | 45.4 | 46.7 | 47.9 | 49.2 |
| 11 months | 41.9 | 43.2 | 44.5 | 45.8 | 47.0 | 48.3 | 49.6 |
| 1 year | 42.2 | 43.5 | 44.8 | 46.1 | 47.4 | 48.6 | 49.9 |
In tables, head circumference is given in centimeters. These values \u200b\u200bwere developed by the WHO (World Health Organization), they are guided by pediatricians in our and other countries. Normally, in the first months, the head should increase in volume by 1.5-2 cm.Starting from 4 months, the increase will be less - about 1 cm.From 6 months, an increase of 0.5 cm is considered normal.
After a year, the size of the baby's head is no longer measured every month, because its growth becomes insignificant. In the first year of life, the volume of the head should grow by 10-12 cm.
Insignificant deviations from the above indicators may not indicate a developmental anomaly, but be an individual norm. If the pediatrician does not register the pathology, then most likely there are no violations. For reassurance, parents can visit another specialist.
When measuring the volume of a newborn's head, the pediatrician must take into account the factor of prematurity. Premature newborn babies have a large head.
Why do I need to measure my head size every month?
From the first years of life, children come under the close supervision of doctors. This is very important for the early detection of diseases and developmental disorders. For a specialist, the circumference of the skull and chest, their compliance with the child's age are of great importance. These indicators can indicate illness or congenital abnormality. Measurements of the head allow you to find out if the brain is developing correctly, if there are deviations in the work of the central nervous system. This data correlates with other possible symptoms of the disease, general health.

Control and indicative measurements are those that were made at the age of 3 and 6 months. The pediatrician enters the measurement results in a special table and each time verifies them with the tables of WHO standards. If a pathology is suspected, he will send the baby for additional examination or for an appointment with a narrow specialist, as a rule, a neurologist or orthopedist. From the age of 2-3, such measurements will no longer be so informative, therefore they are carried out less often.
What are the differences in head size between girls and boys?
The head circumference of a newborn boy is practically the same as that of a girl. As they grow and develop, boys begin to outpace their peers, and their norm rates will be higher.
Heredity must also be taken into account - some boys are born small and with a small head, like their parents. Girls, on the other hand, are quite large, which does not necessarily indicate the development of pathology in them. The pediatrician, assessing the health of the baby, takes into account his personality and genetics.
Technique for measuring head circumference
 To obtain a reliable result, it is necessary to correctly measure the head circumference. For this, a special technique has been developed, which includes the following steps:
To obtain a reliable result, it is necessary to correctly measure the head circumference. For this, a special technique has been developed, which includes the following steps:
- you need to put the child on a horizontal surface, best during sleep or in a calm state;
- use a soft measuring tape to measure the circumference of the skull through the frontal and occipital tubercles; the eyebrows serve as a guide.
It will be easier for a newborn baby to measure it, because at 5-6 months, the baby is likely to spin and cry. The mother needs to reassure the baby so that he remains stationary at the time of measurement.
Measurement of the circumference of a child's head must be carried out as accurately as possible, for a baby even 1-2 millimeters matter. It is necessary to ensure that there is no twisting of the tape and its too tight fit. It is advisable to take measurements with the same centimeter tape at the same doctor. This will avoid distorting the result.
What can deviations indicate?
Slight deviations from the accepted norms for the volume of the head for a newborn are permissible. Parents should be concerned when the head grows disproportionately, has an unnatural shape, or is severely out of size.
It is better to consult another specialist if the local doctor does not see any violations, but there are doubts about the normal development of the child.
Deviations in the shape of the head may indicate rickets or hydrocephalus. They are characterized by a bulge in the frontal or occipital parts. The diagnosis of rickets is usually given to babies at 3-4 months. It disrupts the development of bone tissue. Children's skeleton cannot form properly, because the necessary calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D are poorly absorbed. Rickets can be detected by the following symptoms: poor overgrowth or swelling of the fontanel, bulging forehead, disproportionate head growth, protrusion of the abdomen, etc.
With hydrocephalus, dropsy of the brain, increased intracranial pressure and neurological disorders develop. You can suspect a pathology when the size of the head is 3-4 cm larger than normal, the fontanel is enlarged, the frontal bone protrudes, a pattern of veins is discernible on the head, the baby is restless and often cries. Usually this is a congenital pathology that causes the child a lot of suffering, but in the early stages it is successfully treated.
An enlarged or small skull is a sign of macrocephaly or, conversely, microcephaly. Microcephaly leads to delayed growth of the brain and, as a result, mental retardation. An enlarged skull is also accompanied by a mental retardation and has an extremely poor prognosis. A large head is characteristic of increased intracranial pressure.

Sometimes serious trauma to the skull occurs during childbirth and the tissues in the head become swollen. This happens when a woman in labor does not fulfill the requirements of an obstetrician or gives birth on her own, as well as during an emergency caesarean section. The baby's bones are strongly compressed and deformed. Timely treatment eliminates pathological changes, in the future, the child can live a full life. Usually, all violations in such babies disappear without a trace by the year.
Immediately after giving birth, especially if they were the first, mom is surprised at how the baby's head looks - disproportionately large, slightly elongated upward. As the baby grows and develops, parents may be concerned about the size of the fontanelle, the rate of its overgrowth. So that nothing distracts from the joy of motherhood and fatherhood, it is necessary long before the birth of the baby to learn about all the nuances of its development, including the principles of skull formation, possible deviations from the norm and the dangers to which they entail.
The shape and size of the newborn's head
The skull of a newborn before delivery and for some time afterwards is fastened, practically, only by the skin membrane. And this is not a pathology, but a kind of trick of nature - thus it made it easier for the baby to pass through the birth canal. If a child is born naturally, and not during a caesarean section, then the shape of his head can be round or oval, slightly elongated upward, flattened, ovoid. Do not be alarmed if the newborn's head is not symmetrical or has a characteristic postpartum edema.
Another feature is the size of the newborn's head. The head is disproportionate to the body, its girth is greater than the girth of the chest, at least 2 cm. Such indicators are the norm, and deviations are called hydrocephalus and microcephalus. Both should be the reason for a detailed examination of the baby, for a number of diagnostic measures.
Why hydrocephalus is dangerous
Too large a newborn's head (hydrocephalus) may indicate a build-up of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull. In the first months of life, this does not entail any danger, since most infants under 3 months of age have it outflow through special channels. After being examined by a doctor of narrow specialization, the child is prescribed therapy, and the problem is easily solved, without having time to develop into a serious pathology.
What is myrcocephaly
Microcephaly is the most dangerous for a newborn. A small head is a sign of her underdevelopment, which can affect the formation of the brain long before birth. The cause of this pathology is the mother's alcoholism or drug addiction, intrauterine infections, birth trauma, hormonal diseases.
What is fontanelle
The fontanelle is a non-ossified part of the skull in a newborn, protected by connective elastic tissue. It is needed so that the baby's skull during childbirth can adjust to the shape of the mother's small pelvis and the birth canal. There are six fontanelles on the head of a newborn, but one can observe only one, the largest of them. It is located on the top of the baby's head and is completely overgrown by bone tissue only by 12 months. Its main functions are:
Facilitating the process of childbirth,
Providing optimal space for brain development,
Regulation of heat exchange, cooling of the brain during the period of increasing body temperature,
· Depreciation in the event of a fall.
It is very easy to find the largest fontanelle, diamond-shaped, measuring about 2 by 2 cm, on the baby's head - it is located in the middle of its parietal part. Another fontanelle that can be felt is located at the back of the head, and its size does not exceed 0.5 cm.
During that period, until the fontanelle is overgrown, it is necessary to monitor how it looks. If the fontanelle protrudes too much above the surface of the skull or is too fused, this may be a signal of problems in the development of the child. The fontanelle can sink against the background of dehydration, provoked by diarrhea, high fever. Having noticed this, you need to provide plenty of drink and call a doctor. If the fontanelle bulges, and this is accompanied by changes in the baby's behavior, high fever, vomiting, convulsions, if the bulging is observed for a long time, it is necessary to urgently deliver the baby to a medical institution.
How to care for a fontanelle
The shape of the head, its size and the general development of the baby in the first year of his life are directly related to the fontanelle. Medicine does not put forward special rules for caring for him. The most important thing is to ensure safety, eliminate the risk of injury to the newborn's head in the area of \u200b\u200bthe large and small fontanelles.
In order for the child's head to form correctly, it is necessary to put the baby periodically on the back, one and the other barrel. This measure will not allow parts of the skull to move to one side and will provide minimal stress on the fontanelle. In addition, there are several rules for caring for the fontanel:
When combing, do not touch the teeth of the comb,
Wash the baby's head with neutral means and very carefully,
After bathing, dry your head with blotting movements,
Never put pressure on the fontanel,
There should be no seams on the caps in the fontanel area,
Soften the parietal crusts with baby oil or cream before removing,
· Do not rely only on the pediatrician and independently track the rate of overgrowth of the fontanelle.
The parietal crusts can be distressing to the baby and affect the rate of ossification of the fontanel area. If they are intensively formed, represent a dense layer on the baby's head, then you need to lubricate them with cream not only after bathing, but also before it - in 20-30 minutes.
What to do if the fontanel does not overgrow
Not only slow but too fast bone formation in the fontanel area should be a cause for concern. If the fontanelle does not overgrow, and the baby is already more than a year old, then this may indicate the presence of the following problems:
Development of hydrocephalus,
· metabolic disease,
Bone tissue disease,
Hypothyroidism (thyroid dysfunction).
It is impossible to determine the reasons on your own, and you need a consultation with narrowly specialized doctors - an endocrinologist, a geneticist, a neurologist.
If parents note the rapid overgrowing of the fontanelle, this should also serve as a reason to see a doctor. It is not necessary to wait for a scheduled examination, which is carried out monthly for children under one year old, you can come to the clinic and ask for diagnostic measures - to do blood and urine tests, ultrasound of internal organs, MRI of the head, if there are indications for this. This is necessary if, against the background of rapid overgrowth of the fontanel, symptoms appear:
Nervousness,
Bad, short-term sleep,
· lack of appetite,
Low rates of weight gain,
Thinness,
Unstable work of the digestive tract,
Pallor or cyanosis of the skin.
The rapid overgrowth of the fontanelle can be a signal of the development of disorders in the formation of bone tissues - craniosynostosis, microcephaly, which entails abnormalities in the work of the central nervous system and the formation of the brain. Ossification of the skull in the area of \u200b\u200bthe spring is considered early if it occurs at the age of three months from the date of birth. Parents have the right to insist on diagnostics aimed at identifying the listed developmental problems. But to refuse preventive measures, even if there are no other symptoms of violations, is unreasonable.
In no case should you rely on the opinion of grandmothers, girlfriends or neighbors if the shape of the baby's head, the rate of its growth or overgrowth of the fontanelle cause concern for the parents. It is important to realize that folk methods or self-prescription of vitamin and mineral complexes in such cases can be not only useless, but also very dangerous for the baby.