Subject: Urine formation
Learn how the urinary system works

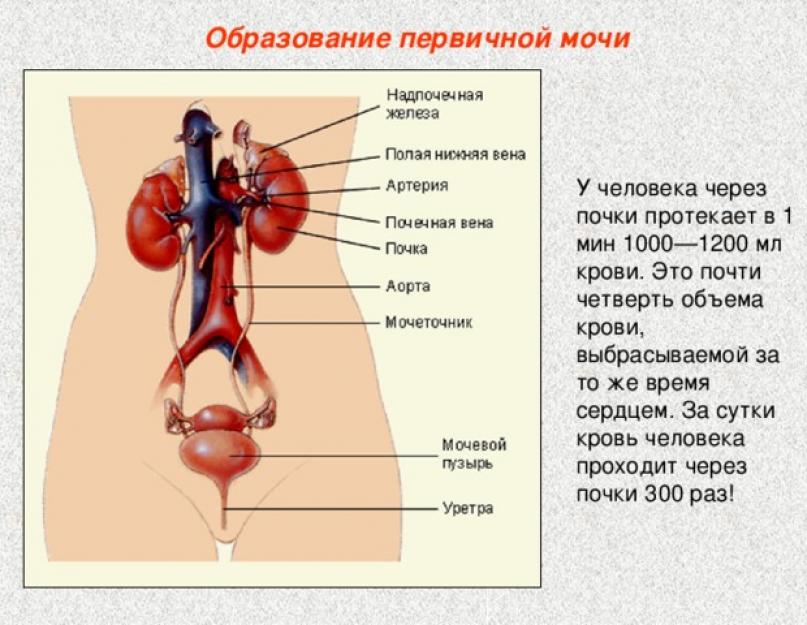
Formation of primary urine
In humans, 1000-1200 ml of blood flows through the kidneys in 1 minute. This is almost a quarter of the volume of blood ejected during the same time by the heart. A person's blood passes through the kidneys 300 times a day!



Formation of primary urine
The supply of blood to the kidneys differs from the supply of blood to other organs of the body in that the blood entering the kidneys sequentially passes two networks of capillaries located one after the other: capillary glomeruli and capillaries that braid the renal tubules. Such an abundant blood supply and a special structure of the capillary network of the kidneys allow the body to quickly get rid of unnecessary decay products and substances brought with the blood.
Urine is formed from blood plasma. However, the composition of urine is significantly different from the composition of blood plasma.

Formation of primary urine
This means that the kidneys produce urine by changing the blood flowing through them. This process takes place in two stages: first, primary urine, and then secondary, or final, urine. Urine formation is carried out through a number of physiological mechanisms, in three stages. Let's see how this happens.
The first step is filtering. There is high blood pressure in the capillary glomerulus, since the afferent arteriole of the glomerulus is almost twice as large in diameter as the efferent one, and about 20% of the fluid - blood plasma from the blood of the capillaries goes into the convoluted tubule.



Formation of primary urine
The walls of the capillaries and the renal capsule act as a filter. They do not allow blood cells and large protein molecules to pass through. But other substances dissolved in the blood plasma easily pass through this filter.
The fluid formed in the cavity of the renal capsule is called primary urine. Formed in a day 150-170 l primary urine. Thus, primary urine is filtered blood plasma. High blood pressure causes blood plasma to filter through the capillary walls into the renal capsule.

The second stage, absorption (reabsorption). From the renal capsule, the primary urine enters the renal tubule. Its walls absorb from primary urine water, amino acids, vitamins and other substances dissolved in it. Substances such as glucose are completely absorbed, others are partially absorbed, and others, such as urea, are not absorbed at all. Therefore, the concentration of urea in the secondary urine increases more than 60 times and increases from 0.03% to 2%.


In connection with such selective absorption, only those substances that are not needed by the body remain in the secondary urine. The substances he needs are again returned to the blood through a network of capillaries that wrap around the renal tubule.
The third stage, secretion. In addition to absorption, some substances are also released into the lumen of the renal tubule. Thus, the cells of the epithelium of the renal tubule secrete ammonia into the urine, some dyes that enter the body, drugs such as penicillin.

With the help of the kidneys, not only the products of the final breakdown of substances or compounds that are unnecessary to it are removed from the body. Sometimes excess blood nutrients, such as glucose, can also be removed. Consequently, in addition to a purely excretory function, the kidneys are involved in maintaining a constant chemical composition of the blood.
Urine formed in the renal tubule drains through the collecting ducts into the renal pelvis. From there it goes through the ureter to the bladder. Under normal conditions, in the absence of hard work and normal nutrition, the amount of urine excreted per day in an adult is 1.2-1.5 liters.



In medical institutions, a urine test is mandatory. It gives an idea not only about the state of the kidneys, but also about the metabolic processes occurring in other tissues, organs, and in the body as a whole.
Urination. In the kidneys, urine is produced continuously, but is excreted from them periodically in separate portions. The excretion of urine is associated with rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the ureters. These contractions push small volumes of urine from the ureters into the bladder.

In the bladder, further additional absorption of water into the blood occurs. When the bubble is filled to a certain limit, it is emptied. Emptying the bladder is a complex reflex act. The natural stimulus of this reflex is the stretching of the bladder. Irritation of receptors embedded in the wall of the bladder causes contraction of its muscles and relaxation of muscle thickenings, resulting in urination.
The center of the urination reflex is located in the spinal cord.

Prevention of kidney disease. The kidneys are vital organs in our body. Violation or cessation of their function inevitably leads to poisoning of the body with those substances that are usually excreted in the urine.
In case of violation of the kidneys, these substances accumulate in the blood and lead to the occurrence of severe conditions, often ending in death.
The cells of the renal tubules are highly sensitive to poisons of various origins, including those produced by pathogens of infectious diseases. Violation of the functions of such cells is accompanied by the cessation of the formation of secondary urine. As a result, a huge amount of water, glucose and other vital substances are lost. There is a serious threat to human life.




Kidney Disease Prevention
The consumption of too spicy food has a harmful effect on the kidneys. Such food often causes impaired kidney function. An even greater evil is the use of alcohol, which destroys the renal epithelium, sharply disrupts or stops the formation of urine. As a result, the body is poisoned by toxic metabolic products.
Currently, in the treatment of patients with severe chronic kidney disease, as well as people who have lost a kidney as a result of injury or other causes, a healthy kidney transplant from another person is used.

- What are the steps in the process of urination?
- Why is there high pressure in the capillary glomerulus?
- How is filtering done?
- What is the composition of primary urine?
- How does reabsorption take place?
- What is the content of urea in blood plasma and secondary urine?
- How does secretion take place?
- In what case can glucose appear in the urine of a healthy person?
- How much primary and secondary urine is formed per day?
- Where is the center of the urination reflex located?

** Test 1. What are the stages of the process of urination?
- Blood supply to the kidney through the renal artery.
- Filtration of blood plasma into the cavity of Bowman's capsules.
- Reabsorption of nutrients by the epithelium of the convoluted tubules.
- Secretion of waste substances into the lumen of the convoluted tubule.
- The movement of secondary urine through the collecting duct into the renal pelvis.
- The movement of secondary urine through the ureters to the bladder.
Test 2. Why is there high pressure in the capillary glomerulus?
- The renal artery is larger than the renal vein.
- The efferent arteriole is larger than the afferent arteriole.
- The afferent arteriole is larger than the efferent arteriole.
- The renal artery is smaller in diameter than the renal vein.

Test 3. How is filtering done?
- Blood plasma from the capillary glomerulus is filtered into the convoluted tubule.
- The blood plasma from the capillary glomerulus is filtered into the cavity of the Bowman's capsule.
- Blood plasma from the capillary glomerulus is filtered into the capillary network.
- The blood plasma from the capillary glomerulus is filtered into the collecting duct.

Test 4. How does reabsorption occur?
- The epithelium of the convoluted tubule reabsorbs water, salts, glucose and all substances that need to be stored in the body and transfers them to the afferent arteriole.
- The epithelium of the convoluted tubule reabsorbs water, salts, glucose and all substances that need to be stored in the body and transfers them to the efferent arteriole.
- The epithelium of the convoluted tubule reabsorbs water, salts, glucose and all substances that need to be stored in the body and transfers them to the renal vein.
- The epithelium of the convoluted tubule reabsorbs water, salts, glucose and all substances that need to be stored in the body and transfers them to the capillary network.
Test 5. What is the composition of primary urine?
- This is normal blood plasma.
- This is blood plasma without proteins.
- This is blood plasma without proteins and fats.
- This is blood plasma without proteins, fats and carbohydrates.

Test 6. What is the content of urea in blood plasma and secondary urine?
- In blood plasma 0.3%, in urine - 3%.
- In blood plasma 0.03%, in urine - 13%.
- In blood plasma 0.003%, in urine - 2%.
- In blood plasma 0.03%, in urine - 2%.
Test 7. How does secretion occur?
- Ammonia and other substances unnecessary for the body are secreted into the lumen of the Bowman's capsule.
- Ammonia and other substances unnecessary for the body are secreted into the lumen of the convoluted tubule.
- Ammonia and other substances unnecessary for the body are secreted into the lumen of the collecting duct.
- Ammonia and other unnecessary substances are secreted into the renal pelvis.

Test 8. In what case can glucose appear in the urine of a healthy person?
- A healthy person should not have glucose in their urine.
- After sleep.
- In the middle of the night
- After eating.
Test 9. How much primary and secondary urine is formed per day?
- Primary urine - 10 liters, secondary 1.2-1.5 liters.
- Primary urine - 100 liters, secondary 1.2-1.5 liters.
- Primary urine - 130 l, secondary 1.2-1.5 l.
- Primary urine - 180 l, secondary 1.2-1.5 l.
Test 10. Where is the center of the urination reflex located?
- In the medulla oblongata.
- In the diencephalon.
- In the cerebral cortex.
- In the spinal cord.
The presence of a genitourinary system in a person makes it possible to quickly remove waste products from the body that were formed during previously ongoing processes. Urine formation is a vital process carried out by the kidneys and is carried out in three main stages: filtration, reabsorption and secretion. Violation in the formation and excretion of urine can lead to certain types of rather serious diseases. At the same time, the studied primary and secondary urine, or rather the result of the analysis, will immediately show the arisen certain disorders, which will be a significant reason for further examination and treatment.

Primary urine is the liquid that is formed in the kidneys after the filtration of low molecular weight substances present in the blood from formed elements and proteins. By the name of the elements included in the primary urine, it can be compared with blood plasma, in which amino acids, creatinine, glucose, urea, low molecular weight complexes and free ions are also present in the exact amount. After the formation of primary urine and its passage through the tubules through the cells of their walls, a large amount of water goes back into the blood, as well as those substances that the body needs for normal life. This whole process of passage and return of the contents of the primary urine is called reabsorption.
In the process of reabsorption, some substances are completely absorbed by the body. These substances are glucose and various amino acids. Mineral salts and water are "taken" by the human blood. All that remains after this whole process is called secondary urine. That is, it is she who is handed over for analysis in the laboratory and examines its composition and other parameters.
Composition of secondary urine

The main components of secondary urine can be called:
- water,
- urea
- ammonia,
- various sulfates,
- chlorine,
- sodium.
The total volume of secondary urine, which includes all of the above components, exceeds one liter per day. It can be large if a person consumes much more water than his body needs, and smaller if the ambient temperature is high enough. The usual color of urine is yellow, due to the presence of bile pigments in the composition, some of which, being absorbed in the intestines, goes into the blood, passes through the filtration by the kidneys, but is not reabsorbed. The frequency of urine excretion from the body is determined by volume.
The need for analysis of the composition of secondary urine
The composition of secondary urine is examined to determine the presence of certain diseases in the human body. In this case, you can quickly diagnose a violation in the work of such organs as the bladder, kidneys and prostate. In addition, urine is analyzed when there is a suspicion of urolithiasis and nephrosclerosis.
Collection of material for research
In order to achieve reliable results, a very important condition is the correct collection of urine. In order to pass the analysis correctly, it is necessary to first perform hygiene procedures of the genital organs. Secondary urine should be collected in a sterile dry container and tightly closed with a lid. All this is explained by the fact that the concentration of substances in the material for research can change under the influence of external factors, as well as the presence of water and detergents in the container. In order to avoid this, there are currently special containers, the use of which will help to minimize the likelihood of obtaining unreliable results.
Features of collecting material for research in children

Children, especially those under the age of one and a half years, cannot control the desire to urinate, which causes certain problems with the collection of material. But in most cases, this analysis is mandatory and is given quite often. That is why secondary urine in children is collected in a special way using special urinals. These elements are attached to thoroughly washed genitals in advance and detached from them after the urine is inside it. The resulting liquid is poured into a sterile container.
Thus, the formation of secondary urine is a rather important process that allows not only to remove excess water and unnecessary substances and elements from the body, but also to diagnose a particular disease in time. This analysis is one of the simplest for both the patient and laboratory assistants, so there are no restrictions on its delivery. But in order to get a reliable result, it is necessary to fulfill a number of requirements when passing this analysis. Compliance with all the rules will be able to accurately make it clear about the presence of violations and decide on the need for treatment.
The process of urine formation consists of 3 links.
1) Glomerular filtration. Ultrafiltration from blood plasma into the glomerular capsule without albuminous fluid, leading to the formation of primary urine. The filtration barrier that serves to filter plasma during the formation of primary urine ensures the preservation of blood cells and proteins. It comes in 3 layers:
The capillary endothelium contains large and small formed elements, but not plasma.
Basement membrane common to capillaries and pogocytes
Inner leaf of the glomerulus capsule.
2) Tubular reabsorption leads to the formation of secondary urine, begins in the proximal tubules of the nephron, is a reversible absorption of water and other substances from the primary urine. Reabsorption of the in-in in different parts of the nephron varies. Most of the v-in is actively adsorbed, and the primary sodium potassium ions with the help of the energy of ATP, secondary glucose, amino acids, without energy expenditure, water, urea, chloride are passively adsorbed. In the proximal section, water, amino acids, proteins, vitamins, trace elements, glucose, and electrolytes are reabsorbed. Water, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chlorine ions are reabsorbed in Henry's loop and distal tubules, while urine is concentrated 4-4.5 times in Henry's loop, in the distal tubules the concentration is selective and depends on the needs of the body. In the collecting ducts, water reabsorption continues, and the concentration of urine is completed.
3) Secretion. In the tubules of the kidneys active in two ways:
The capture of epithelial cells of the nephron of some of the blood and their transfer to the lumen of the tubules, so the org in the bases, potassium ions, protons are transferred.
Synthesis of new in-in in the walls of the tubules and their removal from the kidneys.
Due to active secretion, drugs and some dyes (pinecillin, furescillin) are released from the body. The products of protein metabolism (urea, creatinine) are removed weakly and not filtered at all. Those. thanks to filtration, reapsoption, secretion, the main task of the kidneys is to form urine and remove metabolites with it.
Primary urine is without protein ultrafiltration of blood plasma, the volume is 180 liters per day.
Primary urine composition - blood plasma composition (ultrafiltrate):
water, proteins (albumin), amino acids, glucose, uric acid, urea, creatinine, chlorides, phosphates, potassium, sodium, H +, etc.
The large volume of filtration is due to:
1) rich blood supply to the kidneys
2) large filtration of the surface of the tubules of the glomerulus
3) high pressure in the capillaries.
The glomerular filtration rate depends on:
1) blood volume
2)Filtration pressure
3)Filtration surface
4) number of functional nephrons
The efficiency of pressure filtration is determined by the pressure of 3 forces:
1) blood pressure capillaries (promotes)
2) ancotic blood pressure (prevents) 3) pressure in the capsule (prevents)
It changes along the capillaries, because. increased ancotic pressure.
The glomerular filtration rate is regulated by nervous and humoral mechanisms.
Primary urine is called the liquid that is formed in the kidneys after the process of its purification from protein, blood enzyme particles.
If we consider in more detail the components of the primary urine, you can see the plasma, which is almost completely cleared of protein enzymes. The smallest protein molecules enter the ultrafilter. This is about 3% hemoglobin, the albumin rate is 0.01%.
Specialists distinguish such properties of urine of the primary type.
- A characteristic feature of this liquid is a low osmotic pressure, this is due to the membrane, which is in a state of equilibrium.
- The liquid is released in a large daily volume, this figure can reach 10 liters. If there is about 5 liters of blood in the human body, the kidneys filter more than 1500 liters of blood volume.
Violations in the integral system of education, functionality, fluid excretion signal the body as manifestations of serious diseases.
Place of education
Primary urine begins to form due to nephrin particles, which consist of glomeruli, capsules, interconnected convoluted channels.
The first component, that is, the glomeruli, is a network of capillary particles. They are in a capsule, due to pressure, the volume of blood that enters is filtered, then primary urine is formed.
It is often referred to as the "glomerular ultrafilter". The process of its formation takes place with the help of several interrelated stages:
- The first step is filtering. Through the capillaries, the volume of blood passes through the capsule, the lattice, forming a liquid that does not contain protein.
- Already filtered primary urine goes through the process of reabsorption. It enters the nephron channels, it is in this place that the fluid is enriched with nutrients, glucose.
- After the absorption process, the stage of secretion passes during the day. It is based on the formation of up to 180 liters of primary urine, the remainder goes to the final, secondary urine.
Characteristics of secondary urine
The education and content of this component is influenced by a person's age, gender, and weight category. The composition of the secondary liquid contains water, chlorine, sulfates, sodium, ammonia and. The volume of such a liquid does not exceed a liter, this is the liquid that the body did not have time to assimilate.
If we compare primary and secondary urine, it is worth noting that the former contains useful substances and is absorbed by the body. Secondary urine is not able to be absorbed, it contains mainly acids and urea in its composition. For research, it is used for qualitative diagnosis of the kidneys, prostate, and bladder.
Using the analysis, you can determine pyelonephritis, the development of urolithiasis, or nephrosclerosis.
Thanks to the timely analysis, it is possible to detect the pathology in time, to undergo the course of treatment prescribed by the attending physician.
Diagnostics
In order to obtain a reliable result of secondary urine, it is necessary to observe the rules of hygiene and cleanliness. The true result depends on the concentration of the substance, its indicator may change under the influence of external factors, for example, the presence of detergent residues that remain on the walls of the tank.
To collect the necessary material, you should not use pots or diapers, a urinal is suitable for these purposes.
Secondary urine will show a reliable result if the genitals are clean and the collection time is in the morning.
Doctors advise adhering to several rules that directly affect the quality of indicators:
- Before collecting the material, use a normal liquid indicator, if you overdo it with the amount, the secondary urine will change its original density;
- for 24 hours, exclude alcoholic beverages from your diet, as well as foods that change its color;
- secondary urine can change its characteristics under the influence of drugs, herbal decoctions, or biologics. Therefore, before the procedure, refuse to take them.
In cases where a person is undergoing a course of treatment in parallel, that is, taking specific substances, it is necessary to warn the doctor, or directly the laboratory assistant about this fact.
Analysis results
With deviations from the normal indicator, conclusions can be drawn about poor analysis. Often, such a study indicates the development of diseases that require immediate intervention.
The specialist looks at 4 main characteristics:
- A light yellow shade of urine indicates healthy, normal functionality of the body;
- with the development of the inflammatory process, the urine becomes cloudy, for example, with pyelonephritis, or cystitis;
- indicator 4 - 7 is the norm, acidity deviations indicate the development of pathologies;
- ketone bodies, glucose, hemoglobin should be present in the analysis, erythrocytes can be traced in a moderate amount.
conclusions
It is worth noting that the primary liquid, or secondary, have differences and similarities. The most important of them is that they are interconnected, smoothly passing into each other. If you find yourself with incomprehensible symptoms, you should immediately consult a specialist. Violations, deviations from the norm during the analysis indicate the development of inflammatory processes, for treatment it is necessary to consult and undergo a course of treatment.
Story
Primary urine was first described by Carl Ludwig (1816-1895) in 1842 in his doctoral thesis "Contribution to the theory of the mechanism of urine excretion" (German: "Beiträge zur Lehre vom Mechanismus der Harnabsonderung").
Compound
Primary urine in its composition is a plasma, almost devoid of proteins. Namely, the amount of creatinine, amino acids, glucose, urea, low molecular weight complexes and free ions in the ultrafiltrate coincides with their amount in blood plasma. Due to the fact that the glomerular filter does not pass protein anions, then to maintain the Donnan membrane equilibrium (the product of the concentrations of ions on one side of the membrane is equal to the product of their concentrations on the other side), the concentration of chloride and bicarbonate anions in the primary urine becomes approximately 5% more and, accordingly, the concentration of sodium and potassium cations is proportionally lower than in blood plasma. A small amount of one of the smallest protein molecules enters the ultrafiltrate - almost 3% hemoglobin and about 0.01% albumin.
Properties
Primary urine has the following properties:
- Low osmotic pressure. It occurs due to membrane balance.
- Large daily volume, which is measured in tens of liters. The entire volume of blood passes through the kidneys about 300 times. Because On average, a person has 5 liters of blood, then the kidneys filter about 1500 liters of blood per day and form about 150-180 liters of primary urine.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
GFR is regulated by nervous and humoral mechanisms and affects:
- the tone of the arterioles of the glomeruli and, consequently, the volume of blood flow (plasma flow) and the magnitude of the filtration pressure;
- tone of mesangial cells (connective tissue between the capillaries of the nephron glomerulus) and the filtration surface;
- activity of visceral epithelial cells (or podocytes) and their functions.
Humoral factors such as prostaglandins, atriopeptides, norepinephrine and epinephrine, adenosine, and the like. can both increase and decrease glomerular filtration. The most important role in the constancy of GFR is played by autoregulation of cortical blood flow.
Meaning
Primary urine undergoes further concentration and removal of useful substances from it. The resulting concentrated residue is secondary urine.
Links
- Primary urine (glomerular ultrafiltrate). Regulation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- Trifonov E.V. Pneumatic psychosomatology of man. Russian-English-Russian encyclopedia, 15th edition, 2012 = Tryphonov E.B. Human Pneumapsychosomatology. The Rus.-Engl.-Rus. Encyclopedia, 15th ed., 2012.
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010 .
See what "Primary urine" is in other dictionaries:
I Urine (urina) is a biological fluid produced by the kidneys and excreted from the body through the urinary tract. M.'s education and allocation is one of the most important mechanisms of maintenance of a constancy of the internal environment of an organism. With urine from the body ... ... Medical Encyclopedia
This term has other meanings, see Urine (meanings). A jar of urine Urine (Latin urina) is a type of excrement ... Wikipedia
See Primary urine... Big Medical Dictionary
- (syn. M. provisional) liquid resulting from ultrafiltration of blood plasma in the renal glomeruli; differs from plasma by a low content of colloids, primarily proteins ... Big Medical Dictionary
This article needs to be completely rewritten. There may be explanations on the talk page. Urine therapy is one of the methods of alternative medicine ... Wikipedia
A complex process that continuously takes place in the nephridia and other secretions, organs of invertebrates and in the kidneys of vertebrates ensures the production of urine and its excretion into the urinary system. Urine, as it moves along, will excrete, the organ undergoes, which means ... ...
- (named after the 19th-century English physician W. Bowman, W. Bowman), the cup-shaped blind end of the urinary tubule of the kidneys. Primary urine is formed in the cavity of the Bowman's capsule. * * * BOWMAN'S CAPSULE BOWMAN'S CAPSULE (named after an English doctor of the 19th century W. ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary
This term has other meanings, see Kidney. Kidney Human kidney. Latin name ren ... Wikipedia
Structural functional unit of the kidney (see Fig.), which consists of a renal corpuscle and a tubule 20 50 mm long. In both kidneys there are about 2 million nephrons, the length of all their tubules reaches 100 km. The beginning of the nephron is the capsule of the glomerulus ... ... medical terms
- (from meta ... and nephridia), metamerically located paired will highlight, organs in invertebrates, ch. arr. in annelids. Develop from ectoderm or mesodermal nephroblasts. M. tubular channels opening at one end (ciliary funnel, ... ... Biological encyclopedic dictionary