It's a great time The life of any woman - pregnancy, is sometimes overshadowed by emerging problems, especially with health, which can increase the risk of the impossibility of further favorable existence of the mother and child. One of these troubles can be thrombophilia during pregnancy, which can lead to severe consequences for late recognition - for example, miscarriage. But there is no need to panic - the main thing is to consult a specialist in time, to identify or prevent the development of the disease.
And yet, what is thrombophilia during pregnancy? This is the name of a disease that affects the blood system and consists in its improper performance of its functions, in particular, the blood begins to clot faster and often this happens even inside the body. Symptoms are not expressed, so the disease thrombophilia goes unnoticed by the carrier, although it is noted quite quickly when exposed to certain factors (infections or injuries). This disease poses another danger due to its ability to be transmitted genetically.
Species
There are many types of thrombophilia depending on various factors, for example:
- According to the type of vessels that were susceptible to the disease (that is, arteries, veins, capillaries, as well as a mixed type).
- Due to its occurrence (heredity or acquisition).
- Due to leakage (due to improper circulation, changes or damage to the walls of blood vessels and arteries).
Thrombophilia in pregnant women, which arises due to changes in blood composition, poses a very great danger, since it promises very serious complications.
If blood circulates in the body incorrectly, not all organs receive the dose of oxygen they need, and this affects both the condition of the mother and the development of the child, which is catastrophically disrupted. Thus, the blood circulation between mother and child is irregular and irregular. In a particularly severe case, there is even a possibility of pregnancy fading.
Symptoms
Manifestations accordingly depend on the cause of the onset and development of the disease, its location and degree.
Symptoms of thrombophilia during pregnancy are clearly monitored only in the severe stage, so if they are detected, you cannot delay treatment:
- If the problem is in the veins, then excessive redness and, as well as increased sensitivity, may be noted.
- If the disease affects internal organs, then a disruption in its functioning becomes noticeable.
- Disease of the lung tissue is expressed by breathing problems and excessive blueness skin above the diaphragm line.
- If blood clots get into the heart, they will cause a cerebral infarction in the head.
However, blockage of blood vessels in the lungs can occur - this phenomenon leads to death in most cases.
The development of such a disease in the body is caused by:
- dehydration;
- vascular damage;
- blood cells have stopped performing their functions or are doing it incorrectly;
- development of cancer in the body;
- excessive use of certain medicinal products;
- presence of immunodeficiency viruses ();
- heredity;
- abnormal fetal development;
- serious injuries;
- operations;
- congenital

Diagnostics
Such a disease cannot be diagnosed independently; the diagnosis of thrombophilia is determined only through tests and general symptoms. A quick diagnosis is also often facilitated by the following notes in the medical history:
- Previously noticed thromboses;
- Previously noted disorders during pregnancy.
Since changes in the composition of the blood may not be so noticeable, other studies are also carried out, for example at the gene level. Not only is thrombophilia during pregnancy detected in a woman using such an analysis, but the degree of a person’s susceptibility to this disease is also determined. But in any case, the doctor prescribes this test only if a pathology is suspected, and all expectant mothers are required to take it.
Treatment
Since this pathology is very, very serious, it is worth entrusting its treatment only to trusted doctors. In the initial phase, in the one where the symptoms do not yet bother the patient, immediate treatment is not so strongly required. But already at an advanced stage, treatment of thrombophilia during pregnancy should be carried out under constant control doctors Drug treatment consists of taking antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants.

Although this sounds quite serious and strict, in fact, acetylsalicylic acid, heparin and many vitamins B and E are used in the treatment of thrombophilia.
In addition to taking drugs for thrombophilia, special physical therapy is prescribed; swimming and exercises in water are especially useful in such cases, and for varicose veins of the lower extremities, the use of special stockings may be prescribed.
Prevention
In addition to medications, experts recommend practicing and following a strict diet, which must include many elements contained, for example, in dried fruits, phosphorus-rich fish or berries, especially sour ones.
Have a nice and useful procedure Self-massage can help blood circulate better throughout the body.
To reduce the load on your legs, you should spend less time in an upright position, but slow walks in the fresh air will be beneficial.

Folk remedies
Thrombophilia during pregnancy is treated with means traditional medicine, but it is better to use them not as the main therapy, but as accompanying methods.
This includes:
- Treatment of thrombophilia with leeches. Their blood thinning function is very useful for people with a similar disease. They are used if blockage of the veins has already occurred and darkening of the skin has begun at the site of the damaged vessels. They should not be kept for longer than five or ten minutes, depending on the severity, and they should not be reused. The entire treatment takes on average three to five days.
- A very tasty way to overcome the disease is to eat jam and drink compote made from raspberries. This berry has the same wonderful property prevent blood from thickening. But you shouldn’t overdo it with sweets either. Remember to control your sugar intake.
- Eating garlic also prevents the appearance of blood clots.
Possible consequences
If a woman was unable to track and identify such a pathology in time, she should know what consequences of thrombophilia during pregnancy await her. Depending on the location of the blood clots, they have a serious impact on the system internal organs, seriously disrupting their functions, causing increased swelling and pain in the limbs.
When blood vessels are blocked, very serious diseases can develop, which can even be fatal. This is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since it is between the mother and the fetus.
For this reason, before a planned pregnancy, you need to undergo a fairly serious and lengthy medical examination with many tests and studies in order to identify the presence of such diseases in future parents. If one is detected, specialized treatment for thrombophilia is prescribed in accordance with the individual characteristics of the body.
After the entire course of taking medications, new examinations are carried out to determine the effect of treatment on the patient. To avoid problems and to have a healthy and easy pregnancy, you need to be constantly monitored by a doctor.
The mother has a great responsibility, since she is responsible not only for herself, but also for her unborn child. Such a result as a lack of oxygen in the tissues and organs of the fetus irreparably affects its development not in better side. Thrombophilia is one of the most dangerous diseases for an expectant mother. It is necessary to promptly identify and begin treatment of this disease. The faster the necessary methods are taken, the higher the likelihood of the birth of a developed and healthy baby.
Thrombophilia in itself does not harm; it is pathological when created ideal conditions to aggravate it. Such conditions occur after minimally invasive operations, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and even pregnancy. And in order not to lose a child in the prenatal period or a mother in the postpartum recovery period due to hereditary thrombophilia, it is important to begin preparation before childbirth. And you need to start with tests. Doctors will assess all levels of risk and select the necessary therapy for a successful pregnancy.
What is thrombophilia, the causes of increased thrombosis
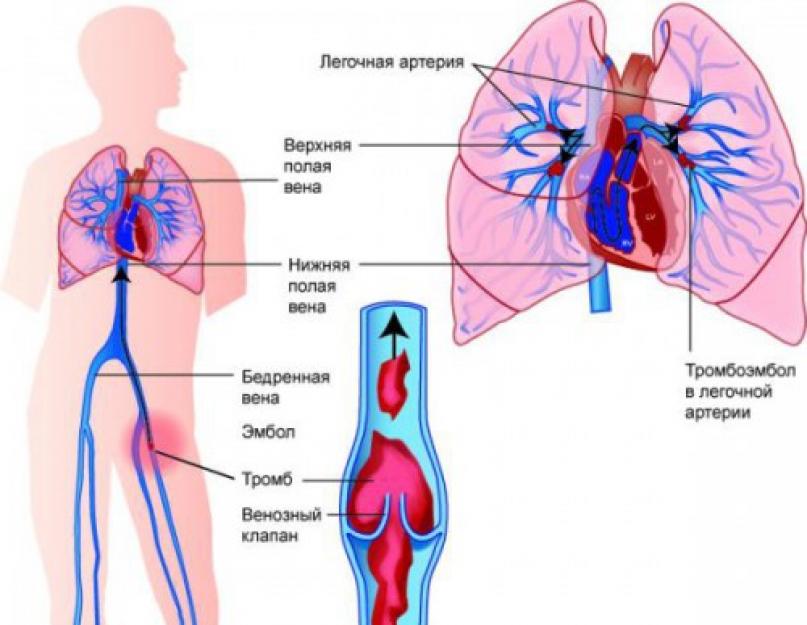
Thrombophilia is an increased predisposition to the development of vascular thrombosis (mainly venous) of various locations due to genetic defects in the hemostatic system. The process of thrombus formation is a natural reaction of the body when blood vessels are damaged, aimed at stopping bleeding. In thrombophilia, the formation of a clot provokes a decrease in the inflow (in the arteries) or outflow (in the vein) of blood. If a blood clot is detached from the wall of an artery or vein, an embolus is formed - a particle that moves with the blood flow and can stick to the walls of other vessels.
 The resulting blood clot is firmly attached to the site of endothelial damage, however, in some cases, the entire blood clot or its fragments can break off and enter other tissues and organs, leading to circulatory disorders
The resulting blood clot is firmly attached to the site of endothelial damage, however, in some cases, the entire blood clot or its fragments can break off and enter other tissues and organs, leading to circulatory disorders Blood clots often clog veins. In addition to the vessels of the lower extremities and the pulmonary artery, mesenteric veins, portal, hepatic, renal, and rarely veins of the upper extremities and brain are susceptible to thrombosis.
This pathology is widespread; up to 40% of the adult population suffers from its consequences, depending on the location of formation:
- leg blood clots:

- thrombosis of the veins and arteries of the intestine - intestinal necrosis and acute inflammation - peritonitis;
 Acute occlusion of mesenteric vessels is manifested by a sharp disturbance of blood circulation in the vascular areas proximal and distal to the site of obstruction, accompanied by severe vasospasm and additional thrombus formation, resulting in acute malnutrition and ischemic damage to the intestinal wall
Acute occlusion of mesenteric vessels is manifested by a sharp disturbance of blood circulation in the vascular areas proximal and distal to the site of obstruction, accompanied by severe vasospasm and additional thrombus formation, resulting in acute malnutrition and ischemic damage to the intestinal wall - thrombosis of cerebral vessels - ischemic stroke- acute circulatory disorder of the cerebral vessels, which can lead to death within 24 hours or instantly;
- thrombosis of the cardiac coronary vessels - myocardial infarction - a form of coronary heart disease characterized by the death of a section of the myocardium due to insufficient blood supply;
 Acute ischemia causes the death of some functional muscle cells (necrosis) and their subsequent replacement with connective tissue fibers, i.e. the formation of a post-infarction scar
Acute ischemia causes the death of some functional muscle cells (necrosis) and their subsequent replacement with connective tissue fibers, i.e. the formation of a post-infarction scar - thrombosis of placental vessels - spontaneous miscarriage;
- hepatic vein thrombosis - ascites or abdominal dropsy, which differs from other diseases by accumulation in abdominal cavity excess liquid.
 The accumulation of peritoneal fluid during ascites is accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, pushing the dome of the diaphragm into the chest cavity
The accumulation of peritoneal fluid during ascites is accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, pushing the dome of the diaphragm into the chest cavity
Causes of increased thrombosis:
- thrombophilia in first-degree relatives;
- blood diseases:

- cancerous formations;
- atrial fibrillation - increased heart rate up to 350–600 beats per minute;
- varicose veins or enlarged veins;
 Varicose veins, or varicose veins, are pathological changes in the veins, accompanied by their saccular expansion, increase in length, formation of convolutions and knot-like tangles, which leads to valve failure and impaired blood flow
Varicose veins, or varicose veins, are pathological changes in the veins, accompanied by their saccular expansion, increase in length, formation of convolutions and knot-like tangles, which leads to valve failure and impaired blood flow - arterial hypertension - constant increase blood pressure from 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and above;
- previous heart attacks and strokes;
- surgical procedures;
- obesity;
- long-term use of hormones.
How does pregnancy affect thrombophilia?
Genetically determined thrombophilia affects generation after generation, but for a long time does not reveal itself at all. But with the onset of pregnancy and a change in blood viscosity, this tendency to form blood clots begins to become excessively active.
Pregnancy increases the formation of blood clots by 4-5 times, because the blood changes its viscosity under the influence of hormones.
Video: researcher, obstetrician-gynecologist, author of books on women’s health E. Berezovskaya on thrombophilia and pregnancy
What is the most dangerous period of pregnancy?
The most dangerous period is up to 10 weeks, when the risk of miscarriage is especially high due to the formation of a blood clot in the vessels of the placenta during its increased nutrition to ensure the vital activity of the fetus. If this milestone was successfully overcome, you should remember that in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy the risk of developing thrombosis will increase again. After 30 weeks, a pregnant woman’s body intensively prepares for childbirth and blood clotting increases noticeably. When preparing for childbirth, the levels of the following estimated coagulation indicators are additionally checked:
- prothrombin or coagulation protein, normal - 8–142%;
- thrombin time or aPTT, during which blood clotting occurs. Normal - 11–17.8 seconds;
- - a plasma protein responsible for the formation of a blood clot. Its normal content is 2.00 - 4.00 g/l;
- atithrombin is a specific protein that ensures the resorption of a blood clot, normally 75–125%.
Possible consequences and complications of recurrent thrombophilia
Hereditary or acquired thrombophilia is considered the most probable cause such obstetric complications as:
- miscarriage;
- IUGR or fetal growth retardation, when its growth and development parameters do not correspond to the obstetric gestational age;
- death of the fetus in the womb or stillbirth;
- placental insufficiency with delayed fetal development and oxygen starvation (hypoxia);
- premature detachment of a normally located placenta - early separation of the placenta from the walls of the uterus that occurred before the birth of the fetus;
- gestosis is a deviation from the normal course of pregnancy, characterized by a set of main symptoms: edema, protein in urine tests, increased pressure;
- eclampsia is the most severe, critical form of gestosis, occurring with convulsive syndrome, loss of consciousness, and the development of post-eclamptic coma;
- fetoplacental insufficiency.
Clinical manifestations of thrombophilia
Depending on where the clot has formed, the symptoms are different:

When thromboembolism recurs, both genetic and acquired, pregnant women often turn not to a hematologist, but to their gynecologist with the confidence that they suffer from late obstetric complications of pregnancy, namely those expected at later gestosis or VSD - vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- headaches;
- hypertension;
- general weakness;
- loss of consciousness;
- increased fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- swelling of the upper and lower extremities;
- leg cramps;
- bluishness or redness of the skin;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- uterine bleeding;
- toxicosis with vomiting.
Methods for diagnosing thrombophilia
First of all, it is necessary to donate blood to study hemostasis - this is a biological system in the body, the function of which is to maintain the liquid state of the blood, stop bleeding in case of damage to the walls of blood vessels and dissolve blood clots that have fulfilled their function. The main blood clotting factors are:
- F5 - accelerin gene, Leiden mutation;
- F2 - prothrombin.
These genes are the most studied and it is known that their violation can lead to severe complications of pregnancy, for example, placental abruption at 25–26 weeks of pregnancy. Based on them, the hetero- or homozygosity of a woman is revealed, i.e. how damaged her genes are. Tests for these two markers are carried out first; you can donate blood for this even after a light breakfast. The analysis period is only two days. Such tests for gene polymorphism are taken only once in a lifetime; there is no need to retake them after treatment.
If necessary, additionally prescribed:
- study of the plasminogen activator gene - fibrin in the diagnosis of PAI-1 and blood coagulation factor XIII. It is known that inhibition of fibrinolysis often leads to disruption of the fetal implantation process. In this regard, a decrease in the fibrinolytic activity of this system is one of the reasons early interruption pregnancy;
- platelet receptor genes; the presence of mutations in these genes leads to increased platelet aggregation and adhesion. Platelets are the first to appear at the site of the defect. They stick (adhere) to damaged endothelial cells, swell and form processes. Parallel to adhesion, the process of platelet aggregation occurs, swelling and gluing them together with the formation of processes and the imposition of aggregates on the site of vessel damage, as a result of which the hemostatic plug or thrombus quickly grows. The following factors need to be diagnosed:
- FBG - fibrinogen gene;
- ITG A2 - platelet integrin gene;
- ITG B3. Such patients are insensitive to aspirin and need chimes;
- F7 - proconvertin gene;
- F13 - fibrin stabilizing factor gene.
- folate cycle genes or genes regulating homocysteine accumulation, indicating a predisposition to thrombophilia. After all, homocysteinemia is a condition in which the content of homocysteine in the blood is elevated above the physiologically acceptable norm and leads to the birth of children with congenital pathology. Their violation indicates that you need to check your homocysteine level:
- MTR - gene encoding the enzyme methionine synthase;
- MTRR - gene encoding the enzyme methionine synthase reductase;
- MTHFR is a gene encoding the enzyme methionine synthase.
Based on the results of the analysis, the severity of the possible manifestation of thrombophilia is determined and recommendations for treatment are given, and sometimes the condition of the pregnant woman is simply monitored.
Table: diagnosis of thrombophilia based on laboratory diagnostic results
| Analysis name | What determines |
| General blood test |
|
| Coagulogram |
|
| Genetic markers of congenital thrombophilia: |
|
| Homocysteine |
|
How to monitor the condition of the fetus if there is an identified tendency to thrombosis
If thrombophilia is diagnosed in a pregnant woman, there will be more monitoring of the condition of the fetus and tests will be prescribed more often.
To monitor the development of the fetus and the safety of the placenta, it is necessary:
- In the first trimester:
- at 8–10 obstetric week- three-dimensional echography of uteroplacental blood flow;
- later ultrasound with Doppler, which reveals areas of reduced blood flow in the placenta.
- In the II and III trimesters:
- When checking ultrasound screening, the following is carried out:
- Doppler ultrasound to measure the nature and speed of blood flow in the vessels;
- fetometry or measurements of the child in utero;
- cardiotocography to record fetal heart rate and uterine tone.
- When checking ultrasound screening, the following is carried out:
Who needs to undergo genetic testing for a hereditary form of thrombophilia?
Genetic tests to diagnose hereditary thrombophilia identify genetic mutations that are important for thrombophilia.
First of all, such studies are prescribed:
- Women who are expected to use hormonal drugs for treatment, and those who are preparing for planned operations caesarean section;
- For women who have a burdened personal history in the past, when chromosomal, hormonal, infectious and uterine causes of miscarriage are excluded:
- with habitual miscarriage during various periods of pregnancy;
- for repeated complications of pregnancy:
- preeclampsia;
- abruptions of a normally located placenta;
- fetal growth retardation syndrome.
- bad IVF experience;
- tendency to minor bleeding (nasal, cervical).
- Women with a complicated family history of thrombosis:
- unclear causeless (idiopathic) thrombosis;
- in the family, close relatives have cases of early stroke, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, sudden death before the age of 50;
- repeated episodes, especially in women under 50 years of age;
- thrombosis of rare localization (in the mesenteric vessels of the intestine, in the cerebral veins);
- complications from the use of oral contraceptives or hormone therapy;
- birth of children with chromosomal abnormalities.
Video: geneticist Z. Bayanovna about thrombophilia genes
Treatment of thrombophilia during pregnancy
Detection of thrombophilia is not at all a sign that a woman will not be able to give birth. If you undergo all examinations on time and plan your pregnancy, there is every chance that the expectant mother will have healthy children.
Treatment started on time will contribute to successful placentation and reliable attachment of the embryo to the wall of the uterus. Compliance with anticoagulant treatment is indicated throughout pregnancy and for 6 weeks after delivery.
If therapy is started late in pregnancy, the woman has little chance of carrying the fetus to term without significant complications.
After conducting all the necessary studies, the doctor will prescribe the following to the woman:
- If the level of homocysteine is normal, then folic acid (vitamin B9) is prescribed in an increased dose throughout pregnancy and is not canceled when the term reaches 12 obstetric weeks:
- Folacin;
- Folio;
- Folic acid 9 months;
- Metafolin is an accessible form of folic acid that is absorbed by almost everyone, since its absorption does not require a long chemical process involving enzymes (as in the metabolism of regular folic acid). The ratio of those who absorb this vitamin and those whose bodies are insensitive to it is approximately the same. To check this, expensive and hard-to-find tests are needed.
- Vitamin complexes are prescribed:
- which contain polyunsaturated fatty acids:
- Femibion natalcea I;
- Angiovitis;
- Vitrum cardio omega - 3;
- Omegamama 9 months;
- Wessel due f.
- magnesium and B6 preparations, 1 tablet 2 times a day for 1 month:
- Magne B6 - forte;
- Magnelis B6.
- which contain polyunsaturated fatty acids:
- In some cases, the use of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) - and its derivatives Dalteparin, Enoxaparin, Fraxiparin - is indicated as antithrombic therapy:

- Progesterone preparations:

- Additionally, anticoagulants are prescribed to slow down blood clotting processes:
- Warfarin, which blocks the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent blood coagulation factors (II, VII, IX, X) in the liver, reduces their concentration in plasma;
- Pradaxa or thrombin inhibitor, which in turn is responsible for the process of converting fibrinogen into fibrin and the formation of a blood clot.
Video: obstetrician-gynecologist I. I. Tyan about congenital thrombophilia and pregnancy management tactics
Diet
All patients with an increased risk of thrombosis are prescribed an antithrombotic diet according to (J. Casper, 1973); food should be rich in folates and B vitamins.
Thrombophilia disease is dangerous and difficult to treat. Thrombophilia is a tendency of the body to form blood clots in blood vessels. This disease can be acquired or hereditary. The basis of this disease is high blood clotting.
Thrombophilia is dangerous for pregnancy. The full development of the baby requires good blood circulation, since it is thanks to the movement of blood that the child receives oxygen and the substances necessary for life. If blood clots begin to form during pregnancy, this leads to pathologies. Thrombophilia poses a danger to both the life of the mother and the life of the baby.
Often during pregnancy, a woman is unaware of this disease and learns about the diagnosis after a comprehensive examination. Despite this, thrombophilia has a number of symptoms that are ignored by women. These are symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia. Thrombophilia and pregnancy planning are compatible if the pathology is diagnosed in time and treatment is started correctly.
If a person has undergone any surgery or been injured, acquired thrombophilia may begin to develop. Genetic thrombophilia is passed from parents to children. There are cases when pathology occurs as a result of a mutation. Genetic thrombophilia cannot be detected in the body because there are no symptoms. Certain symptoms begin to appear when fractures, injuries occur, or when a woman becomes pregnant.
Why does pregnancy provoke the development of pathology? As it turns out, circulatory disorders and bearing a child are strongly interconnected.
Blood clotting increases in the body from the moment of conception. This is how the body reacts to pregnancy so that during the birth process the woman does not die from blood loss. However, there is a negative side to this idea of nature, due to the fact that blood clotting is increased, blood vessels become clogged with clots, which in turn can lead to miscarriage or cause premature birth.
Genetic thrombophilia manifests itself most often during pregnancy. From the moment of conception, another circulatory system appears in a woman’s body – the placental. Of course, this creates additional stress on the body. The formation of a new circulatory system is a prerequisite for the development of genetic thrombophilia.
Congenital thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is not at all dangerous for humans, but changes occur from the moment of pregnancy. If a woman has signs of hereditary thrombophilia, then the likelihood of thrombosis increases significantly. The risk of miscarriage also increases. If a woman experiences symptoms of thrombophilia during pregnancy, she is likely to give birth prematurely. It should be noted that premature birth is a positive end to pregnancy, since in most cases thrombophilia leads to a frozen pregnancy.
The formation of blood clots in the vessels leads to oxygen starvation of the fetus, and its growth and development is suspended. If the child does not receive vital substances during pregnancy, this can lead to processes such as:
- placental abruption;
- development of pathologies in the fetus;
- death of a child;
- miscarriage;
- gestosis;
- premature birth;
- preeclampsia.
Consequences of thrombophilia
- In the first trimester pregnancy develops without pathologies, but after the tenth week there is a danger to the fetus.
- In the second trimester the likelihood of complications is reduced, and pregnancy proceeds smoothly.
- A new round begins after the thirtieth week of pregnancy. This period is the most dangerous and a woman may begin to develop gestosis or other pathologies.

Diagnosis of thrombophilia
It is very difficult to determine thrombophilia through examination, despite the fact that a woman may complain of heaviness in her legs or physical exhaustion. Therefore, there is a special expensive diagnosis. According to statistics, thrombophilia is diagnosed in a small percentage of women, so it is irrational to examine every woman. It is for this reason that a woman learns about the presence of complications only after an unsuccessful pregnancy.
There are a number of indicators that indicate the presence of thrombophilia:
- the presence of genetic thrombophilia in relatives;
- miscarriages;
- complications and pathologies in previous pregnancies;
- hemorrhage into the skin of a newborn baby.
Thrombophilia can be diagnosed by doing a blood test. This analysis takes place in two stages:
- The first stage includes blood screening, with the help of which the link in which the disorder occurs is detected.
- The second stage includes complete blood count, which helps to identify pathology during pregnancy.
Only through screening will a specialist be able to obtain information about the woman’s condition.
It is necessary to prevent the development of thrombophilia even before conception. Treatment at the stage of pregnancy planning will help conception succeed. If you start treatment at a later stage, it will be difficult to carry the child to term without pathologies. To give birth healthy child a woman must follow strict rules:
- It is necessary to control foci of infection, which are located in the mouth and genital area. If there is an inflammatory process, then the process of blood clots may begin.
- Taking special medications which lead to inhibition of blood clotting.
- Treatment with anticoagulants throughout pregnancy, as well as for a certain time after childbirth.
How to give birth to a healthy baby with thrombophilia?
Planning pregnancy with thrombophilia is only possible if the woman is under the supervision of specialists. During pregnancy itself, doctors pay great attention to the woman’s condition and the development of the fetus. Throughout pregnancy, women should undergo constant ultrasound examinations, as well as monitor placental circulation. Only with the help of total control is it possible to diagnose the presence of complications on early stages.
Already in the second and third trimester, doctors monitor the condition of the fetus using methods such as fetometry and cardiotocography. In order to avoid complications, a woman should undergo antithrombotic therapy. Such prevention can be considered successful if the expectant mother does not have a risk of developing pathologies:
- gestosis with complications;
- thrombosis;
- placental abruption;
- risk of miscarriage.
As a result of therapy, all indicators return to normal and pregnancy proceeds without deviations.

Treatment of thrombophilia
Concepts such as thrombophilia and pregnancy planning, if they are interrelated, require the following treatment:
- wearing an elastic bandage and compression garments;
- avoiding prolonged standing or sitting;
- massage;
- swimming;
- phytotherapy;
- proper nutrition;
- electromagnetic therapy.
Complications of thrombophilia
Often, during treatment, women experience side effects from taking medications. There is increased formation of blood clots in the vessels. Especially strong side effects have contraceptives that contain estrogen and heparin preparations.
In order to avoid side symptoms, doctors write a prescription for drugs that mitigate side effects. For example, acetylsalicylic acid has such properties. The specialist regularly monitors the woman’s coagulogram in order to avoid the development of early complications during pregnancy.
Thrombophilia and pregnancy planning are far from mutually exclusive concepts. Many women often associate this diagnosis with infertility, but this is not the case. If you completely follow the treatment program, which a specialist will help you draw up individually, then giving birth to a healthy child is quite possible.
There is a high probability that a woman who has thrombophilia will give birth prematurely. But modern medicine works wonders and premature babies are not inferior in development to babies born on time. With the help modern technologies premature babies quickly reach normal indicators characteristic of children born after 9 months.
As you may have noted, thrombophilia and pregnancy planning are compatible concepts if the expectant mother approaches pregnancy responsibly and believes only in the best.
Thrombophilia is a disease that was discovered quite recently, so experts are still working on studying it. This pathology poses a particular danger to pregnant patients. While carrying a child, a woman’s body weakens and loses the ability to fight pathologies. Qualified specialists advise that before planning a pregnancy, be sure to be examined in order to prevent unwanted reactions of the body that harm both mother and baby.
How dangerous is the predisposition to blood clots during pregnancy? What methods of diagnosing thrombophilia are the most effective?
The concept of thrombophilia and its consequences during pregnancy
Thrombophilia is a pathological condition of the body, accompanied by an increased tendency to develop blood clots. Normally, the activity of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems in the circulatory mechanism should be in the correct balance. The diagnosis is made when the factors of one of the systems are significantly weakened. Often, at an early stage of development, the disease is asymptomatic and is diagnosed purely by chance, for example, during injuries, surgical operations, during pregnancy.
One of the features of the “interesting position” is the increase in blood clotting to potentially compensate for blood loss during childbirth, preventing placental abruption and loss of the child. Increased coagulation rates are the first cause of blood clots.
Women who are prone to increased blood clot formation, or patients who were diagnosed with thrombophilia before pregnancy, should carefully listen to any changes in their body. They can carry and give birth to a healthy baby, but despite this, they are at risk of developing various complications in the 1st and 3rd trimesters, especially if blood clots form in the vessels adjacent to the place where the fetus is located. Thrombophilia in the expectant mother proceeds very smoothly, in the early stages it is generally asymptomatic. The consequences of thrombosis for pregnant girls include:
- regressing pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis;
- placental abruption or insufficiency;
- premature labor;
- stillbirth;
- pathologies of child development.
Causes of pathology
Dear reader!
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to know how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free!
Symptoms of thrombophilia and the degree of their manifestation depend on various factors - age, physical condition, etc. During pregnancy, the patient may be bothered by absolutely all signs of the disease. In pregnant girls they manifest themselves to the highest degree. This occurs due to the appearance of a third circle of blood circulation (placental) in the expectant mother, which causes congestion in the blood circulation. There are no capillaries in the mother's placenta, so blood immediately penetrates from the arteries into the placenta, where it flows between the chorionic villi, flowing into the umbilical cord.
IN recent years the number of people suffering from congenital thrombophilia has increased. Hereditary factors:
- Protein C deficiency. Impaired synthesis of anticoagulants, which include protein C, can cause excessive thrombus formation.
- Weakened factor in the coagulation system. Progression of the disease can occur against the background of blood clotting pathology.
- Genetically determined lack of antithrombin. This substance is one of the anticoagulants, but, unlike protein C, its deficiency can be either congenital or acquired.
- Gene mutation. In this case, the child, while still in the mother’s womb, due to a primary mutation, receives genes that provoke the development of the disease.
In addition to hereditary factors, thrombophilia can be caused by acquired causes. These include:
- autoimmune diseases;
- dysfunction of the cardiovascular system;
- dehydration caused by polycythemia;
- oncological pathologies;
- prolonged use of catheters;
- living in an environmentally unfavorable area.
Types of thrombophilia and accompanying symptoms
Doctors classify thrombophilia by etiology:
- Primary - genetically determined. The first symptoms appear in childhood.
- Secondary - acquired. The patient usually finds out about it by accident during an unscheduled examination.
The following types of thrombophilia are also distinguished:
- Hematogenous. It develops as a result of pathologies developing in the coagulation system. With hematogenous thrombophilia, the risk of developing dangerous conditions such as heart attack and ischemia increases.
- Vascular. The development of the disease is associated with pathologies accompanied by vascular damage, for example, atherosclerosis.
- Hypodynamic. In this case, the pathology can be caused by impaired blood flow.
Signs of thrombophilia appear long after the onset of its development. Main symptoms:
- pain and swelling at the site of thrombus formation;
- shortness of breath and pain in the chest when inhaling;
- cough with bloody discharge;
- numbness of the limbs;
- increased heart rate;
- unnatural fatigue;
- weakness;
- frequent headaches;
- slow response to current events.
All of the above signs can bother the patient with other diseases. A pregnant woman should remember the need to make an accurate diagnosis only after a series of diagnostic measures.
Diagnosis of the disease during pregnancy
Confirmation of the diagnosis of thrombophilia is carried out after the patient has undergone examination. Diagnosis of the disease involves taking a blood test twice. For the first time, the study is carried out as part of a screening test. In this case, a specialist can detect the localization of pathology in the coagulation system even in a nonspecific blood test. The second time, the patient must undergo a series of specific tests to clarify the diagnosis of thrombophilia.
A nonspecific blood test can identify a number of disorders that may indicate the development of thrombophilia:
- increased blood density;
- increased concentration of platelets and red blood cells;
- imbalance in the volume of formed elements in plasma;
- decreased erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
If the listed symptoms are detected, the pregnant woman is referred to a specialist. The hematologist usually prescribes specific tests to diagnose parameters such as aPTT, thrombin time and prothrombin index, as well as fibrinogen content.
Features of the treatment of thrombophilia in pregnant women
Treatment of thrombophilia in pregnant patients requires urgency. Ideally, therapy should begin long before pregnancy is planned. If the disease was detected during pregnancy, 3 highly specialized specialists - a gynecologist, a hematologist and a geneticist - will take part in drawing up a course of treatment. Therapy for thrombophilia requires an integrated approach. In order to achieve effectiveness, doctors recommend that patients in the position:
- take prescribed medications;
- eat according to the diet prescribed by your doctor;
- engage in physical therapy;
- be constantly on the move.
Thrombophilia is a disease that allows patients with this diagnosis to bear and safely give birth to a healthy baby, provided that all recommendations of highly specialized specialists are followed.
A pregnant woman must be responsible for her own well-being and the health of her child. A pregnant woman must regularly see a gynecologist, hematologist and geneticist. If suspicious symptoms appear, the patient must notify the doctor.
Drug therapy
Therapy depends on the severity, form of thrombophilia and stage of pregnancy. If a woman has genetic thrombophilia, then treatment should begin when planning pregnancy or in its early stages. It is impossible to achieve a complete recovery in patients with genetic thrombophilia, however drug treatment helps stabilize the pregnant woman's condition. Replacement therapy for them includes injections with drugs that replenish the missing elements of the coagulation system, or the administration of plasma with a dropper.
Treatment of the acquired form with anticoagulants is carried out only when more than 3 threatening factors are combined. An expectant mother with the acquired form is usually prescribed the following medications:
- acetylsalicylic acid;
- drugs with heparin - Dalteparin, Fraxiparin;
- folic acid;
- nicotinic acid;
- vitamins B and E.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating as many blood clots as possible. The drug course of treatment lasts from 2 to 4 weeks. In some cases, drug therapy is necessary for patients for life. Treatment is canceled several days before delivery or cesarean section. It is much easier for doctors to stop a pregnant woman from taking the drug if she has a planned cesarean section.
During natural delivery, a woman is hospitalized several weeks before the expected date of birth in order to monitor her condition after discontinuation of medications.
Three days after completing the medication course, the pregnant woman is sent to undergo all necessary tests. If the main blood and urine parameters increase, gynecologists, taking into account all the risks, decide on artificial childbirth.
Diet food
Complex therapy for thrombophilia also includes adherence to a strict diet. Patients should diversify their diet healthy products which help thin the blood. The diet for thrombophilia includes greens, ginger, seafood, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as dried fruits. Basic nutritional rules for patients diagnosed with thrombophilia:
- maximum limitation of fried and spicy foods;
- eliminating herbs and spices from the diet;
- eliminating foods rich in cholesterol.
Plasma transfusion
Blood plasma transfusion is another method of treating thrombophilia in pregnant women. If the patient’s disease is mild, she can be helped by intravenous injections with lyophilized plasma or dried donor blood. In severe forms, fibrinolytic agents are added to the plasma medicines. Injections are made into the place where the blood vessel is blocked.
Folk remedies
The use of folk remedies must be agreed with the attending physician. All of them become effective only in combination with medications, the dosage of which must be determined only by a gynecologist. Effective folk remedies, helping to eliminate blood clots and stabilize the condition of a pregnant woman without the risk of developing unpleasant consequences:
- tea drink made from cranberries or meadowsweet;
- grape juice;
- infusions of various herbs and their seeds - sweet clover, horse chestnut or Japanese sophora.
Tea, as a rule, should be consumed several times a day, half a glass. Infusions are prepared in the proportion of 100 g of seeds or herbs per 0.5 liter of alcohol. The duration of their infusion is 14 days. At the end of the above period, the broth must be decanted. The dosage of the finished infusion is 20 ml 3 times a day.
Possible complications
A predisposition to the formation of blood clots is a dangerous condition that is fraught with complications. Delayed or ineffective treatment, non-compliance with diet are the main prerequisites for the development of unpleasant consequences. These include:
- ischemia;
- gangrene;
- regressive pregnancy if the affected vessel is located close to the placenta;
- necrosis of intestinal tissue;
- an inflammatory process affecting the entire abdominal cavity.
Women planning a pregnancy must approach the issue of diagnosis very responsibly in order to avoid unpleasant complications in the future. Proper nutrition, including products that dilute the lymph, good sleep, walks in the fresh air, avoiding psycho-emotional stress - the main measures to prevent such a dangerous condition as thrombophilia.
Diseases, since her immunity is significantly reduced. Therefore, doctors always strongly recommend that expectant mothers, if they have chronic diseases in their bodies, plan pregnancy. This means thorough medical examination and identification possible problems with the aim of healing them, preparing the body to bear a child. After all, during pregnancy it will be difficult to treat diseases due to negative influence drugs for the fetus. So, what is the threat? to the expectant mother thrombophilia? What kind of disease is this and how to treat it for pregnant women?
Briefly about thrombophilia
Thrombophilia is a disorder in the body that causes it to develop a tendency to form blood clots (blockages). The disease can be caused by genetic failures or failures physiological nature. The disease manifests itself in different ways. Very often, it does not make itself felt at all, and in the event of injury, surgery, or pregnancy, dangerous health problems can arise due to this disorder.
There are several types of thrombophilia. It can be acquired or hereditary (congenital). Acquired occurs as a result of injuries and operations, and hereditary is transmitted to a person by inheritance or appears as a result of various mutations. In the latter case, doctors talk about disorders at the genetic level.
In addition to the above division of thrombophilia, depending on the causes of occurrence, there is another classification of the disease:
- Hematogenous thrombophilia. This type of it is the most dangerous, and especially for pregnant women. It can lead to disability or death.
- Vascular thrombophilia. This type includes atherosclerosis and vasculitis.
- Hemodynamic thrombophilia is associated with disorders in the circulatory system.
What are the risks of thrombophilia during pregnancy?
It often happens that genetic thrombophilia first manifests itself during pregnancy. This is due to the emergence of the third circle of blood circulation - the placental. It puts additional stress on the circulatory system. The placental circle also has features that promote the formation of blood clots. The placenta is generally devoid of capillaries, and the mother’s blood immediately enters the placenta, where it flows between the chorionic villi and then enters the umbilical cord.
A feature of the pregnant woman’s body is an increase in blood clotting. This is due to the need to reduce blood loss during childbirth or other complications (placental abruption, miscarriage). But increased clotting increases the risk of blood clots. And in the case of a congenital type of thrombophilia in the expectant mother, this risk is already quite high.
In most cases, thrombophilia is not dangerous for women, but when pregnancy occurs, everything changes. The risk of thrombosis in such women increases 5-6 times! And the main danger is possible, which with thrombophilia can occur both during a short period of pregnancy and in the third trimester. If a woman with thrombophilia manages to carry a baby to term, the birth usually occurs ahead of schedule. This may be between 35 and 37 weeks. This outcome is generally considered favorable.
In addition, blood clots in the vessels of the placenta can provoke placental insufficiency. And this, in turn, can lead to delayed fetal development and oxygen starvation ().
In this case, the body of the unborn baby stops receiving nutrients, which results in placental abruption and fetal malformations, fading pregnancy and miscarriages, and premature birth.
Doctors state that complications appear after 10 weeks of pregnancy. Before this period, there is no data on the effect of thrombophilia on childbearing. It is believed that this disease does not affect pregnancy up to 10 weeks.
The second trimester of pregnancy for a woman with thrombophilia is usually calm. And the risk increases after 30 weeks. During this period, phytoplacental insufficiency and severe forms of gestosis often develop.
Diagnosis of thrombophlebitis
Unfortunately, this diagnosis is very difficult. After all, the symptoms of the disease are similar to those of varicose veins. This is heaviness in the legs and fatigue, pain in the lower extremities. In addition, diagnostic methods are expensive. There is no point in carrying out such a diagnosis on all pregnant women, since thrombophilia occurs only in 0.1-0.5% of people.
For this reason, women often learn about their diagnosis after an unsuccessful pregnancy or several such pregnancies, subject to supervision by a qualified and experienced specialist. That is why you should pay special attention to the choice of your attending gynecologist.
What can make a doctor be wary and suggest that his patient take tests for thrombophilia? This could be several factors:
- Miscarriage. The term refers to the experience of two or more pregnancies in the past that did not result in childbirth. This includes the fading of the child’s development, miscarriages, premature birth, and death of the baby.
- The presence of complications in previous pregnancies: placental insufficiency and placental abruption, severe forms.
- Formation of blood clots during hormonal contraception.
- The presence of thrombotic complications in the woman’s relatives.
- She herself has such complications.
- Several IVF attempts that ended in failure.
If the doctor has identified one of these factors, then this is the basis for sending the woman for a consultation with a specialist (gemologist or geneticist) for additional examination to make a diagnosis of “thrombophilia”. This examination is multi-stage and includes a number of tests and screenings.
Treatment of thrombophlebitis in an expectant mother
If, after examinations, a woman is diagnosed with this, then the doctor prescribes treatment immediately, without delay. The course of therapy is prescribed jointly by a gemologist, geneticist and gynecologist. It usually consists of drug therapy, diet and regimen. Doctors' orders should be strictly followed.
Drug therapy includes anticoagulants. These are drugs that reduce blood clotting. All of them are prescribed strictly on an individual basis, and there is no universal medicine that would be equally suitable for all women.
The diet of a pregnant woman with thrombophlebitis includes foods that reduce blood clotting. Such products include dried fruits and seafood, berries and ginger.
As for the regimen and other prescriptions, doctors recommend practicing slow, systematic walking and swimming, as well as physical therapy. You need to wear compression garments and practice self-massage. It is highly discouraged for pregnant women with thrombophilia to stand for long periods of time. And if such a woman’s work involves a long standing position, then it is better to think about how to avoid this. Perhaps you need to talk with management about changing working conditions or transferring to another position. Another taboo for such a woman is lifting and carrying heavy objects.
All therapeutic and preventive measures help improve blood flow and prevent the formation of blood clots.
We must not forget that pregnancy in women with thrombophilia must proceed under the careful and systematic supervision of doctors. Such a future mother will need to regularly visit not only her gynecologist, but also a hemologist.
So, thrombophilia is not a death sentence and is not synonymous with infertility. If you strictly follow all medical recommendations, the chances of carrying and giving birth to a healthy child are very high. Of course, you also need to take into account the fact that it is unlikely that you will be able to carry your baby to 40 weeks. But childbirth at 35-37 is considered a good result. Premature baby At the level of today's medicine, this does not at all mean a sick child. Modern medical technologies and equipment make it possible to care for children who were born at an earlier stage.
Therefore, the expectant mother needs to remember the risks every day, follow her doctor’s orders and be optimistic.
If a woman has thrombophilia, it is very important for her to plan her pregnancy. Treatment of thrombophilia with such planning differs little from treatment after conception. However, the advantage of this approach is prevention. After all, preventing the development of problems is always much easier than solving them after they appear.
Especially for Elena TOLOCHIK