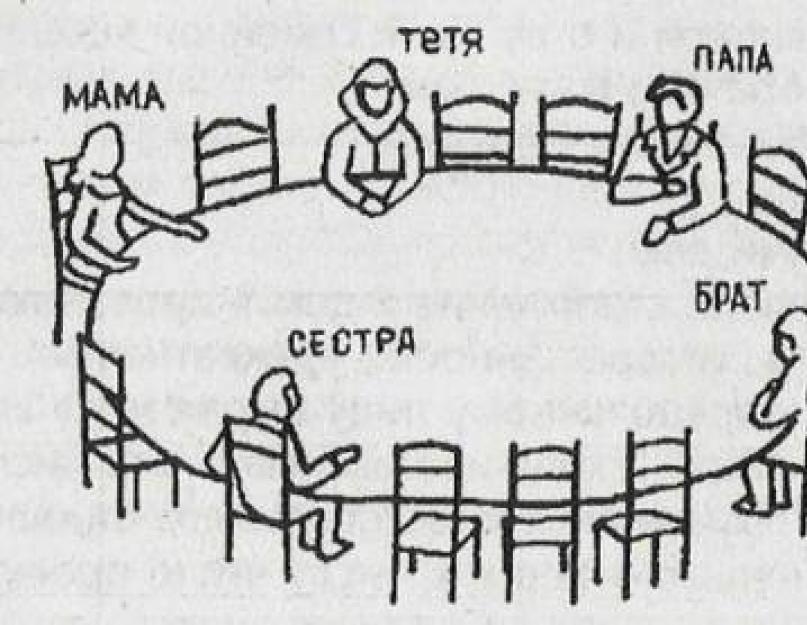
n1.DOC.
Family of animals
Purpose: The test is designed to identify features of intra-day relationships. He will help clarify the child's relationship towards members of his family, how he perceives them and its family role, as well as the characteristics of relationships that cause a disturbing and conflict feelings.When examining adults, this test is often more informative than the tests of the Family Drawing and the Dynamic Family Figure. Like the test "Family drawing", it is available to children from four years old.
Testing. The sheet of paper is placed in front of the surveyed horizontally. Instructions: "Draw a family consisting of animals so that all family members were different animals." It can be explained that we are talking about a fabulous family, since in fact the animal animals are consisting of identical animals.
The examined does not say that an image of his own family is supposed. On the contrary, the instructions should be drawn some abstract family. However, the associations of the surveyed are still determined by its self-sustaining in their family.
The survey can say that it does not know how to draw animals. Then he explains that it is not scary, and if it is not clear who he painted, he will say who it is, and the verifier will write down. After the end of the drawing, the verifier finds out what animals are these and who they are in the family (who is what family member). Answers are fixed in the protocol. Asking questions, it is impossible to utter the words "Mom", "Dad", "Child", "Grandma" and others. It is necessary to use a neutral phrase "family member".
Discuss the drawing just like in the Family Drawing Test.
If the examined "closes" from the verifier, then the test "family of animals" often turns out to be more important than the tests "Family Drawing" and "Dynamic Family Figure", since its focus is less obvious. It can be used instead of the dough "Family Family" or in combination with it for additional data.
There are cases when in the Drawing Family Dash, the surveyed reproduces real family relationships, and in the test "animal family" - idealized (such as he would like to see them). The reverse relation: To make a favorable impression, the examined is depicted in the Drawing Distribution of the Family. The meaningful analysis of the figures allows you to establish which option takes place in each case.
Interview "Magic World"
Projective technique.
Purpose: Studying needs, meaningful experiences and child problems. It is a half-ended interview in which the overall "logic" (KANVA) of asked questions is scheduled.
The first part of the diagnostic complex can be attributed to the catharsis method. In an interview, the child is invited to identify himself with an almighty wizard who can do everything that wants, in a magical country and in our real world: to turn into any creature, in any animal, become a small or adult, the boy becomes a girl and vice versa, etc. . In the course of an interview, identification with an almighty wizard weakens, and at the end of the interview the psychologist brings the child from the role of a wizard.
The survey is recommended to be held alone with the child. Answers to interview questions should be recorded literally. It is not recommended to use a tape record, as it can make tension in communication, cause a feedback, stiffness of the child, distract it from the conversation content. In turn, emotional contact with the child during the interview is necessary to transition to the further phase of diagnostic work or to psychocorrection. After each response, the child should ask why he would do something or another would turn into someone, etc.
This technique is a convenient tool to establish contact with the child, allowing him to survive in the game many of many significant moments for it. This is the psychotherapeutic effect of this technique.
Text technique.
Do you like fairy tales? Little children always love fairy tales. Of course, you are no longer small ("But, I think you will like such a few fabulous game.
Imagine that you have a magic rocket that has transferred you to a fabulous country. There is everything, as in a fairy tale: and people fabulous, and you too. Can you imagine this?
A. - And now tell me, who would you like to be in this fabulous country? Why?
B. - Who would you like to be in a fabulous country? Why? We are detaining here for a minute. Now imagine that you are a wizard (Fairy): You are very strong, with the help of magic you can all you want. You can create, change, fold, make it so that anything completely disappeared.
So tell me, the wizard, what would you do? And for what? You are still a wizard (fairy). You sit in the rocket and come back, in the usual world. First of all, let's go to your home - imagine it.
Now you have at home. You are an almighty wizard, what would you do? (Additional questions: for dad, for mom, etc.).
Then the wizard goes to school.
In your power to do something, change, destroy, do the way you want.
Now you're at school. What would you do? (Additional questions: for teachers, classmates?). Why?
Now you are a wizard, play with the guys. What would you do for them? Why?
I almost forgot about you!
A. - What would you do for yourself? Why?
B. - What would you change or destroyed? Why?
And for me, the wizard, what would you do? Why?
Thank you, you are a real wizard!
If you became a wizard, you could make any kind of appearance, would turn into someone or what you want.
A. - Tell me what or who would you like to turn into? Why?
B. - And what or who you would never want to turn into? Why?
You can turn into any animal.
A. - Would you like animals to become? Why?
B. - And what animals do you want to be? Why? Of course, you know many animals and beast. I will call you different animals, and you will talk, I would like to become someone from them or not, and why.
A) cat,
C) small goats, deer,
G) a monkey
K) Dog,
L) bird (for example, tit).
You coped perfectly with the task.
You are a wizard, you have great opportunities, you can choose one of three: to become a small child, an adult or stay as you are.
A. - Tell me who you want to be a little, adult or like there? Why?
B. - Why don't you want to become ... (1 not selected option)?
V. - And why ... (2nd not selected option)?
Would you like to become a girl (boy)? Why?
You coped perfectly with the task, but each game ends, and our too. And now you are not a wizard again, but (name, surname of the child).
And by the way, do you like your name? I do not like? Why? And surname? I do not like? Why? Would you like to be called something different? Why? And what do you call your parents, friends in class guys?
Very good, let's imagine (only it will not be a fabulous game) that all your desires are performed, any, but only 3.
And why and, b, in?
Excellent. And think:
A. - What are the most afraid of children? Why?
B. - What gives children the greatest joy? Why?
V. - What brings them the greatest chagrins? Why?
Well done! What did you like most in the game?
Interpretation.
The interpretation of the data is largely based on the answers of the child to questions "why", "Why", since children speak of them about their needs, meaningful experiences. Another basis for interpretation is a meaningful analysis of the answers, which allows you to deepen the idea of \u200b\u200bthe child's experiences and the real everyday situation. Non-verbal manifestations also give a lot of information for a psychologist practice. It is according to them that one can judge the depth of the experiencing of the child, subjective significance of certain problems that he mentions. Finally, interesting results gives a formal analysis of statements: their length, exploration, vocabulary, grammatical construction can confirm or cast doubt on the assumptions arising during the interpretation of the results.
In general, when interpreting results, it should be borne in mind that the identification of a child with a wizard is asked by the instruction and, therefore, is conscious, as a result of which the child's statements may be subject to socially approved responses, i.e. The desire to show yourself in the best light.
"Completion of the Offer" Methods for Children
(V. Mikhala variant)
Purpose:Projective method of research research. The test refers to the methods of supplement and partly to associative methods and is aimed at diagnosing a child's relationship to parents, brothers, sisters, child informal and formal groups, teachers, school, their own abilities, as well as to identify the goals, values, conflicts and significant experiences . Provided by V. Mikhal, a sequence of 24 sentences is a modification of the SAKS test (SSCT) for children.
This test can be applied by itself, but the author of the methodology recommends applying it after the interview with the "Magic World". All child answers should be recorded literally.
The test version presented here is slightly changed in comparison with the Russian translation of the original. Stylistic translation errors have been eliminated and the procedure for proposals has been changed.
Instruction.
Every morning...
Many authors, including Michal, recommend to fix the reaction time with the help of the stopwatch. At the same time, it can make an excessive nervousness into communication with a psychologist and distract the child. Therefore, it is better to use the clock with a second arrow, making it unnoticed while the child thinks about the answer, count about himself 3 s. And put the point in the protocol after each such interval. The test must be carried out individually and only orally.
The presented list of sentences are grouped by the diagnostic focus on the study of the child's relationship towards various persons and various problems - to mother, father, brothers, sisters, peers; to school, teachers; form for the future, etc. The sequence number before the start of each sentence corresponds to its place in the list, offered for diagnostic use. The order can be changed, but so that the proposals on one topic are evenly distributed, and not grouped together.
Instruction.
I can offer you this game. I will call you the beginning of the sentence, and you - finish it.
Now - Attention! You need to answer quickly and every time that it will come to mind first, but so that the proposal completed by meaning. Before start the game, you can practice slightly. For example, I say the beginning of the sentence:
Every morning...
Praise the child, tell me that he understood everything correctly, and if it seemed that he said, not the first end of the sentence, which came to his head, remind him of the instruction again. You can offer another example:
Much would give me to ...
If necessary, explain the rule again.
Stimulus material.
1. I think people are more ...
2. Child in the family ...
3. We love mom, and ...
4. We are among children, but ...
5. My brother (sister) ...
6. I am quite agile to ...
7. Fathers sometimes ...
8. The children with whom I play ...
9. What would our dad ...
10. My close thinking about me that I ...
11. If my brother (sister) ...
12. My friends me often ...
13. I want me to ...
14. Sick child ...
15. I thought my mother most often ...
16. If there were no school ...
17. I'm all shaking when ...
18. When I think about school, then ...
19. If all the guys knew, as I am afraid ...
20. Would be very happy if I ...
21. I am the weakest ...
23. My teacher (teacher, teacher) ...
24. Always dream ...
Key.
Proposals in the methodology are grouped into the following categories:
A) attitude to the mother - 3, 15;
B) attitude to Father -7.9;
C) attitude towards brothers, sisters - 5, 11;
D) family attitude - 2, 10;
E) attitude to peers - 4.8, 12;
E) attitude to teachers and school - 23, 16, 18;
G) attitude towards people as a whole - 1;
H) attitude to its own abilities - 6, 21;
And) negative experiences, fears - 13, 17, 19;
K) attitude to the disease - 14;
L) Dreams and plans for the future - 20, 22, 24.
Interpretation.
The basis of interpretation is a meaningful analysis of the answers, the frequency of an additional part of the sentence, the response time, as well as the statements of the child about how the proposed phrases correspond to reality (according to our data, children speak quite often).
The social position of the child is investigating proposals aimed at studying his relationship to the group of peers, teachers, parents and family members. It should be noted that cases where there are signs of tensions, conflict in all the end of the phrases of this group, the psychological practice of psychologist, since deadaption in all spheres of interpersonal relations is the symptomal of anomalous personality development. The author of the methodology, after Sax, recommends putting points on answers (2 points - serious violations that require psychotherapy, 1 point - moderate violations).
The child's self-imminent is studied using proposals aimed at studying significant child experiences, an assessment of their capabilities, as well as reflexive self-esteem formed by the beginning of adolescence. So, the answer is a 12-year-old child: "I don't know what I think about myself" on the proposal: "My lovers think about me that I ..." indicates the delay of the formation of reflexive assessment, but may be a manifestation of psychological protection. In this case, the proposals for family members will have neutral emotional color or contain signs of conflict. The example above shows how, firstly, the same answer in a different context may mean different features of the identity of the child and, secondly, as a proposal can be confirmed or refuted on the basis of the same test of unfinished proposals.
To interpret individual proposals, they are grouped into the following categories:
A) attitude to mother;
B) attitude to the father;
C) attitude towards brothers, sisters;
D) family attitude;
E) attitude to peers;
E) attitude to teachers and school;
G) attitude towards people as a whole;
H) attitude to its own abilities;
And) negative experiences, fears;
K) attitude to the disease;
L) dreams and plans for the future.
Method "Unfinished proposals" (Saksa-Levi test)
The variant of this method developed by Sax and Levi includes 60 unfinished proposals, which can be divided into 15 groups characterizing a system of relations to a family examined to the family, to representatives of their or the opposite sex, to sexual relations, to the supervisory position and subordinate. Some groups of proposals are related to a person experienced fears and concerns, to the sense of awareness of their own guilt, indicate its attitude to the past and future, affect relationships with parents and friends, their own life goals.
For each group of proposals, a characteristic is displayed that defines this system of relations as positive, negative or indifferent.
This technique needs to be confirmed by other tests, as its reliability and validity of it is small, which is associated with a small number of proposals, "working" on one scale.
Key
| N p / n | Groups of proposals | NN tasks |
|||
| 1 | Attitude to Father | 1 | 16 | 31 | 46 |
| 2 | Attitude towards me | 2 | 17 | 32 | 47 |
| 3 | Unrealized opportunities | 3 | 18 | 33 | 48 |
| 4 | Attitude to subordinates | 4 | 19 | 34 | 49 |
| 5 | Attitude to the future | 5 | 20 | 35 | 50 |
| 6 | Attitude to higher persons | 6 | 21 | 36 | 51 |
| 7 | Fears and fears | 7 | 22 | 37 | 52 |
| 8 | Attitude towards friends | 8 | 23 | 38 | 53 |
| 9 | Attitude towards your past | 9 | 24 | 39 | 54 |
| 10 | Attitude to the persons of the opposite sex | 10 | 25 | 40 | 55 |
| 11 | Sexual attitude | 11 | 26 | 41 | 56 |
| 12 | Relationship to the family | 12 | 27 | 42 | 57 |
| 13 | Attitude towards employees | 13 | 28 | 43 | 58 |
| 14 | Attitude towards mother | 14 | 29 | 44 | 59 |
| 15 | Guilt | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 |
Such a quantitative assessment facilitates the identification of a disharmonic relationship system. But more importantly, of course, a qualitative study of additional proposals.
The study of the "unfinished sentences" should precede the establishment of contact with the surveyed for obtaining sincere, natural responses. But even if the test examines the study as an undesirable procedure and, seeking to hide the world of its deep experiences, gives formal, conditional answers, an experimental psychologist can extract a mass of information reflecting the system of personal relationships.
Method "Unfinished sentences"
Blank tested ____________________________________________
Instruction:"On the dough form you need to complete proposals with one or more words" .
1. I think my father is rare
2. If everything is against me, then
3. I always wanted
4. If I used to manage
5. The future seems to me
6. My bosses
7. I know that it is stupid, but I'm afraid
8. I think that a true friend
9. When I was a child
10. Ideal Women (Men) is for me
11. When I see a woman next to a man
12. Compared to most of the other my family
13. It works best for me with
14. My mother and me
15. I would do everything to forget
16. If my father only wanted
17. I think that I am quite capable to
18. I could be very happy if
19. If anyone works under my leadership
20. I hope on
21. My teachers at school
22. Most of my comrades do not know that I am afraid
23. I do not like people who
24. Once upon
25. I think that most young men (girls)
26. A married life seems to me
27. My family draws me as with
28. People with whom I work
29. My mother
30. My biggest mistake was
31. I would like my father
32. My greatest weakness is
33. My hidden desire in life is
34. My subordinates
35. The day will come when
36. When my boss is approaching me
37. I would like to stop afraid
38. Most of all love those people who
39. If I had become young again
40. I believe that most women (men)
41. If I had a normal sex life
42. Most families known to me
43. I love working with people who
44. I believe that most mothers
45. When I was young, I felt guilt if
46. \u200b\u200bI think my father
47. When I start not to take, I
48. Most of all I would like in life
49. When I give another order
50. When will be old
51. People whose superiority on themselves I admit
52. My fears more than once made me
53. When I do not, my friends
54. My most lively childhood memories is
55. I really do not like when women (men)
56. My sex life
57. When I was a kid, my family
58. People who work with me
59. I love my mother, but
60. The worst thing I happened to do is
Methodology Rena Gila
For the study of the scope of interpersonal relations of the child and his perception of intrameal relations, a children's projective method of Rena Gillee is intended. The purpose of the methodology is to study the social adaptability of the child, as well as its relationship with others.The technique is visual-verbal, consists of 42 pictures with the image of children or children and adults, as well as text tasks. Her focus is to identify behavioral features in a variety of life situations, important to the child and affecting its relationship with other people.
Before you start working with the method of the child, it is reported that answers are waiting for questions about pictures. The child considers drawings, listens or reads questions and responds. The child must choose a place among those depicted people, or identify himself with a character who occupy one or another in the group. He can choose it closer or further from a certain person. In text tasks, the child is invited to choose a typical form of behavior. Thus, the methodology allows you to obtain information about the child's attitude to different people around it (to the family surrounding) and phenomena.
Simplicity and schematics that distinguish the method of R. Gille from other projective tests, not only make it easier for the test child, but make it possible to relatively greater formalization. In addition to the qualitative assessment of the results, the children's projective methodology of interpersonal relations allows you to present the results of a psychological examination for a number of variables and quantitatively.
Psychological material characterizing the child's personal relationship system can be divided into two large groups of variables:
1) variables characterizing the child's specific personal relationships: attitude to the family environment (mother, father, grandmother, sister, etc.), attitude towards a friend or girlfriend, to an authoritative adult, etc.
2) variables characterizing the child himself and manifested in various respects: sociability, density, desire for dominance, social adequacy of behavior.
Total distinguished 12 signs:
- Attitude to the mother,
- Attitude to the Father,
- Attitude towards mother and father as a family couple,
- Attitude towards brothers and sisters,
- attitude to grandmother and grandfather,
- Attitude towards a friend,
- attitude to the teacher,
- curiosity,
- desire for domination,
- sociability
- density,
- adequacy.
The attitude to a certain person is expressed by the number of elections of this person, based on the maximum number of tasks aimed at identifying the corresponding relationship.
The method of R. Zhilil cannot be attributed to the number of purely projective, it is a transition form between the questionnaire and projective tests. This is its great advantage. It can be used as a tool of deep-studying personality.
Testing and then refer to the key to evaluate the results obtained.
Key
| № scale | Value of scale | Task numbers | General quantity tasks |
| 1 | Attitude towards mother | 1-4, 8-15, 17-19, 27, 38, 40-42 | 20 |
| 2 | Attitude to Father | 1-5, 8-15, 17-19, 37, 40-42 | 20 |
| 3 | Attitude towards mother and father as parental couple | 1-4, 6-8, 14, 17, 19 | 10 |
| 4 | Attitude towards brothers and sisters | 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8-19, 30, 40, 42 | 20 |
| 5 | Attitude towards grandmother and grandfather | 1, 4, 7-13, 17-19, 30, 40, 41 | 15 |
| 6 | Attitude towards friend (girlfriend) | 1, 4, 8-19, 25, 30, 33-35, 40 | 20 |
| 7 | Attitude to the teacher (authoritative adult) | 1, 4, 5, 9, 11, 13, 17, 19, 26, 28-30, 32, 40 | 15 |
| 8 | Curiosity | 5, 22-24, 26, 28-32 | 10 |
| 9 | Leadership | 20-22, 39 | 4 |
| 10 | Sociability | 16, 22-24 | 4 |
| 11 | Close, beardlessness | 9, 10, 14-16, 17, 19, 22-24, 29, 30, 40-42 | 15 |
| 12 | Social adequacy of behavior | 9, 25, 28, 32-38 | 10 |
Stimulus Material
Here is a table, followed by different people. Observe the cross, where you sit down.

Denate the cross where you sit down.

And now place several people and yourself around this table. Observe their related relationships (dad, mom, brother, sister) or (friend, comrade, classmate).

At the head of the table sits the man you know well.
Where would you sit?
Who is this person?

You, together with your family, will spend holidays from the owners who have a big house. Your family has already taken several rooms. Choose a room for yourself.
Once again at acquaintances. List the room of some people and your room.
It was decided to present a surprise one person.
Do you want to do it?
Who?
Or maybe you do not care?
Write below
You have the opportunity to leave for a few days to relax, but where you go, only two free places: one for you, second for another person.
Who would you take with you?
Write below.
You lost something that is very expensive.
Who will you tell me about this trouble?
Write below.
Your teeth hurt, and you have to go to the dentist to snatch the sick tooth.
Will you go alone?
Or with someone?
If you go with someone, then who is this person?
You passed the exam.
Who will you tell about it first?
Write below
You are walking outside the city. Denote the cross, where you are.

Another walk. Observe where you this time.

Where are you this time?

Now this figure is posted several people and yourself. Draw or mark crossbars.
Sign what kind of people

You and some other gave gifts. Someone received a gift much better than others.
Who would you like to see in his place?
Or maybe you do not care?
Write.
You are going to the long road, go far from your relatives.
Who would you give up the strongest?
Write below.
Here are your comrades go for a walk. Denote the cross, where you are.

Who do you like to play:
with your comrades of your age?
younger than you?
older than you?
Emphasize one of the possible answers.
This is a playground for games. Remarking where you are.

Here are your comrades. They quarrel on the reason unknown to you. Observe the cross, where you will be.

These are your comrades, quarreled because of the rules of the game. Remark where you are.

Comrade instructively pushed you and dumped from his feet. What will you do:
will you cry?
you complain to the teacher?
will you hit him?
will you make a remark?
would you say anything?
Stress one of the answers.
Here is a person, well known to you. He says something sitting on the chairs. You are among them. Obstimate the cross where you are.

Do you help your mother?
Few?
Seldom?
Stress one of the answers.
These people stand around the table, and one of them explains something. You are among those who listen. Remark where you are.

You and your comrades on a walk, one woman explains to you something. Obstimate the cross where you are.

During the walk, everyone is located on the grass. Remarking where you are.

These are people who look at an interesting performance. Obstimate the cross where you are.

A teacher shows table students. Obstimate the cross where you are.

One of the comrades laughs at you. What will you do:
Will you cry?
Find your shoulders?
Will you laugh at him?
Will you call him beat?
One of the comrades laughs at your friend. What you do:
Will you cry?
Find your shoulders?
Will you laugh at him?
Will you call him beat?
Stress out one of these answers.
Comrade took your handle without permission. What will you do:
Cry?
To complain?
Shout?
Try to take away?
Will you start to beat him?
Stress out one of these answers.
You play in the lotto (or in checkers, or to another game), and lose two times in a row. You're not happy. What will you do:
Cry?
Continue to play next?
Do you say nothing?
Will you get angry?
Stress one of these answers
Father does not allow you to walk. What will you do:
Do not answer anything?
Inflatable?
Will you cry?
Catch up?
Stress out one of these answers.
Mom does not allow you to go for a walk. What will you do:
Do not answer anything?
Inflatable?
Will you cry?
Catch up?
Let's try to go against the prohibition?
Stress out one of these answers.
The teacher came out and entrusted you supervision of the class. Are you able to fulfill this order? Write below.
You went to the movies along with your family. The cinema has many free places. Where do you sit down? Where are those who came with you sit down?

In the cinema a lot of empty places. Your relatives have already taken their places. Observe the cross, where you sit down.

Again in the cinema. Where will you sit?

Test animals Szzzo 1
Animal test is used to determine the main trends and values \u200b\u200bof the child 5-12 years. It is a set of questions that establish what animals the child would like to be, if he could turn into it, whatever he would like to become and why. At first, the child must have a spontaneous choice, and then express sympathy or antipathy for animals, the names of which reads the researcher. Each reaction is a child to justify (Table 7.10). Interpretation comes from "portraits of animals" and their polarity indices.
Table 7.10. Identification category with polarity animals
|
The modification of this test is a projective interview with the "Magic World", which, compiled by N. D. Ignatiev, we give 17:
Test "Magic World"
Instruction. Little children love fairy tales. Of course, you are no longer small, but I think you will like such a little fabulous game. Imagine that we have a magic rocket that moved us to the magic country. Everything is there as in a fairy tale: and people are fabulous, and you too ... You can imagine that.
1. Now tell me who you would like to be in this fabulous country 1 and why do you want to be ...? And who would not want to be in a fabulous country "Why?
We will be held at a minute in a fabulous country. Now imagine that you are a wizard (magician, fairy): you have a huge force, you can all want. You can create, change, fold or make something completely disappeared ...
2. So tell me, the wizard, what would you do? What for? For what?
You are still a wizard (fairy). We sit down with you in the rocket and come back, in the usual world for us. First of all, let's go to your home - imagine as much as possible.
3. Now you have at home. You are an almighty wizard. What would you do? And why? What for? What would you do for mom (dad, sisters, grandparents)?
Additional questions: What for? Why?
Then the wizard goes to school. In your power to create something, change or destroy, do the way you want.
4. Now you're at school. What would you do? And why? Why? What for? What would you do for the teacher? For classmates?
Additional questions.
Now you are a wizard, play with the guys.
5. What would you like for the guys? What for? Why?
I almost forgot about you.
6. What would you do for yourself? Why? What would you change or completely destroyed? Why? For what?
7. Well, for me, the wizard, what would you do? Why?
Thank you, the wizard, you are the real wizard.
If you were a wizard, I could make any kind of appearance.
8. Tell me what would you like to turn? or who? Why? And what or who you would not want to turn? Why?
You can turn into any animal.
9. What animals do you like to be the most? Why?
Of course, you know many animals and beast. I will call animals, and
you will talk, I would like to be such an animal or not (+, -, in brackets Motivation): Cat; a lion; Little goat, deer; snake; eagle; mouse; a monkey; tiger; hare; dog; bird, such as tit; worm.
You coped perfectly with the task.
You are a wizard, you have a lot of power ... You can choose one of three options:
□ Become a small child;
□ Stay as it is;
□ Become an adult.
10. Tell me, who would you like to be a small child, stay as it is, or become an adult? Why? What for? Why don't you want to become ...? Why? Why don't you want to become ...? Why?
11. Now tell me, would you like to be a girl or boy? Why?
You coped perfectly with the role of the wizard. However, each game ends, even a wizard playing. Now you are no longer a wizard, you again ... (F. I. O.)
12. By the way, do you like your name? (If not like, then why?) And the name? (If not, why?)
You are a very smart boy (girl). Let's try this, but this will not be a fabulous game. Imagine that your greatest desires are fulfilled, such as those who ever fulfill, or maybe such that are unlikely to ever be executed. Let it be your innermost desires. However, each game has its own rules, and our game has a rule: you can choose only three desires.
You perfectly coped with this question, and now think about the following:
13. What are the most afraid of children? What gives children the greatest chagrins?
Our game is over.
How did she like you? What did you like most?
Praise and ask the necessary questions.
Duration of testing - 25-30 minutes.
Interpretation of the results of the test "Magic World"
Approbation for 93 children (53 boys and 40 girls).
Who would you like to be?
Frequency (%) of the most common answers (Table 7.11, 7.12):
fabulous heroes ........................ 74.1
animals .................................... 11.8.
real faces ............................. 9.7
other options ........................ 2.2
i do not know ........................................... 2.2
Real faces: Mom, teacher, cook, captain, cosmonaut ... To evaluate stereotype, we use the coefficient expressed as a percentage, the relative frequency of the most common answers (inversely proportional to the originality indicator).
50-70% of the same responses are a high stereotype ratio. 30% - average stereotype coefficient. 19.4% - low stereotype coefficient.
Explanations are very diverse: reveal the motives of the child and are the basis of interpretation.
Who would not like to become? Frequency (%) of the most common answers (Table 7.13, 7.14):
fabulous heroes ..................... 62.4%
animals .................................... 8.6%
real faces ........................ 17.2%
Continentation has a large stereo coefficient (26.9%) and a greater frequency of real persons.
Real faces: servant, waitress, "bad person", cook, "man". Depending on the floor: the boys prefer the wizard, which can actively participate in the magic world, the girls - the princess.
Depending on the age: among girls, development trend is more distinct: with age increases the frequency of identification with a fabulous hero:
Ontogenetic profile:
girls ........................... 63% -86-90
boys ........................ 75% -64-85
Some responses have both positive and negative selection results (Princess), other only positive (cat) or only negative (snake).
The ratio of the difference in positive and negative elections to the total number of all elections of the same object is called the polarity index:
 |
where / is the number of identifications; K - number of content.
As follows from the formula, the polarity index can take any values \u200b\u200b- from 1.0 to -1.0. Positive values \u200b\u200bshow that positive elections prevail, negative - on the contrary. Boundary values \u200b\u200bhave the following psychological meaning:
1.0- Extreme positive object chosen by all respondents;
0 - an ambivalent object; - 1.0 - an extreme negative object excluded by all.
Polarity index for the first two test questions:
prince, Princess ................................ 0.8
king, Queen ................................ 0.6
wizard ...................................... -0.46
heck................................................ - 0.50
dragon ............................................. -0.82
cat................................................. . 1.0 ■ * ■
snake................................................. . - 1.0
The most important for interpretation are the answers to the question "Why?". The motives of choice are diverse: worried personality, determined by the position of the child. It is personal explanations that are useful for diagnostic conclusions, for example: Identification:
□ with the fairy ("makes other nasty");
□ with a cat ("Everyone can play with it");
□ with a child ("Maybe all the time with mom");
continiate:
□ with a dog ("One day I was bitten");
□ With a person ("Must die").
(Interpretation capabilities are given in a sequence of descending the number of coincident explanations (Table 7.15-7.21):
Prince, Princess (P \u003d 0,80):
a) the need to cause admiration, to be the center;
b) the desire for wealth, luxury, abundance;
c) the need to be noble, responsive;
d) the need to dominate, manage others (rejected as "bad" quality).
King, Queen (R ~ 0,69):
a) the need to dominate, organize, manage others, control, interfere (dominant, partially aggressive position):
b) the need to help, protect others;
c) The need to conquer, cause admiration, to be the center of attention (exposure or exhibition position; rejected due to "bad" qualities).
Wizard (R. = -0,46):
a) the desire for power, strength;
b) the need for creativity, ingenuity, activity;
c) the need to assist, protect others (protective position);
d) the desire for wealth, abundance (rejected because of the "bad" qualities, no other appearance, the hatred of people - the need for affiliation).
The dragon (P \u003d -0.82) is rejected due to cruelty, aggressiveness, ugly type, the choice of a dragon is an indicator of insecurity, aggressiveness or other violations.
Replies options: "I would turn the whole world inside out", "would have turned a person in a stone," "so that people do not quarrel", "so that I don't have glasses", "so that no one is dying."
| Table 7.15. What would you do? (absolute frequency) |
For additional questions, most often choose: for mom:
□ Clothing items ......................................... 35.5%
□ Municipal equipment ....................... 20.4%
□ Less work on home (beauty, health) for dad:
□ clothing items ........................................ 29.0%
□ Machine ................................................ ......... 26.9%
□ Less work, high salary, to return home from work before, so that it was younger.
Sign of violation (if it does not contradict the grounds of choice) - I don't know the answer, or an indifferent, or negative answer "nothing".
If a child lists "gifts", then you can say: "Well, all these are useful things, but you are an almighty wizard, you can wish not only things" - sometimes it is possible to get valuable information. Optimal is the cliché: "... good, and what else?".
Negative position in relation to school had 18% of children. The stereo coefficient is high enough.
For more questions, children are more often chosen for the teacher:
clothing items ................................................ ............................................ 20.4%
other gifts................................................ ............................................. 20.4%
to make teachers not grieved .............................................. ............................. 12.9%
so that the teacher was: good, fair, better explained the material ... 4.3%
Obviously "jump" between the 10th and 12th year: this trend corresponds to ontogenesis and is visible in other positions.
I would like to turn into ...?
Animal .................................. 35.5%
Fabulous hero .................... 23.7%
Another person ....................... 16.1%
Literary hero ............. 3.2%
Item ..................................... 3.2%
Stay yourself ......... 3.2%
I do not know ..................................... 16.1%
The coefficient of stereotype is low.
Twelve identifications were selected according to the results of preliminary experience with 27 animals. A forced choice with a large number of animals reduces the risk of surface, random association with spontaneous selection and allows you to cause many differentiated positions. With the help of such elections and their rationale, the child indirectly describes the features of his own personality.
Positive selection of small animals (mouse, worm, snake), if it does not contradict the rationale for choice, is a sign of violation or inaptability, no unsafebility.
"Characteristics" of animals
Cat (p \u003d 0,53):
a) the need to be useful to help others;
b) the need to be attractive, charming, beautiful;
c) the need to be loved, the need for affection, in defense;
d) security, home, convenience;
e) the need for physical agility, dexterity.
Failure due to aggressiveness, flattering, the desire to avoid aggressiveness: "People are tormented and offended."
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
Identification with a cat according to the choice of girls is extremely positive, for boys - moderately positive (for 12-year-old even ambivalent: Identify it as a harmful animal: "Catching birds", "Supplement", "aggressive").
Lion (p \u003d 0.01). Dominant position, the desire for power, management, the need for social significance (prestige, authority), the need for strength:
a) an aggressive position, the need to attack, bite;
b) the need for freedom, independence;
c) the desire to be beautiful, cause admiration.
Failure due to aggressiveness due to the fact that it sits in a cell (the need for freedom).
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
In identification motivation prevail: aggressiveness, dominance, autonomy, partially aggressiveness, physical strength.
Little Goat, Olennok (r - 9,40):
a) the need for beautiful appearance, be charming;
b) the need for confidence, security, maternal protection;
c) the need for freedom.
Rejected due to defenselessness, vulnerabilities, graveness, cowardiness. Ontogenetic polarity profile:
Eagle (p \u003d 0.29):
a) the need for freedom, "takeoff";
b) the need to be useful, recognition, exclusivity (king of birds);
c) the need for dominance (king of birds);
d) partially aggressive and protective position.
Rejected due to aggressiveness, cruelty, vulnerability, gloominess. Ontogenetic polarity index profile: Motivation of the choice: "Freedom" - 5% girls, 30% of boys; Aggressiveness is 0% of girls, 4% of boys.
Approbation for 93 children (53 boys and 40 girls).
Who would you like to be?
Frequency (%) of the most common answers (Table 7.11, 7.12):
Fabulous heroes ........................ 74.1
Animals .................................... 11.8. %
Real faces ............................. 9.7
Other options ........................ 2.2
I do not know ........................................... 2.2
Table 7.11 . Fabulous heroes (absolute frequency)
School age
Table 7.12. Animals (absolute frequency)
|
Girls, Years |
Boys, Years |
Frequency, |
|||||
Real faces: Mom, teacher, cook, captain, cosmonaut ...
To estimate the stereotype, we use the coefficient, expressed as a percentage, the relative frequency of the most common responses (inversely proportional to the originality indicator).
50-70% of the same responses are a high stereotype ratio.
30% - average stereotype coefficient.
19.4% - low stereotype coefficient.
Explanations are very diverse: reveal the motives of the child and are the basis of interpretation.
Who would not like to become?
Frequency (%) of the most common answers (Table 7.13, 7.14):
Fabulous heroes ........... 62.4%
Animals ........................ 8.6%
Real faces ............... 17.2%
Continentation has a large stereo coefficient (26.9%) and a greater frequency of real persons.
Table 7.13. Fabulous heroes (absolute frequency)
|
Choice |
Girls, Years |
Boys, Years |
Frequency, |
||||
|
Sorcerer, witch | |||||||
|
Princess |
Note. In this table and tab. 7.14-7.20 In the "Frequency" column, only significant values \u200b\u200bare indicated.
Table 7.14. Animals (absolute frequency)
Real faces: servant, waitress, "bad person", cook, "man". Depending on the floor: the boys prefer the wizard, which can actively participate in the magic world, the girls - the princess.
CHAPTER 7. DIAGNOSTICS Must fully- Motivational AND Volvea Spheres Personality
Depending on the age: among girls, development trend is more distinct: with age increases the frequency of identification with a fabulous hero:
Ontogenetic profile:
Girls ................ 63% -86-90
Boys .............. 75% -64-85
Some responses have both positive and negative selection results (Princess), other only positive (cat) or only negative (snake).
The ratio of the difference in positive and negative elections to the total number of all elections of the same object is called the polarity index:
I.- K.
Where / is accounted for identifications; TO-The number of content.
As follows from the formula, the polarity index can take any values \u200b\u200b- from 1.0 to -1.0. Positive values \u200b\u200bshow that positive elections prevail, negative - on the contrary. Boundary values \u200b\u200bhave the following psychological meaning:
1.0- Extreme positive object chosen by all respondents; 0 - an ambivalent object; - 1.0 - an extreme negative object excluded by all.
Polarity index for the first two test questions:
Prince, Princess ................ 0.8
King, Queen ................. 0,6
Wizard ....................... -0.46
Damn ................................... -0.50
Dragon .............................. -0.82.
Cat ................................... 1.0 -
Snake .................................... - 1.0
The most important for interpretation are the answers to the question "Why?". The motives of choice are diverse: worried personality, determined by the position of the child. It is personal explanations that are useful for diagnostic conclusions, for example:
Identification:
□ with the fairy ("makes other nasty");
□ with a cat ("Everyone can play with it");
□ with a child ("Maybe all the time with mom");
^ L.
School age
Continiate:
Q with a dog ("Once I was bitten by");
□ With a person ("Must die").
Interpretation portraits of objects
(Interpretation capabilities are given in a sequence of descending the number of coincident explanations (Table 7.15-7.21): Prince, Princess (P \u003d0,80):
A) the need to cause admiration, to be the center;
B) the desire for wealth, luxury, abundance;
C) the need to be noble, responsive;
D) the need to dominate, manage others (rejected as "
Well "quality).
King, Queen (p= 0,69):
A) the need to dominate, organize, manage others, con
TROL, intervene (dominant, partially aggressive position):
B) the need to help, protect others;
C) the need to condone, cause admiration, be the center of the city
mania (exposure or exhibition position; rejected due to
"Bad" qualities).
Wizard (R.= -0,46):
A) the desire for power, strength;
B) the need for creativity, ingenuity, activity;
C) need to assist, protect others (protective
);
D) the desire for wealth, abundance (rejected due to "bad" qualities,
Nasty appearance, hatred of people - the need for affiliation).
Dragon (R.\u003d -0.82) rejected due to cruelty, aggressiveness, ugly type, the choice of the dragon is an indicator of inaptability, aggressiveness or other violations.
Replies options: "I would turn the whole world inside out", "would have turned a person in a stone," "so that people do not quarrel", "so that I don't have glasses", "so that no one is dying."
Table 7.15. What would you do? (absolute frequency)
Chapter 7. Diagnostics of the Motivational and Volware Personality
Table 7.16. What would you do at home? (absolute frequency)
|
Choice |
Girls, Years |
Boys, |
Frequency, |
|||
|
Utilitarian subjects | ||||||
|
Communal | ||||||
|
Equipment | ||||||
|
Health to everyone |
For additional questions, most often choose: for mom:
□ clothing items ........................................ 35.5%
□ Municipal equipment ..................... 20.4%
□ Less work on home (beauty, health) for dad:
Q clothing items ...................................... 29.0%
□ Machine ................................................ ........ 26.9%
Q Less work, high salary, to return home from work before, to be younger.
Sign of violation (if it does not contradict the grounds of choice) - I don't know the answer, or an indifferent, or negative answer "nothing".
If a child lists "gifts", then you can say: "Well, all these are useful things, but you are an almighty wizard, you can wish not only things" - sometimes it is possible to get valuable information. Optimal is the cliché: "... good, and what else?".
Table 7.17. What would you do you INSchool?
Negative position in relation to school had 18% of children. The stereo coefficient is high enough.
For more questions, children are more often chosen for the teacher:
Clothing items ................................................ ........................................ 20.4%
Other gifts................................................ ............................................. 20.4%
To make teachers not grieved .............................................. .......................... 12.9%
So that the teacher was: good, fair, it was better explained by the material 4.3%
Table 7.18. Position to the teacher
Obviously "jump" between the 10th and 12th year: this trend corresponds to Ontogenesis and visible on other positions.
School age
I would like to turn into ...?
Animal ....................... 35.5%
Fabulous hero ........... 23.7%
Another person .............. 16.1%
Literary hero ...... 3.2%
Item ......................... 3.2%
Stay yourself. 3.2%
I do not know .......................... 16.1%
The coefficient of stereotype is low.
Table 7.19. What animal would you like to turn?
|
Choice |
Girls, Years |
Boys, |
Frequency, |
||
|
A monkey | |||||
|
ABOUT 0 | |||||
Table 7.20. Whatever animals do you want to be? (Spontaneous Identification)
|
Choice |
Girls, Years |
Boys, |
Frequency, |
||
|
ABOUT 3 | |||||
Twelve identifications were selected according to the results of preliminary experience with 27 animals. A forced choice with a large number of animals reduces the risk of surface, random association with spontaneous selection and allows you to cause many differentiated positions. With the help of such elections and their rationale, the child indirectly describes the features of his own personality.
Positive selection of small animals (mouse, worm, snake), if it does not contradict the rationale for choice, is a sign of violation or inaptability, no unsafebility.
"Characteristics" of animals
Cat (p \u003d0,53):
A) the need to be useful to help others;
B) the need to be attractive, charming, Beautiful;
CHAPTER 7. DIAGNOSTICS Must fully- Motivational AND Volvea Spheres Personality
C) the need to be loved, the need for affection, in defense;
D) security, home, convenience;
E) the need for physical agility, dexterity.
Failure due to aggressiveness, flattering, the desire to avoid aggressiveness: "People are tormented and offended."
Identification with a cat according to the choice of girls is extremely positive, for boys - moderately positive (for 12-year-old even ambivalent: Identify it as a harmful animal: "Catching birds", "Supplement", "aggressive").
Lion (R.\u003d 0.01). Dominant position, the desire for power, management, the need for social significance (prestige, authority), the need for strength:
A) an aggressive position, the need to attack, bite;
B) the need for freedom, independence;
C) the desire to be beautiful, cause admiration.
Failure due to aggressiveness due to the fact that it sits in a cage (needIn freedom).
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
In identification motivation prevail: aggressiveness, dominance, autonomy, partially aggressiveness, physical strength.
School age
Little goats, deer (r -9,40):
A) the need for beautiful appearance, be charming;
B) the need for confidence, security, maternal protection;
C) the need for freedom.
Rejected due to defenselessness, vulnerabilities, graveness, cowardiness. Ontogenetic polarity profile:
Snake (R.\u003d 0.78): The need for considerable aggressiveness or response or sharply defensive position. Rejects due to aggressiveness, cunning, dislike, due to defenselessness, vulnerability, slowness, squeamishness.
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
Eagle (R.= 0,29):
A) the need for freedom, "takeoff";
B) the need to be useful, recognition, exclusivity (king of birds);
C) the need for dominance (king of birds);
D) partially aggressive and protective position.
Rejected due to aggressiveness, cruelty, vulnerability, gloominess. Ontogenetic polarity index profile: Motivation of the choice: "Freedom" - 5% girls, 30% of boys; Aggressiveness is 0% of girls, 4% of boys.
Mouse (R.\u003d -0.94) is selected only in exceptional cases (pedantic position). Rejects due to the lack of sufficient security, protection, confidence, due to the danger, harmfulness, nasty appearance, contempt for others (causes a feeling of squeamishness, disgusting).
Identification with the mouse is an abnormal, justification of the choice also contain signs of general insecurity, socialization violations.
Monkey (R.= 0,68):
A) the need for physical agility, physical perfection, joy of movement, playfulness, activity;
CHAPTER 7. DIAGNOSTICS Must fully- Motivational AND Volvea Spheres Personality
B) the need for delicacies, sweets;
C) clown position, the need to be in sight Cause surprise;
D) the need to be intelligent "inventive;
E) the need to be cute, attractive.
Rejects due to "squealing", "because the monkey".
Tiger (R.=0,14):
BUT) Need for physical strength;
B) the need for beautiful appearance;
C) exclusively aggressive position, the need to attack,
run, destroy;
D) the need to cause fear.
Rejects due to aggressiveness, harmfulness, due to continuous persecution, lack of freedom ("in a cell").
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
Hare (p \u003d-0.51) Choose due to mobility, movements, activity:
A) the need to cause surprise, be beautiful;
B) the need of freedom.
Rejects due to defenselessness, constant persecution, due to the harmfulness, lack of beauty, cowardiness, constant fatal danger. Dog (R.= 0,53):
A) the need to be useful to help people take care of others
protect, guard, watch;
B) the need for beautiful appearance, be cute;
C) an aggressive position ("can bite") or a protective position;
D) the need for security, protection, home, sensitivity,
Lying someone, have someone for yourself.
Rejected due to aggressiveness, dependence, lack of freedom, subordination, humiliating position. Bird(for example, cinema) (R= 0,59):
A) the need of freedom, "takeoff", independence;
B) the need to be loved;
School age
C) the need to bring joy;
D) the need to be useful;
E) the need for beautiful appearance;
E) the need for confidence, avoid danger;
G) the need for impressions in knowledge.
Rejected due to defenselessness, constant danger.
Ontogenetic polarity index profile:
Worm (R.\u003d 0.91). It is selected only in exceptional cases (due to the utility: "the soil"). Rejected due to defenselessness, vulnerabilities, due to an unpleasant habitat, disgusting appearance, harmfulness, feelings of squeamishness.
Projective technique. Designed to explore the needs, meaningful experiences and problems of the child. It is a semi-ended-based, in which the overall "logic" (KANVA) of the questions specified is scheduled.
The first part of the diagnostic complex can be attributed to the catharsis method. In an interview, the child is invited to identify himself with an almighty wizard, which can do everything that wants, in a magical country and in our real world: to turn into any creature, in any animal, small or adult, the boy becomes a girl and vice versa, etc. In the course of an interview, identification with an almighty wizard weakens, and at the end of the interview the psychologist brings the child from the role of a wizard.
The survey is recommended to be held alone with the child. Answers to an interview should be recorded literally. It is not recommended to use a tape record, as it can make tension in communication, cause a feedback, stiffness of the child, distract it from the conversation content. In turn, emotional with the child during the interview is necessary to transition to the further phase of diagnostic work or to psychocorrection. After each response, the child should ask why he would do something or another would turn into someone, etc.
This technique is a convenient tool to establish contact with the child, allowing him to survive in the game many of many significant moments for it. This is the psychotherapeutic effect of this technique.
Text techniqueDo you like fairy tales? Little children always love fairy tales. Of course, you are no longer small (Aya), but I think you will like such a few fabulous game.
Imagine that you have a magic rocket that has transferred you to a fabulous country. There is everything, as in a fairy tale: and people fabulous, and you too. Can you imagine this?
but. - And now tell me, who would you like to be in this fabulous country? Why?
b. - And who would you like to be in a fabulous country? Why? We are detaining here for a minute. Now imagine that you (Fairy): You are very strong, with the help of magic you can all you want. You can create, change, fold, make it so that anything completely disappeared.
So tell me, the wizard, what would you do? And for what? You are still a wizard (fairy). You sit in the rocket and come back, in the usual world. First of all, let's go to your home - imagine it.
Now you have at home. You are an almighty wizard, what would you do? (Additional questions: for dad, for mom, etc.).
Then the wizard goes to school.
In your power to do something, change, destroy, do the way you want.
Now you're at school. What would you do? (Additional questions: for teachers, classmates?). Why?
Now you are a wizard, play with the guys. What would you do for them? Why?
I almost forgot about you!
but. - What would you do for yourself? Why?
b. - What would you change or destroy? Why?
And for me, the wizard, what would you do? Why?
Thank you, you are a real wizard!
If you became a wizard, you could make any kind of appearance, would turn into someone or what you want.
but. - Tell me, what or who would you like to turn into? Why?
b. - And what or who you would never want to turn into? Why?
You can turn into any animal.
but. - Would you like animals to become? Why?
b. - And what animals do you want to be? Why? Of course, you know the beasts and beast. I will call you different animals, and you will talk, I would like to become someone from them or not, and why.
c) small goats, deer,
g) a monkey
k) Dog,
l) bird (for example, tit).
You coped perfectly with the task.
You are a wizard, you have great opportunities, you can choose one of three: to become a small child, an adult or stay as you are.
but. - Tell me who you want to be small, adults or like there? Why?
b. "Why don't you want to become ... (1st not selected option)?"
in. - Why ... (2nd not selected option)?
Would you like to become a girl (boy)? Why?
You coped perfectly with the task, but each game ends, and our too. And now you are not a wizard again, but (name, child).
And by the way, do you like your name? I do not like? Why? And surname? I do not like? Why? Would you like to be called something different? Why? And what do you call your parents, friends in class guys?
Very good, let's imagine (only it will not be a fabulous game) that all your desires are performed, any, but only 3.
And why and, b, in?
Excellent. And think:
but. - What are the most afraid of children? Why?
b. - What gives children the greatest joy? Why?
in. - And what brings them the greatest chagrins? Why?
Well done! What did you like most in the game?
InterpretationThe interpretation of the data is largely based on the answers of the child to questions "why", "Why", since children speak of them about their needs, meaningful experiences. Another basis for interpretation is a meaningful analysis of the answers, which allows you to deepen the idea of \u200b\u200bthe child's experiences and the real everyday situation. Non-verbal manifestations also give a lot of information for a psychologist practice. It is according to them that one can judge the depth of the experiencing of the child, subjective significance of certain problems that he mentions. Finally, interesting results gives a formal analysis of statements: their length, exploration, vocabulary, grammatical construction can confirm or cast doubt on the assumptions arising during the interpretation of the results.
In general, when interpreting results, it should be borne in mind that the identification of a child with a wizard is asked by the instruction and, therefore, is conscious, as a result of which the child's statements may be subject to socially approved responses, i.e. The desire to show yourself in the best light.
Views: 9576
Category: Psychodiagnostic techniques »Projective techniques
Interview "Magic World" (L. D. Stolyarenko)
This diagnosis can be attributed to the catharsis method. In an interview, the child is invited to identify himself with an almighty wizard who can do everything that wants, in a magical country and in our real world: to turn into any creature, to any animal, to become a small or adult, the boy becomes a girl and vice versa, etc. P. In the course of an interview with Identification with the Almighty Wizard weakens, and at the end of the interview the psychologist brings the child from the role of a wizard.
This technique is a convenient tool to establish contact with the child, allowing him to survive in the game many of many significant moments for it. This is the psychotherapeutic effect of this technique. After each response, the child should ask why he made this or that matter, turned into someone, etc. These explanations are the basis for the meaningful interpretation of the results.
The survey is recommended to be held alone with the child. Answers to interview questions should be recorded literally. It is not recommended to use a voice recorder because it can make tension in communication, cause a feedback, stiffness of the child, distract it from the conversation content. In turn, emotional contact with the child during the interviews is necessary to transition to the next stage of diagnostic work or to psychocorrection.
Text technique
- Do you like fairy tales? Little children always love fairy tales. You certainly are not small (Aya), but I think you will like this, a little fabulous game.
1.
- Imagine that you have a magic rocket that has transferred you to a fabulous country. There is everything, as in a fairy tale: and people fabulous, and you too. Can you imagine this?
a) - And now tell me, who would you like to be in a fabulous country? Why?
b) - Who would you like to be in a fabulous country? Why? - We are still detaining here. Now imagine that you are a wizard (Fairy): You are very strong, with the help of magic you can all you want. You can create, change, fold, make it so that anything completely disappeared.
2.
- So tell me, the wizard, what would you do? And for what? You are still a wizard (fairy). You sit in the rocket and come back, in the usual world. First of all, let's go to your home - imagine it.
3.
- Now you have at home. You are an almighty wizard, what would you do? (Additional questions: for dad, for mom? Etc.).
- Then the wizard goes to school. In your power to do something, change, destroy, do the way you want.
4.
- Now you're at school. What would you do? (Additional questions: for teachers, classmates?). Why?
5.
-Teer you, the wizard, play with the guys. What would you do for them? Why?
- I almost forgot about you!
6.
a) - What would you do for yourself? Why?
b) - What would you change or destroyed? Why?
7.
- And for me, the wizard, what would you do? Why?
- Thank you, you are a real wizard!
"If you became a wizard, you could make any kind of an appearance would turn into anyone or what you want."
8.
a) - Tell me what or who would you like to turn into? Why?
b) - And what or who you will not want to turn into anyone? Why? - You can turn into any animal.
9.
a) - What animals would you like to become? Why?
b) - And what animals do you want to be? Why?
Of course, you know many animals and beast. I will call you different animals, and you will talk, I would like to become someone from them or not and why.
- cat,
- a lion,
- little goats, deer,
- snake,
- eagle,
- mouse,
- a monkey,
- tiger,
- hare,
- dog,
- bird (for example, cinema).
- You coped perfectly with the task.
"You are a wizard, you have great opportunities, you can choose one of three: become a small child, adults or stay as you are.
11.
but. - Tell me who you want to be small, adults or like there? Why?
b. "Why don't you want to become ... (1st not selected option)?"
in. - Why ... (2nd not selected option)?
- Would you like to become a girl (boy)? Why?
- You coped perfectly with the task, but each game ends, and our too. And now you are not a wizard again, but (name, surname of the child).
- And by the way, do you like your name? Do not like? Why? And surname? Do not like? Why? And what do you call your parents, friends in class guys?
- Very good, let's imagine (only it will not be a fabulous game) that all your desires are performed, any, but only 3.
14.
a B C?
- And why and, b, in?
- Excellent. And think:
but. - What is the most afraid of children? Why?
b. - What gives children the greatest joy? Why?
in. - And what brings them the greatest chagrins? Why?
- Well done! What did you like most in the game?
Interpretation of results
The interpretation of the data is largely based on the answers of the child to questions "why", "why", since children speak of their needs, meaningful experiences. Another basis for interpretation is a meaningful analysis of the answers, which allows you to deepen the idea of \u200b\u200bthe child's experiences and the real everyday situation. Non-verbal manifestations also give a lot of information for a psychologist practice. It is according to them that one can judge the depth of the experiencing of the child, subjective significance of certain problems that he mentions. Finally, interesting results gives a formal analysis of statements: their length, exploration, vocabulary, grammatical construction can confirm whether to question the assumptions arising during the interpretation of the results.
In general, when interpreting results, it should be borne in mind that the identification of a child with a wizard is asked by the instruction and, therefore, is conscious, as a result of which the child's statements may be subject to socially approved responses, i.e. The desire to show yourself in the best light.